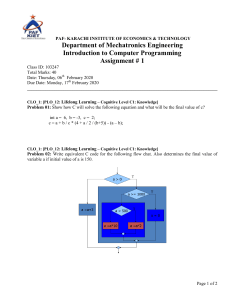
STUDENT HAND BOOK BS ACCOUNTING & FINANCE DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE & ACCOUNTING NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF MODERN LANGUAGES (NUML) SECTOR H-9 ISLAMABAD Course Title: Principles of Accounting Course Code: FIN 112 Credit Hours: 3+0 Course Instructor: Muhammad Irfan Khadim Mode of Contact" You can contact your course instructor in the following ways: Email: ikhadim@numl.edu.pk Meeting: By appointment via e-mail PREREQUISITES: None Textbook: “FINANCIAL & MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING (The Basis for Business Decisions’ - 15th edition (Chapter 1_5) Authors: Robert F. Meigs Walter B Meigs Jan R. Williams Susan F. Haka Mark S. Bettner Joseph V. Carcello Reference Material: Fundamentals of Accounting by Libby & Libby (8th Edition) Course Description: Fundamentals of Accounting is a course that covers the fundamentals of accounting with the newcomer in mind. Accounting is more than just memorizing terms and procedures. This course assumes students have no prior knowledge about accounting or finance, and delivers lessons and examples to build accounting skills. Specifically, this class addresses accounting terminology, revenue, expenses, net income, the accounting equation, debits, credits, and balancing the accounting formula, the accounting structure, the accounting cycle, journals, ledgers, the trial balance and more. It also guides students to learn how to read financial statements properly, and how to grab meaningful information from the balance sheet, income statements and cash flow statements. Course Objectives: The objective of this course is as under: 1. To provide an introductory knowledge of accounting to first-Semester students. 2. While a general overview of accounting principles relating to the preparation of financial and managerial reports will be presented, the primary focus is to illuminate how accounting information is utilized by a variety of stakeholders in planning, controlling and investing decisions. 3. After completing this course, students will have a solid understanding of accounting in today's world. 4. They will understand how and why financial transactions are documented, they will know what cash flow is and how to improve it, and they will know what profit is, how it's interpreted and what influences its growth Course Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of this course, students will be able to: 1. Identify why accounting is a necessary skill. 2. Summarize the history of accounting. 3. Identify and describe assets, liabilities and owners' equity. 4. Recognize and compare the major financial reports. 5. Describe and create a company's Income Statement. 6. Compare and contrast a company's revenue, expenses, income, and retained earnings. 7. Solve worksheet problems involving income statements, revenue, expenses, and net income. 8. Identify the key elements of a Balance Sheet. 9. Balance the accounting equation and properly chart debits and credits. 10. Describe the key elements of bookkeeping. 11. Avoid the pitfalls of bad bookkeeping habits. 12. Describe the accounting cycle. ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENT WITH WEIGHTS: SNR ITEMS 1 Mid Term Exam 2 End Term Exam 3 Internal Evaluation Breakdown Quiz(s) Assignements(s) Class Participation Présentations Case Discussion Lab Work/Practical Project MARKS 30 50 5 5 5 5 Any Other Total 20 GRAND TOTAL 20 100 COURSE CONTENTS: Lecture Scheduled Topic Learning Activity Assessment Activity PLOi CLO Thinking Level PLO 1 CLO 1 Knowledge PLO 1 CLO 3 Knowledge PLO 1 CLO 3 Comprehension 01 Introduction to Accounting. ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Accounting Information. Types of Accounting Information. Role of Accounting Information in making Lecture decisions. Importance of Accounting Information for internal and external users. Accounting Systems. 02 Introduction to Accounting. ■ Basic Terms. Business and its types. ■ Types of Accounts (Assets, Liabilities ■ Capital, Expense and Revenue. ■ Types of Accounts. ■ Accounting Cycle. ■ Accounting Period, Fiscal Year ■ Credit, Debit, 03 Accounting cycle ( Basics) Lecture ■ How to balance the fundamental accounting equation; ■ Debits and Credits; Lecture ■ Double Entry Accounting; Diagrams and Charts; Real World Example; Quiz # 1 04 Accounting cycle ( Basics) ■ Cash and credit transaction. ■ Effect of Transactions on Accounting Equation. ■ Source Documents ■ General Journal. Journalizing the events of increase in capital, increase and decrease in Assets and Liabilities. Lecture Q&A PLO 1 CLO 9 Knowledge PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension PLO 1 CLO 12 Comprehension PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension PLO 2 CLO 4 Comprehension PLO 4 CLO Comprehension 05 Accounting cycle ( Journal) Lecture ■ General Journal. Accrual Basis Accounting 06 Accounting cycle ( Journal) Lecture & Case ■ Applying Matching and Realization principle in let Recognizing expenses and Revenue. 