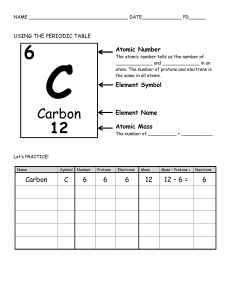
8 Science Quarter 3-Module 3: ATOMS Learner’s Activity Sheet Photo Credit: Basic Model of the Atom - Atomic Theory (thoughtco.com) February 28, 2022 OVERVIEW In the previous module, you have learned how atom was conceptualized by atomists and philosophers, how the atomic theory was formulated, and how atom and the presence of its subatomic particles are proven using various experiments conducted by different scientists. Here, you are going to learn the relationship of each subatomic particles in an element. Nuclear (Atomic) Symbol Notation Protons, neutrons and electrons are not just parts of an atom but is essential in identifying an atom and its chemical behavior. To determine the protons. electrons, and neutrons in an atom of an element, we are using the Nuclear Symbol Notation/ Atomic Symbol Notation, where: A= mass number Z= atomic number X= symbol of the element Let’s say for example, we used the element Boron. What could be its Nuclear Symbol Notation? It will be: Why? Because B is the symbol of the element Boron while the mass number and the atomic number are given in the periodic table of elements. Note that mass number and atomic number must be rounded off to a while number. The atomic number (Z) is the number of the protons of an element and can be sued to identify the atom. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different number of neutrons. On the other hand, Mass number is symbolized as (A) is the sum of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus. mass number is obtained from rounding off the value of the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of an element is determined by a device called mass spectrometer. Formulas to get the value of atomic number (Z), mass number (A), number of electrons (e -) number of protons (p+) and number of neutrons (n0): 1. Atomic number is equal to number of protons and number of electrons. Element Atomic Number (Z) Number of Protons (p+) Number of Electrons (e-) Gold 79 79 79 2. Mass number subtracted to the atomic number will give you the number of neutrons. Element Atomic Number Mass Number Number of Number of (Z) Protons (p+) Neutrons (n0) Silver 47 108 47 61 Number of Electrons (e-) 47 Ions Negative charge particles can move freely from one atom to another which make the atom produce a charge, turning an atom into an ion. Ion is a charged particle. There are two (2) types of ions namely, anion and cation. Anions have a net negative charge because they have more electrons than protons. Cations have a net positive charge because they have more protons than electrons. It there is an equal number of electrons and protons in atom, the charge will be neutral, also called as at ground state. The charge of the electrons and the charge of the protons cancel each other causing an uncharged atom. When an uncharged atom received additional electrons, the overall charge will be negative due to greater number of electrons than the protons. Example: Ion Atomic Number Number of Protons Number of Electrons Overall Charge Fe3+ 26 26 23 +3 Ions are important for our health. They exist in various forms and can be found even in a bottled water, energy drinks and ion supply drinks including Pocari sweat and Gatorade. These ions or electrolytes supply drinks are created to replenish lost ions in the body during sweating. It is also easily absorbed by the body due to its component that is almost similar to bodily fluids. Ions can also be found in nature. Positive ions are commonly found in polluted, contaminated, and dusty areas which can cause irritation and allergies whereas Negative ions are usually abundant in nature spots like mountains, hills, forests, and waterfalls, and is believed to generate biochemical reactions that increase levels of the serotonin, a mood chemical which is a natural antidepressant, antistress, and increase our energy during daytime. LET’S TRY! (PRE-ASSESSMENT) Encircle the following words in the puzzle. Then, write a description for each word on the blank. 