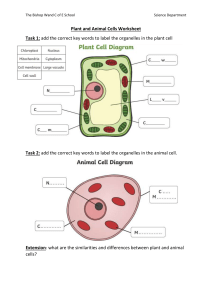
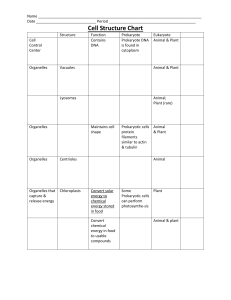
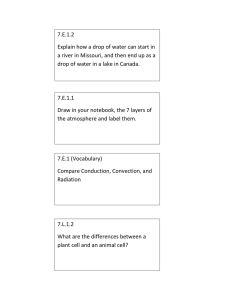
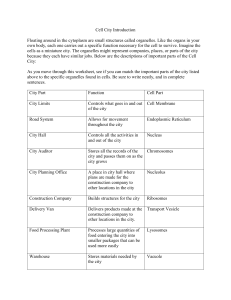
VCE Biology – Unit 1 Cell size, structure and function • • • cells as the basic structural feature of life on Earth, including the distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells surface area to volume ratio as an important factor in explaining the limitations of cell size and the need for internal compartments (organelles) with specific cellular functions the ultrastructure of plant and animal cells in terms of their organelles and identification of these organelles using the light microscope and electron micrographs Task 1 Identify the cell type (prokaryote or eukaryote) for each of the following cells. Justify your choice. Cell type: Justification: Cell type: Justification: Cell type: Justification: Task 2 List the structures found in all cells. Task 3 The diagram below is an Escherichia coli cell, a typical bacterial cell. Label the structures seen in this cell. Task 4 Label the organelles shown in the diagrams of the plant and animal cell below (after you decide which one is which). Task 5 The following cells are either plant or animal cells. Determine the cell type, justify your choice and label organelles.