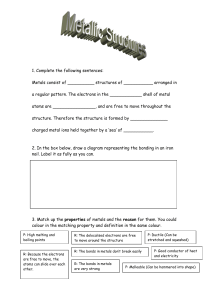
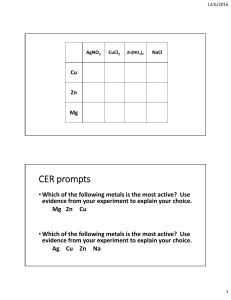
Chapter 7/Lesson 3 Metallic Bonds P: Objectives Describe the structure of a metal crystal. Identify properties of metals. Introduction HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=EVV3TPAQ2-A HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=B1Y2Q6YX1BQ WHAT ARE METALS: HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=VOUFTUVF4QK HTTPS://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=S08QDOTD0W0 Metallic Bonding Video Metals Metals are made up of closely packed cations surrounded by electrons, rather than neutral atoms or ions Outer electron clouds of the metal ions overlap What are Metals? On the periodic table, a diagonal or stair step line drawn from boron (B) to polonium (Po) separates the metals from the nonmetals. Elements on this line are metalloids, sometimes called semimetals; elements to the lower left are metals; elements to the upper right are nonmetals. Almost 80% of the elements on the periodic table are metals. Metallic Bond Model Electron sea model – metals in a solid contribute their valence electrons to form a “sea of electrons” ◦ Valence electrons are not held by any specific atom and can move easily from one atom to the next Delocalized electrons –are free to move in the “sea of electrons” Online Worksheet ONLINE WORKSHEET FILL IN THE BLANKS Metallic Bonds The valence electrons of metal atoms can drift freely from one part of the metal to another- this is sometimes called a “sea of electrons” Metallic bonds consist of the attraction between these free floating electrons and the positively charged metal ions (cations). This attraction is the “bond” that holds metals together. Metallic Bond Definition: The attraction of the delocalized electrons for the positively charged metal ions Metal bonded to metal Each ion is bonded to all neighboring cations by the “sea” of valence electrons Properties of Metals In general, metals have moderately high melting and boiling points Good conductors of heat and electricity Malleable and Ductile ◦ Mobile electrons can easily be pushed or pulled past each other Physical Properties of Metals Lusterous- they are shiny! High density- atoms are tightly packed. Good conductors of electricity and heat. ◦ Reason- electrons can flow freely. Physical Properties of Metals Ductile- they can be drawn into wires AND Malleable- they can be hammered into shapes ◦ Reason- cations can slide easily past each other because the sea of electrons insulates them and prevents strong repulsions. …on the other hand IONIC COMPOUNDS ARE BRIT TLE AND BREAK EASILY? WHY Game Time Properties of metals Matching Properties Hit the correct mole game Physical Properties of Metals Metal ions are arranged in very compact orderly patterns. –Similar to the way apples are stacked at the grocery store. Pure metals form the simplest kinds of crystals Structure of Metals Metal atoms are arranged in very compact and orderly patterns Metals that contain just one kind of atom are among the simplest forms of all crystalline solids Game Time Metallic Bonds Game Chemical Properties of Metals Most metals are chemically unstable and will react will oxygen in the air- that is they form oxides- over varying timescales (for example iron rusts over years and potassium burns in seconds). Chemical Properties of Metals -The alkali metals react quickest followed by the alkaline earth metals. -The transition metals take much longer to oxidize (such as iron, copper, zinc, nickel). Others, like palladium, platinum and gold, do not react with the atmosphere at all. -Some metals form a barrier layer of oxide on their surface which cannot be penetrated by further oxygen molecules and thus retain their shiny appearance and good conductivity for many decades (like aluminium, some steels, and titanium). Alloys Very few metals that you encounter daily are pure metals. Most metals are alloys, a mixture of two or more elements of which at least one is a metal. Alloys are important because their properties are often superior to those of their component elements. • Examples: • Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc • Sterling silver is an alloy of silver (92%) and copper (8%) • Stainless Steel is an alloy of iron (81%), chromium (18%), nickel (1%), and trace amounts of carbon. • Examples: • Sterling silver is harder and more durable than pure silver, but still soft enough to make jewelry and tableware. • Brass is harder and easier to shape than either copper or zinc Alloy is a mixture of two or more elements (at least one must be a metal) Metal Alloys Alloy has metallic properties often superior to those of their component elements -Bronze: copper + tin -Steel: iron + carbon + other metals -Sterling silver: silver + copper Zn Brass though a magnifier Brass at the atomic level Cu 2 common types of Alloys Substitutional: one metal about the size of the other replaces it examples: Brass, pewter, 10-carat gold Interstitial: one metal smaller than the other fits between it example: Carbon steel Types of Alloys SUBSTITUTIONAL Atoms have relatively the same size INTERSTITIAL Atoms of different sizes