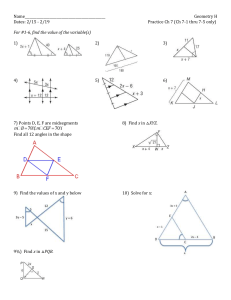
NAME DATE 7-4 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention Parallel Lines and Proportional Parts Proportional Parts within Triangles In any triangle, a line parallel to one side of a triangle separates the other two sides proportionally. This is the Triangle Proportionality Theorem. The converse is also true. R X T RX SY RX SY , then − . RS RS =− . If − =− , then XY If XY XT YT XT YT S Y −− −− −− If X and Y are the midpoints of RT and ST, then XY is a midsegment of the triangle. The Triangle Midsegment Theorem states that a midsegment is parallel to the third side and is half its length. −− 1 and XY = − RS If XY is a midsegment, then XY RS. 2 −− −− In ABC, EF CB. Find x. Example 1 E 6 Example 2 In GHJ, HK = 5, KG = 10, and JL is one-half the length −− −−− −− of LG. Is HK KL? C ) 18 A x + 22 F x+2 + B , - −− −−− AF AE Since EF CB, − =− . FB EC ( 6x + 132 = 18x + 36 96 = 12x 8=x Using the converse of the Triangle Proportionality Theorem, show that JL HK − =− . KG LG Let JL = x and LG = 2 x. JL x 1 − =− =− 2 2 10 2x LG 1 1 Since − = −, the sides are proportional and 2 2 −−− −− 5 HK 1 − =− =− KG HJ KL. Exercises ALGEBRA Find the value of x. 1. 5 7 7 2. x 5 x 4. Chapter 7 5. 17.5 3. x 9 x 11 x + 12 30 10 18 x 8 24 20 35 12 33 5 6. x x + 10 30 10 24 10 Glencoe Geometry Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. x + 22 18 −=− x+2 6 NAME DATE 7-4 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention (continued) Parallel Lines and Proportional Parts Proportional Parts with Parallel Lines When three or more parallel lines cut two transversals, they separate the transversals into proportional parts. If the ratio of the parts is 1, then the parallel lines separate the transversals into congruent parts. s t 1 2 c a d b v w n x 4 5 6 If 1 2 3, a c then − =− . b Example u 3 d m If 4 5 6 and u w − v = 1, then − x = 1. Refer to lines 1, 2, and 3 above. If a = 3, b = 8, and c = 5, find d. 3 5 1 1 2 3 so − =− . Then 3d = 40 and d = 13 − . 8 3 d Exercises ALGEBRA Find x and y. 1. 5x 2. 3x 12 2x - 6 x+3 x=8 x=9 3. 4. 2x + 4 3x - 1 3 x 4 1 y = 3− 3 6. 32 16 x+4 y x = 12 Chapter 7 y+2 8 2y + 2 x = 5; y = 2 5. y 5 3y Lesson 7-4 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. x + 12 12 y+3 y=3 25 Glencoe Geometry