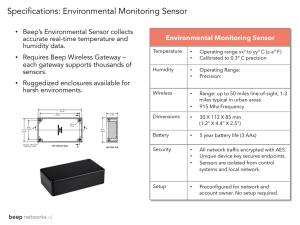
Smart Sensors Teacher : Dr. Le Anh Tuan Student : Nguyen Xuan Truong Contents Acknowledgement What is Smart sensor? Shift to Smarter sensor Evolution Third-Fourth-Fifth Block Diagram IoT Top IoT Smart Sensors Temperature Sensor Proximity Sensor Pressure Sensor Gas & Smoke Sensor Accelerometer Sensor Level Sensor Motion Detection Sensor Optical Sensor Gyroscope Sensor Water Quality Sensor A Smarter W orld Pros and Cons Video Credits Acknowlegment We would like to thank our teachers Mr. Ayushman Banerjee sir and Mrs. Nira Konar ma’am for his excellent guidance and immense support, throughout this presentation. A special note of thanks to our friends and classmates, who directly or indirectly helped us in making this presentation a success. What is Smart Sensor? A sensor is basically an element that produces a signal relating to the quantity to be measured. A sensor producing an output when combined with some interfacing hardwares is termed to be an intelligent or smart sensor, which is a more acceptable term now. Sensors +Interfacing Hardwares =Smart Sensors This type of sensor is different from other type because it carries out functions like ranging, calibration and decision making for communications and utilization of data. Shift to Smarter Sensors Now a days, sensors come integrated with many sensing elements within a single silicon chip, providing high accuracy , userfriendliness, accessibility and flexibility making sensors smarter and intelligent. It uses both standard bus or wireless network to communicate with one another or with microcontrollers. Intelligent sensor consists of a chain of analog and digital blocks, each of which provides a specific function. Evolution Fifth Generation Sensors Equivalent to intelligent or today’s smart sensors. Fourth Generation Sensors Addition of memory cells for calibration. Third Generation Sensors Digital Intelligence and temperature compensation on the same micro chip as before. Second Generation Sensors Pure analog system. Had MEMS sensor with analog amplification and ADC converter First Generation Devices Little electronics with MEMS(MicroElectro-Mechanical-System) sensor element combined with analog amplification on a micro chip. Third- Fourth- Fifth Fourth Generation Sensors Third Generation Sensors Fifth Generation Sensors Block Diagram Display Interface Module Sensor Memory Processor Communication Amplifying and Conditioning ADC DSP Offset Adjustment and Temperature Compensation Smart Sensors will fuel the Age of Sm art Everything. “ IoT The Internet of Things is the concept of connecting any device to the Internet and to other connected devices. The IoT is a giant network of connected and share data about the way they are used and about the environment around them. That includes an extraordinary number of objects- from smart microwaves,which automatically cook your food, to self- driving cars, and then to wearable fitness devices that measure your heart rate and uses information to suggest exercise plans. Top IoT Smart Sensors Temperature Sensors Proximity Sensor Pressure Sensor Gas & Smoke Sensor Accelerometer Sensors Level Sensors Image Sensors Motion Detection Sensors Optical Sensors Gyroscope Sensors Temperature Sensors A device, used to measure amount of heat energy that allows to detect a physical change in temperature from a particular source and converts the data for a device or user, is known as a Temperature Sensor. Thermisters RTD Infrared Sensor IC (Semiconductor) Proximity Sensors A device that detects the presence or absence of a nearby object, or properties of that object, and converts it into signal which can be easily read by user or a simple electronic instrument without getting in contact with them. Ultrasonic Sensor PhotoElectric Sensor Capacitive Proximity Sensor Pressure Sensors A pressure sensor is a device that senses pressure and converts it into an electric signal. Here, the amount depends upon the level of pressure applied. Air Pressure Sensor Water Pressure Sensor Low Pressure Sensor Gas & Smoke Sensors Gas sensors re specifically used to monitor changes of the air quality and detect the presence of various gases. A smoke sensor is a device that senses smoke (airborne particulates & gases ) and it’s level. LPG Sensor Alcohol Sensor Photoelectric Smoke Sensor Ionization Smoke Sensor Accelerometer Sensors Accelerometer is a transducer that is used to measure the physical or measurable acceleration experienced by an object due to inertial forces and converts the mechanical motion into an electrical output. Linear Hall-Effect Accelerometer Piezoelectric Accelerometer Capacitive Accelerometer Level Sensors A sensor which is used to determining the level or amount of fluids, liquids or other substances that flow in an open or closed system is called Level sensor. Liquid Level Sensor Capacitive Level Sensor Float Type Level Sensor Motion Detection Sensors A motion detector is an electronic device which is used to detect the physical movement(motion) in a given area and it transforms motion into an electric signal ;motion of any object or motion of human beings. Ultrasonic Sensor PIR(Passive Infrared) Sensor Microwave Sensor Optical Sensors A sensor which measures the physical quantity of light rays and convert it into electrical signal which can be easily readable by user or an electronic instrument/device is called optical sensor. Photodetecter Pyrometer Infrared Sensor Proximity Sensor Gyroscope Sensors A sensor or device which is used to measure the angular rate or angular velocity is known as Gyro sensors. The most important application is monitoring the orientation of an object. Ring Laser Gyroscope Optical Gyroscope Digital Gyroscope Vibrating Gyroscope Water Quality Sensors Water quality sensors are used to detect the water quality and Ion monitoring primarily in water distribution systems. pH Sensor Turbidity Sensor Water Conductivity Sensor A Smarter World Forest Fire Detection Air Pollution Snow Level Monitoring Landslide Prevention Earthquake Detection. Smart Cities Smart Packing Smartphone Detection Traffic Congestion Smart Lighting Waste Management Smart Roads Smart Environ ment Smart Grid Tank Level Photovoltaic Installations Water Flow Smart Water Portable Water Monitoring Chemical Leak Detection Pollution Level Water Leakages River Floods Smart Metering Security & Emergenc ies Perimeter Access Control Liquid Presence Radiation Levels Explosive and Hazardous Gases Pros and Cons Contains both actuators & sensors, so complex circuitry Minimum Interconnecting Cables High Reliability and Performance Easy to Design, Use and Maintain Small Rugged Packaging and Flexible System Smart Sensors Cost of Wired Smart Sensors are higher Calibration requires an External Processor Predefined Embedded Functions have to be given during the design Thanks!