07 Accounting cycle (Ledger) ■ General Journal and its relationship to ledger. ■ Posting (Process of transferring information Lecture from the journal to the individual accounts in the Ledger. ■ Types of Ledgers. 08 Accounting cycle (Trial Balance) ■ Trial Balance, Its Uses and Limitations. ■ Errors in trial balance, suspense account Lecture Assignment 1 09 Accounting cycle (Financial Statements) ■ Financial Statements. Nature and general Lecture purpose of Financial Statements. Relevant Accounting Principles Lecture 10 Accounting cycle (Financial Statements) Quiz # 2 11 12 13 14 ■ Purpose of the Income Statement; Multi-Step Income Statement; What are ■ Retained Earnings, Revenue, Expenses, Net Income, Income Tax Accounting cycle (Financial Statements) ■ Statement of Retained Earnings and Classified Balance Sheet. Lecture ■ Relation of Income statement, Statement of Owners Equity and Balance Sheet. Accounting cycle (Financial Statements) ■ Incomplete Income statement and balance Lecture & Case sheet let ■ Rectifying errors in income statement and balance sheet Accounting cycle (Financial Statements) ■ Rectifying errors in income statement and Lecture balance sheet ■ Accounting principles and conventions Accounting cycle Practice from journal to Balance Sheet. Accounting Cycle.Lecture 5 Assignment 2 Quiz 3 15 Accounting cycle (Adjusting Entries) ■ Need for adjusting entries, ■ Types of Adjusting Entries. ■ The concept of Depreciation. Lecture ■ Accumulated Depreciation. Book Value. Contra Asset Account. Depreciate able Assets. Useful Life. 16 Accounting cycle (Adjusting Entries) ■ ■ Converting Assets to Expenses; Prepaid Expenses, Accrued Expenses Lecture Q&A PLO 4 CLO 8 Comprehension PLO 4 CLO 8 Comprehension PLO 4 CLO 8 Comprehension PLO 2 CLO 8 Comprehension PLO 2 CLO 6 Knowledge PLO 2 CLO 6 Comprehension 17 Accounting cycle (Adjusting Entries) ■ Converting liabilities to Revenue. ■ Accruing uncollected revenue. 18 Accounting cycle (Adjusted Trial Balance) ■ Purpose of Adjusted Trial Balance. ■ Effects of Adjusting Entries on Financial Statements 19 Accounting cycle (Supplemental Topic) ■ Preparing a Work Sheet and its uses. Lecture Lecture Assignment 3 Quiz 4 Lecture PLO 2 CLO 6 Comprehension PLO 2 CLO 7,8 Comprehension PLO 2 CLO 7 Comprehension 20 Accounting cycle (Closing Entries) Closing Temporary Accounts. Lecture Q&A PLO 2 CLO 12 Comprehension Lecture Quiz 5 PLO 2 CLO 12 Comprehension PLO 1 CLO 1 knowledge 21 Accounting cycle (After Closing Trail balance) ■ Prepare after closing trail balance 22 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns ■ ■ Introduction to Merchandising Concerns. Operating cycle of Merchandising Companies Lecture 23 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns Lecture Q&A PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension Lecture Q&A PLO 2 CLO 10 Comprehension PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension ■ Journal Entries in Periodic & Perpetual Systems 24 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns’ ■ ■ Credit terms, Cash discounts, Returns of Unsatisfactory ,Merchandising Exercise 25 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns ■ Special cases in Merchandising Companies Net Lecture & Case let method. 26 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns ■ Special cases in Merchandising Companies Net method. 27 Accounting for Merchandising Concerns ■ Practice Questions and cases 28 Cases Discussions/ Projects/ Presentation 29 Cases Discussions/ Projects/ Presentation 30 Cases Discussions/ Projects/ Presentation 31 Cases Discussions/ Projects/ Presentation Lecture Assignment 4 PLO 1 CLO 10 Comprehension Lecture Quiz 6 PLO 2 CLO 10 Comprehension Presentations Q&A PLO 3 CLO 1-12 Application Presentations Q&A PLO 3 Presentations Q&A PLO 3 Presentations Q&A PLO 3 32 Revision Lecture Q & A for orally ask questions from previous lecture. Case let: a small case discuss in the book. PLO 3 CLO 1-12 CLO 1-12 CLO 1-12 CLO 1-12 Application Application ion Application Comprehension