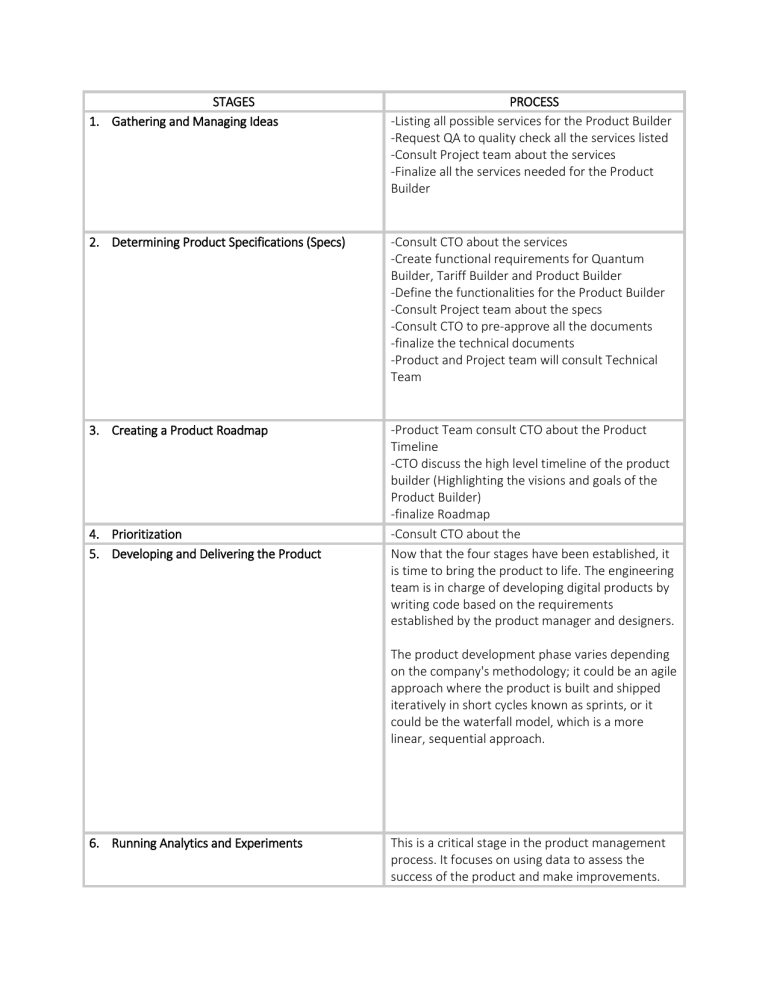
STAGES 1. Gathering and Managing Ideas PROCESS -Listing all possible services for the Product Builder -Request QA to quality check all the services listed -Consult Project team about the services -Finalize all the services needed for the Product Builder 2. Determining Product Specifications (Specs) -Consult CTO about the services -Create functional requirements for Quantum Builder, Tariff Builder and Product Builder -Define the functionalities for the Product Builder -Consult Project team about the specs -Consult CTO to pre-approve all the documents -finalize the technical documents -Product and Project team will consult Technical Team 3. Creating a Product Roadmap -Product Team consult CTO about the Product Timeline -CTO discuss the high level timeline of the product builder (Highlighting the visions and goals of the Product Builder) -finalize Roadmap -Consult CTO about the Now that the four stages have been established, it is time to bring the product to life. The engineering team is in charge of developing digital products by writing code based on the requirements established by the product manager and designers. 4. Prioritization 5. Developing and Delivering the Product The product development phase varies depending on the company's methodology; it could be an agile approach where the product is built and shipped iteratively in short cycles known as sprints, or it could be the waterfall model, which is a more linear, sequential approach. 6. Running Analytics and Experiments This is a critical stage in the product management process. It focuses on using data to assess the success of the product and make improvements. Product managers can also run various experiments on different user groups to test different scenarios or feature versions. The data from these experiments allows the product team to improve the product and increase its chances of success. 7. Gathering Customer/ User Feedback The final stage in product management process is to capture the feedback from the customers. There are various ways to capture the user feedback. For example, a prompt can be used to rate their experience while using the product, or through a survey and etc. It is important to gather all the feedbacks of the customer, which the product manager must organize and analyze. These comments are used to make the product better. This step returns us to the beginning of the product management process: capturing and managing ideas.