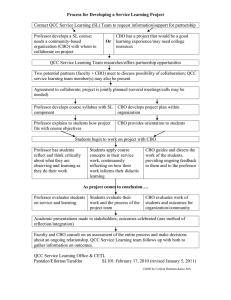
COMMUNITY ORGANIZING The Helping Process STEPS IN THE CO HELPING PROCESS • • • • • • • • • • Community Entry Integration/Immersion Social Investigation Problem identification and prioritization Core group formation Formalizing the organization Community planning Plan implementation Evaluation Phase out COMMUNITY ENTRY - the process where the Community Organizer (CO) officially enters the community Importance: Community Organizer (CO) is introduced to local authorities and other key people in the community. It is the first step by the Community Organizer (CO) towards integration into the community COMMUNITY ENTRY . Preparation Role of the agency • Clarify why it wants to work in the community. • Develop criteria for target community • Select target community using the criteria • Develop criteria for contact person and host family COMMUNITY ENTRY Process Tasks of the Community Organizer (CO) • Visit the house of contact person • Together with the contact person, pay courtesy call to local authorities and key people in the community • Stay temporarily with host family recommended by contact person INTEGRATION / IMMERSION the process of staying and living together with the people in the community and experience their way of life get to know the culture, economy, leader, history, lifestyle, etc. INTEGRATION / IMMERSION continuing process of establishing rapport with and among members of the community for the purpose of establishing or developing a relationship of mutual respect, trust and open communication INTEGRATION / IMMERSION Objectives: 1. understand and adapt to the culture and lifestyle of the community 2. develop organizational cohesiveness among members of the community 3. facilitate better working relationship and therefore collective, effective and efficient action INTEGRATION/IMMERSION Objectives: (con’t.) 4. define the roles of the CO and the people 5. to build contacts INTEGRATION / IMMERSION Principles: - avoid imposing your own culture on people - be honest about your limitations - choose a modest dwelling (lifestyle) - -Community respect should be cultivated - avoid raising expectations by promising Clearly describe what be realistically offered - be open to learn from people INTEGRATION / IMMERSION Integration/Immersion Methods - LESS principle - participate in their economic activities - join in social events - visit homes - converse with people one-on-one INTEGRATION / IMMERSION . Important advice for the Community Organizer (CO) • Be humble • Be polite • Respect local belief, religion and culture • Do not get drunk • Do not make promises that will not be fulfilled. • Do not flirt • Do not talk about political parties SOCIAL INVESTIGATION - process of systematically learning and analyzing the various structures in the community – political, economic, socio-cultural - gathering and analysis of data about a community and its issues - the results will serve as basis for organizing or for issue(s) planning and strategizing SOCIAL INVESTIGATION Guidelines: 1. have a working knowledge of both the objective and subjective realities of the community 2. make an accurate ad comprehensive assessment of the various realities of the community SOCIAL INVESTIGATION Guidelines (con’t.): 3. avoid pushing for projects conceived mainly on the change agent’s perception of problems. People do not often identify with these projects. Hence, the are not sustained and are short lived. SOCIAL INVESTIGATION Methodology 1. Conducting surveys 2. Interviewing individuals on a one-on-one basis 3. discussing in small groups 4. gathering and reviewing secondary data 5. observation 6. use natural and subtle data gathering methods rather than pen and paper style 7. develop an atmosphere of mutual trust COMMUNITY PROFILE: ELEMENTS Should be comprehensive in coverage How different aspects of the life of the community are interrelated 1. The area as a place to live – quality of the physical environment and people’s attitudes to living there; the extent t which needs are matched with resources; and the extent to which local facilities meet people’s goals &n aspirations COMMUNITY PROFILE: ELEMENTS 2. The area as a social community – residents’ involvement in the social life of the community; the extent to which the community is supportive; formal and informal networks 3. The area as an economic community – income levels and employment prospects of local residents; prosperity and viability of local shops 4. The area as a political community – systems and structures of political representation and local area management; the extent to which local people COMMUNITY PROFILE: ELEMENTS • Can influence the decision s that affect them; the degree of involvement in local decision making; participation in community organizations 5. The area as personal space – degree of attachment that people have to the local area; memories and life experiences of local people 6. The area as part of its city – infrastructural, economic and social linkages between the local area and the city/district of which it is a part; the specific local identity that differentiates the community from the rest of the area/district COMMUNITY PROFILE: ELEMENTS • Our definition refers to needs and resources both of which are important for a full understanding of a community • Resources – assets held in the area and put to use for the benefit of the community - intangible resources that are sources of strength and potential within the community • Need as legitimate basis on which to make at least some decisions about the allocation of resources PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION - collective identification and prioritization of community problems - consider real needs, capabilities, organizational impact, urgency of problems PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION • Criteria for selection of first problem requiring action: - a substantial number are affected, are interested in, or have been acting on the problem - problem is simple; within people capability o solve and can easily be resolved: to develop confidence in themselves and their problem solving skills PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION • the problem when tackled should not create unnecessary division in the