1. cation2. atomic mass3. proton4. isotope5. atomic number6. neutron7. anion8. electron- N O I N A D A X A B I A P K N P K V V R H T P X Q T O Q N E U H K T B S O Q S O D G H P U R G I Y A N M E M C H N O K P H T O E W M M I K H M R Y X C T H N I C M I X A L T F Q E S L O C T N O Y K X G P Q T G X C C A O U L A H I C T T N L P K P P M C L S C F N C O R G D M W B K N W S J J X Z R M O L N E U T R O N K H F W P L J N R A Q Q F L I Y I N F T I G O I C Q H V P Q T W T V J W Z B E Y Z W M F N U A X W F S U L Content Standards: • The learners demonstrate understanding of the particle nature of matter as basis for explaining properties, physical changes, and structure of substances and mixtures. Performance Standards: • The learners should be able to present how water behaves in its different states within the water cycle. Most Essential Learning Competency: • Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a particular atom. S8MT-IIIe-f-10 E C V H O F F L P C E Q D O J THIRD QUARTER WEEK 5: WRITTEN WORK No. 1 For the learner: This worksheet contains activities atoms and the subatomic particles. You may answer directly to this activity sheets and make sure to follow the directions stated in each part of the activity. Answer all questions the best that you can and please write legibly. For the parents: Learners may require your guidance in following the directions and answering the questions in each part of the activity. Make sure that they answer each part of the worksheet. Objectives: • • • Compute the number of protons, electrons, neutrons and mass number of aneutral atom. Explain the transformation of a neutral atom into an anion and cation. Draw an atomic model given the number of sub-atomic particles. ACTIVITY #1 – CONSTRUCTING ATOMIC MODEL WHAT I NEED (MATERIALS) ▪ ▪ writing and coloring materials worksheets WHAT TO DO (PROCEDURE) 1. Draw an atom showing and labeling the nucleus and electron clouds. 2. Label all parts of this atom, calculate overall charge and mass. Show all work. + O O + + Protons Neutrons Mass - O Protons + Electrons Overall Charge 3. Draw an atom of beryllium showing all parts. Make the atom have an overall charge of +3 and a mass of 9. + Protons Neutrons Mass Protons + Electrons Overall Charge 4. Draw an atom of Carbon. Remember, the atomic number is the same as the number of Protons. Make the atom neutral. (an overall charge of 0) + Protons Neutrons Mass Protons + Electrons Overall Charge 5. Draw an atom of Aluminum, use your book to find the Atomic number and the mass. Make the atom neutral. +____________ +____________ 6. Draw an atom of Neon, use your book to find its atomic number and mass. Make it have an overall charge of -4. +____________ +____________ THIRD QUARTER WEEK 5: WRITTEN WORK No. 2 For the learner: This worksheet contains activities about number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom. You may answer directly to this activity sheets and make sure to follow the directions stated in each part of the activity. Answer all questions the best that you can and please write legibly. For the parents: Learners may require your guidance in following the directions and answering the questions in each part of the activity. Make sure that they answer each part of the worksheet. Objective/s: • • Determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom. Recognize that an element is identified by the number of protons in the nucleus. ACTIVITY #2 – CALCULATING THE NUMBER OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES WHAT I NEED (MATERIALS) ▪ Worksheet ▪ Pen WHAT TO DO (PROCEDURE) Part A: Complete the given table: The first row is a given example. Name of Element Element Symbol Mass Number Number Boron B 11 Sodium __________ __________ Atomic Protons Neutrons Electrons 5 5 6 5 24 11 __________ __________ __________ Y 89 __________ __________ __________ 39 Copper __________ __________ 29 __________ 35 __________ __________ Tc 98 __________ 43 __________ __________ __________ Pb 207 __________ __________ __________ __________ Thallium __________ 204 81 __________ __________ __________ __________ H __________ __________ __________ 0 __________ Oxygen __________ __________ __________ __________ 8 __________ __________ N __________ __________ 7 __________ __________ __________ Ba __________ __________ __________ __________ 56 Calcium __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ Si __________ __________ __________ __________ 14 Argon __________ __________ 18 __________ __________ __________ Guide Questions: 1. How do you get the number of p + of a neutral atom given the number of e- and A? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the mass number of an atom with 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How to compute for the number of n0? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. How to determine the mass number of an atom given the atomic mass (amu)? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Give the A, Z and n0 of an element whose symbol is Cf. