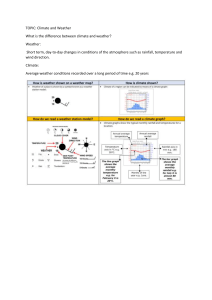
The Earth, along with all of the other planets in our solar system, began to form out of these semi-solid objects that we call planetoids. This process is related to what scientists call the Solar Nebula Theory, which discusses the Origins of the solar system. The earth was initially very hot and molten when it first formed 4.5 billion years ago. As the Earth sat for millions of years, the surface started to cool slowly over time. This is when the actual solid surface of Earth begin to form. But it was still very hot inside the Earth, THe heat from the deep within the crack in the Earth’s surface. These cracks in the Earth were where the first volcanoes began to form, release magma, heat, and many gases trapped under the Earth's new crust. What are Cyanobacteria Cyanobacteria are microbes that primarily in seawater. They are believed to have been the first organisms on Earth to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. In this process, they produce organic carbon, the building blocks of life’s molecules, and release oxygen gas (O2). The O2 enters into the seawater, and from there some of it escapes into the atmosphere. Evidence from the Rock Record Iron (Fe) - is extremely reactive to oxygen. If we look at the state of Fe in the rock, we can learn a great deal about atmospheric evolution. Banded Iron Formation (BIF) - deep water deposits in which layers of iron-rich minerals alternate with iron-poor layers. These are common in rocks 2.0-2.8 bya. They do not form today. Banded Iron Formation (BIF) Evidence from the Rock Record Red beds: are never found in rocks older than 2.3 bya, but common during the Phanerozoic time. Conclusion: the amount of O2 in the atmosphere has increased over time Current Atmosphere Characteristics Permanent gases: ( together 99.96%) (N) Nitrogen 78% (O) Oxygen 21 % (Ar) Argon ~ 0.9 % Current Atmosphere Characteristics Variable gases (changes depending on how much Oxygen is in the atmosphere) - Makes up from 4% to less than 1 % (CO2) Carbon Dioxide (O3) Ozone (H2O) Water Conclusion - - The composition of Earth’s atmosphere has changed over geologic time. Earth’s atmosphere is unique in the solar system in that it contains substantial oxygen. The most primitive atmosphere was composed of mainly helium and hydrogen. The early atmosphere contained mostly CO2, CO and water vapor. This atmosphere was then modified by early photosynthetic life. Early photosynthetic life such as cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) consumed carbon dioxide and generate oxygen. It was only after early photosynthetic life generated oxygen that animal life became possible.