community, especially at the initial stage • the problem may be urgent. A problem which cannot be set aside because it will worsen if not attended to should be considered for action PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION Objectives: - ensure that organizational activities or projects are based on people’s genuine needs - provide people with the opportunity to develop their problem solving skills and confidence - develop people’s confidence in the process - develop among other residents the credibility of the group tackling the issue/problem Criteria in Identifying Community Problems • The problem occurs too frequently (frequency) • The problem has lasted for a while (duration) • The problem affects many people (scope, or range) • The problem is disrupting to personal or community life, and possibly intense (severity) • The problem deprives people of legal or moral rights (equity) • The issue is perceived as a problem (perception) PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION Methodology - one-on-one groundworking - calling a meeting of residents for identification and problem analysis (cause-effect-action) - problem prioritization - gut feeling of people; systematic method PROBLEM/ ISSUE IDENTIFICATION and PRIORITIZATION Tasks of Community Organizer (CO) • Observe and talk to people in the community • Identify potential core group members using criteria • Select and recruit 5-7 potential core group members. Women should be included. • Conduct orientation meeting with all core group members. Introduce and explain the work of the agency. Explain and clarify responsibilities of core group members CORE GROUP FORMATION Process The agency develops criteria for selecting core group members which may include the following: • Leadership • Integrity • Availability • Commitment • Knowledge and skills CORE GROUP FORMATION - made up of 5-7 individuals from the community selected and recruited by the Community Organizer (CO) to help facilitate the formation of the Community Based Organization (CBO) Importance The core group works together with the Community Organizer (CO) and provides community leadership towards the formation of the Community Based Organization (CBO) FORMALIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION Community Based Organization (CBO) is an association of people living in the same geographic location Importance The Community Based Organization (CBO) is a structure that provides people with opportunities to work together to solve common problems affecting their lives FORMALIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION Process The task of Community Organizer in CBO formation is to help the core group members to: • Identify and analyze community problems • Brainstorm and prioritize solutions • Discuss and determine the importance of CBO formation • Identify steps for CBO formation • Develop criteria for CBO leaders FORMALIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION Process Steps in Community Based Organization (CBO) formation the core group is responsible for the following activities: a. Planning for the community meeting • Determine the purpose of the meeting • Determine suitable place and time • Plan the agenda and clarify responsibilities • Announce the schedule, purpose and participants of the meeting FORMALIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION Activities during the community meeting • • • • • Clearly explain the purpose and agenda Present community problems affecting community and the need to solve problems by working together Present the idea and get approval for the formation of the Community Based Organization (CBO) Present the idea of the need to elect 5-7 CBO leaders. Discuss the process for nomination and election Present the responsibilities of CBO leaders and their term of office FORMALIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION Activities after the community meeting • • The CO should meet with the newly elected CBO leaders after the community meeting The CO will arrange the time, place and agenda for the first formal meeting of the CBO leaders COMMUNITY CAPACITY BUILDING Definition the process of developing and strengthening knowledge, skills and experience of the CBO leaders and members Importance Developing the capacity of the CBO leaders and members will ensure greater community participation, self-reliance and sustainability of the organization COMMUNITY CAPACITY BUILDING 1. Definition “Community Capacity Building” is the process of developing and strengthening knowledge, skills and experience of the CBO leaders and members. 2. Importance Developing the capacity of the CBO leaders and members will ensure greater community participation, self-reliance and sustainability of the organization. COMMUNITY CAPACITY BUILDING Process Tasks of the CBO leaders: • Conduct assessment of training needs of CBO leaders and members • Develop plan based on training needs • Identify available internal and external resources to meet training needs • Training of first line and second line of CBO leaders COMMUNITY CAPACITY BUILDING Basic skills needed by the Community Based Organization (CBO) • Facilitating CBO and community meeting • Recording of minutes of the meeting • Research and data gathering • Planning • Monitoring and evaluation • Communication skills • Management skills • Financial skills • Project proposal making COMMUNITY PLANNING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING Definition the process of developing a community action plan based on priorities, objectives and resources towards community problem solving Importance Community planning provides opportunities for the community members to participate in decision making, thus ensuring ownership of the problem solving process. It also enables them to identify and formulate solutions to their common problems together COMMUNITY PLANNING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING Process The tasks of the planning committee are: • Review community priorities based on the result of the PCR and develop community action plan: – Identify possible project/s – Set up project objectives – Identify target groups – Identify activities and persons responsible – Identify resources needed – Develop budget – Develop strategy on how