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ WHAT I CAN DO ABOUT IT (APPLICATION) Relate the three (3) subatomic particles in your life as an enhanced science 8 student. WHAT I LEARNED (GENERALIZATION) Write down in the box what you have learned from the lesson . THIRD QUARTER WEEK 6: WRITTEN WORK No. 1 For the learner: This worksheet contains activities about subatomic particles, anions, and cations. You may answer directly to this activity sheets and make sure to follow the directions stated in each part of the activity. Answer all questions the best that you can and please write legibly. For the parents: Learners may require your guidance in following the directions and answering the questions in each part of the activity. Make sure that they answer each part of the worksheet. Objectives: • • Compute for the number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and mass number of a neutral, negative and positive atom. Explain the transformation of a neutral atom into an anion and cation. ACTIVITY #1 – WHAT’S THE CHARGE (Part 1)? WHAT I NEED (MATERIALS) ▪ Worksheet ▪ Pen WHAT TO DO (PROCEDURE) Part A: Directions: Choose the term that best completes the second relationship. 1. Black:white anion: __________________ (cation, anion, metal) 2. Male:female proton: _________________ (atom, electron, neutron) 3. Atom: proton house: _________________ (school, nucleus, planet, brick) 4. Neutron: neutral Electron: ________________ (negative, positive) 5. Plant: narra anion: _________________ (cation, sodium ion, chloride ion) Part B: Complete the table below: Atom Symbol Mass Number Protons Lithium +1 3Li _________ _________ Oxygen _________ _________ Neon _________ Nitrogen Fluorine Number of Electrons Neutrons Net Charge _________ 4 +1 8 _________ 8 -2 20 _________ _________ 10 0 _________ 14 _________ 10 7 _________ _________ _________ _________ 10 10 -1 Analysis: ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ THIRD QUARTER WEEK 6: PERFORMANCE TASK No. 1 For the learner: This worksheet contains activities about subatomic particles, anions, and cations. You may answer directly to this activity sheets and make sure to follow the directions stated in each part of the activity. Answer all questions the best that you can and please write legibly. For the parents: Learners may require your guidance in following the directions and answering the questions in each part of the activity. Make sure that they answer each part of the worksheet. Objectives: • Compute for the number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and mass number of a neutral, negative and positive atom. Explain the transformation of a neutral atom into an anion and cation. • ACTIVITY #2 – WHAT’S THE CHARGE (Part 2)? WHAT I NEED (MATERIALS) ▪ ▪ phet simulation cellphone/ laptop/ tablet/ desktop WHAT TO DO (PROCEDURE) 1. Download the simulation here: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/build-an-atom/latest/build-an- atom_en.html 2. Follow the link and manipulate and play with the simulation for 10 minutes and answer the questions given in the analysis part of the activity. ANALYSIS: Fill-up the missing information using the simulation. Atom Symbol Mass Number Protons Number of Electrons Neutrons Net Charge Lithium +1 3Li _______ _______ _______ 4 _______ Oxygen _______ _______ _______ _______ 8 -2 Neon _______ 20 _______ _______ _______ 0 Guide Questions: 1. What sub-atomic particle determines the identity of the atom? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What makes an atom a positive and a negative ion? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. In what case an atom is considered neutral? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. How do you determine the mass number of an atom? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Label the numerical information of the given atomic symbol below: +2 40 Ca 20 6. Click the “game” menu and try to play level 1 to check your concepts. WHAT I LEARNED (GENERALIZATION) Write down in the box what you have learned from the lesson . REFERENCES: • https://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch6/index.php#:~:text=The%20number%20of%2 0protons%2C%20neutrons,to%20the%20number%20of%20protons. • https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-chemistry/chapter/the-structure-of-the-atom/ • https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/build-an-atom/latest/build-an-atom_en.html • https://www.webmd.com/balance/features/negative-ions-create-positivevibes#:~:text=Think%20mountains%2C%20waterfalls%2C%20and%20beaches,and%20boost%20our%20 daytime%20energy.