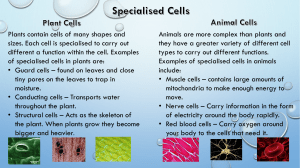
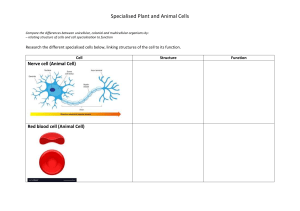
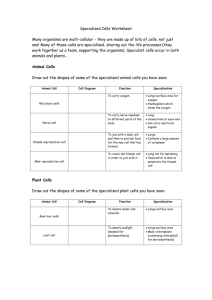
Student Expectations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Turn off your camera. Mute your microphone (unless your teacher asks you to unmute). Engage in the lesson and only use the chat facility to ask or answer questions related to the lesson. All lesson are recorded & stored . If necessary these will be viewed by Mrs Wilson and your Head of Year. Inappropriate behaviour will result in a phone call or a home visit during the lesson and you will be removed from the lesson by the teacher. At the start of the lesson either, open an e-mail addressed to victor.oczadly@astreadearne.org, have a word document or have pen & paper available to make notes/complete the lesson tasks. Send your work to your teacher at the end of each session (victor.oczadly@astreadearne.org). In the case of hand written work, take a photo & email that. Please note: if you fail to follow these expectations, you will not be able to access Dearne Home Learning and will attend school for face to face teaching. Tuesday, 21 February 2023 1. Last Lesson Identify the stain to view • An onion cell • A cheek cell 3. Last topic 2. Last week 5. Challenge Covert these measurements 0.5cm = ? mm = 5mm 23mm = ? μm = 23000μm 15mm = ? μm = 15000μm 200μm = ? mm = 0.2mm Sketch an energy profile diagram for an exothermic reaction How do we convert cm to mm? How do we convert mm to μm? x10 x1000 4. Last Year Name an organ system. Give 3 organs within it. Success is the result of preparation, hard work and learning from failure What do you recall about these specialised cells? Are they all the same? Plant root hair cells Red Blood cells Nerve cells Muscle cells Sperm cells Specialised Cells 21 February 2023 To explore how cells become differentiated to become specialised State some examples of specialised cells Describe the process of differentiation • Sperm , Nerve, Muscle, Root Hair, Xylem • Differentiate • Specialised Relate the structure of the specialised cells to their function How do we go from this unspecialised to this specialised cell? Cell differentiation Cell differentiation This process involves the cells structure changing to allow the cell to complete a particular job it will now be known as a specialised cell. Once an animal cell is differentiated it will lose the ability to repeat the process whereas in plants a special section called a meristem allows the cells to differentiate over and over. Can you define these key terms using the information above? Differentiation Specialised Specialised Cells We now know that cells are different. Why? 1. BETWEEN SPECIES: Different types of organisms live in different environments. Their cells are adapted to survive in those environments. (Write examples on your sheet – think animal vs. plant vs. bacteria) 2. WITHIN A SPECIES: Multi-cellular organisms’ cells carry out specific jobs. We say that they are specialised. This means that they need to be a certain shape and have special structures and proteins that help them do the job/function properly. (Write examples of different organs/cell types on your sheet). Complete the table C H A L L E N G E Create your own table outlining the cell structure, function and adaptations Create your own way to represent the information you find, a cell profile, a spider diagram You must include name, function, adaptations Who am I? • I have and increased surface area to absorb sunlight • I am large & have my own food source • I have long cells with lots of connections? • Transport water in plants, I am long and hollow • I have a large surface area & no nucleus • My job is to carry male DNA to the female DNA • I am in plant roots Who am I? • I have and increased surface area to absorb sunlight Palisade Cell • I am large & have my own food source Egg Cell Nerve Cell • I have long cells with lots of connections? Xylem Cell • Transport water in plants, I am long and hollow • I have a large surface area & no nucleusRed Blood Cell • My job is to carry male DNA to the female DNA Sperm Cell • I am in plant roots Root Hair Cell C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E C H A L L E N G E Tuesday, 21 February 2023 Complete the following questions about our learning Group the following into animal or plant cell Sperm cell, xylem cell, nerve cell, root hair cell, muscle cell Describe the basic stages to view an onion cell Convert the following 1m to mm 5 um to mm Success is the result of preparation, hard work and learning from failure Life is really tough at the moment. There is always someone for you to talk to: School Support Mrs Crawford (Mental Wellbeing Lead Practitioner) kirsty.crawford@astreadearne.org Your Head of Year firstname.surname@astreadearne.org Mrs Dowling (Designated Safeguarding Officer) katie.dowling@astreadearne.org Telephone Support Mrs Fisher (Deputy Designated Safeguarding Officer) sally.fisher@astreadearne.org Childline - 0800 1111 Websites MIND - 01226 211188 / 01709 919929 YOUNG MINDS www.youngminds.co.uk SHOUT www.giveusashout.org SELF HARM www.selfharm.co.uk www.nhs/conditions/selfharm www.harmless.org.uk SUICIDAL TEENS www.papyrus-uk.org CHILDLINE www.childline.org.uk NSPCC www.nspcc.org.uk THE MIX www.themix.org.uk NIGHTLINE www.nightline.ac.uk Bereavement Services - 0800 048 5224 SHOUT - Text to 85258 TADS - 01226 872120 Targeted Youth Support - 08000345340 NSPCC - 0800 1111 APP Support BLUEICE CALMHARM CATCH IT CHILL PANDA