to access to resources needed COMMUNITY PLANNING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING Process The tasks are: • Review community priorities based on the results and call a community meeting to present community action plan. Presentation, validation and approval of community action plan by community members. • Finalize community action plan based on suggestions and recommendation of community members COMMUNITY RESOURCE MOBILIZATION Definition the process of utilizing people and their resources towards accomplishing desired changes in the community Importance The community needs resources in order to implement its projects and activities. Community resource mobilization enables the community to maximize the use of available local resources towards achieving problem solving objectives. External resources should only be utilized if local resources are not available COMMUNITY RESOURCE MOBILIZATION Process Role of the CBO Leaders in mobilizing community resources: • Establish clear and regular communication and feedback system with community members • Secure commitments of community members towards a particular cause • Follow-up and monitor commitments of community members • Delegate responsibilities in problem solving to maximize participation PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION - implementation by people of their issue/problem plan; fact to face contact between those affected by the problem and those who are responsible for making decisions about the problem - provides people concrete experience and direct contact with the unresponsive structures/systems and authorities in society PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION B. Project Monitoring Monitoring is the assessment of the project implementation process and activities and to check, whether the results are achieving the objectives of the desired change. Monitoring should be regularly done during the implementation process PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION Definition C. Evaluation Evaluation is the process of assessing the impact of the projects and activities of the community. It is concerned with determining the accomplishments of goals and objectives. The community members should conduct the evaluation themselves at the completion of a project or activity. 2. Importance The “Community Action Plan” is the vehicle to achieve desired community changes. A regular monitoring and evaluation process will ensure effective achievement of activities and desired results. PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION Importance The community action plan is the vehicle to achieve desired community changes. A regular monitoring and evaluation process will ensure effective achievement of activities and desired results PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION The tasks of the “CBO leaders” during project implementation are the following: A. Project Implementation • Oversee and direct the implementation of projects and activities. • Clarify roles of each member in projects or activities. • Motivate the community members to contribute to the projects and activities. Mobilize the use of community resources for the projects or activities. PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION • • • Conduct regular consultation and feedback with community members. Manage inter-personal relationships and conflict management. Facilitate team building activities. Conduct an information and advocacy campaign on the “Community Action Plan”. PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION Definition A. Project implementation It is the process of carrying out projects and activities towards achieving the desired change. Through implementation, plans are mobilized into a series of actions that will lead toward accomplishment of the goals and objectives. . EVALUATION - assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of actions to determine if the objectives were achieved or not Objectives: a) identify strengths and weaknesses b) reinforce the strengths and rectify the weaknesses c) learn from the experience EVALUATION Reflection: - drawing out learning/lessons from actions or experiences - develops the necessary awareness, values and attitudinal foundations in people to sustain action and organizational activities PHASE OUT PHASE OUT Community exit is the process whereby the Community Organizer (CO) gradually leaves the community as the Community Based Organization (CBO) moves towards independence and self-reliance PHASE OUT Importance The community exit strategy enables the Community Based Organization (CBO) to grow and gradually develop into a mature selfgoverning and self-reliant association independent. The CBO needs to grow and develop into a self-governing and self- reliant institution at its own pace and on its own time. At the initial stage of Community Organizing process, the CO takes a major role in leading the CBO in the problem solving process. PHASE OUT • As the capacity of the CBO leaders and members gradually develop, they should assume more responsibilities and move towards becoming independent and self-reliant. • The role of the CO should change from initiating, leading and managing to facilitating and coordinating of development activities. PHASE OUT Process The Community Based Organization (CBO) needs to establish federations, actively participate in networks and build strategic alliances with other groups and organizations in a continuing basis. These partnerships will enable the CBO to give and receive support from other CBOs, groups and organizations. PHASE OUT The tasks of the Community Organizer (CO) in enabling CBO leaders to move towards becoming an independent CBO: • Continuing education for CBO leaders and members, especially developing second and third line of leaders • Strengthening communication and resource mobilization skills, especially local fundraising PHASE OUT • • • Establishing strong support system through networking and building alliances with government and non-government organizations Establish linkages and networking with other organizations at the village, commune, district, province and national level. Join CBO federations with similar values and objectives for mutual benefit where appropriate. Thanks! 59