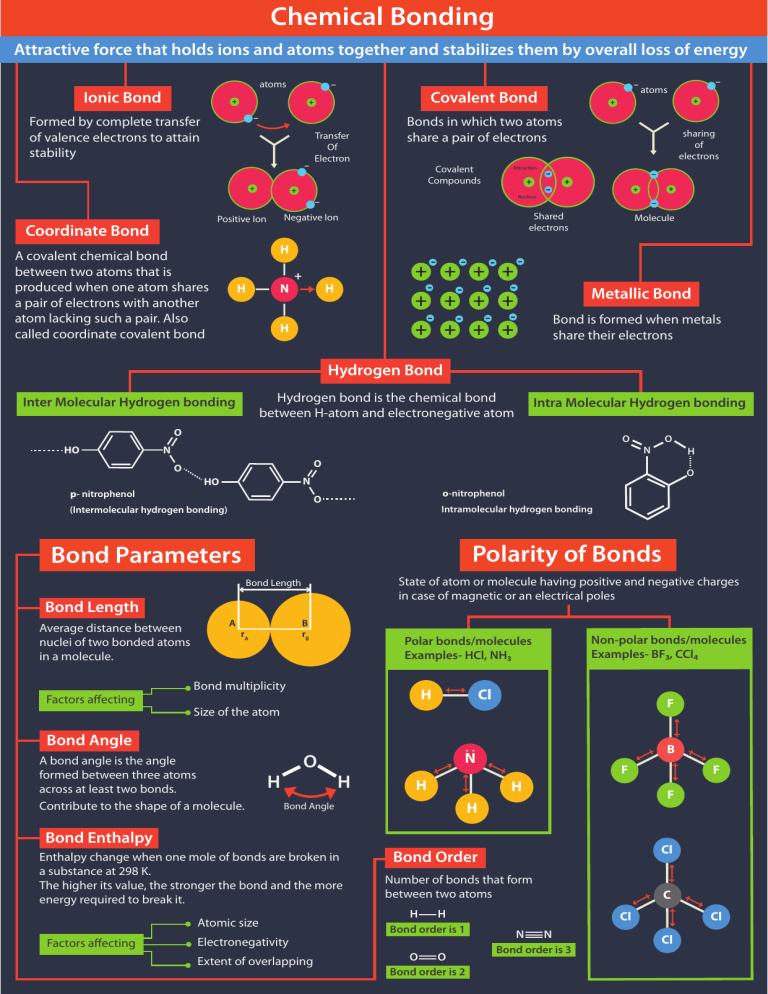
Chemical Bonding Attractive force that holds ions and atoms together and stabilizes them by overall loss of energy atoms Ionic Bond - + Covalent Bond + - Formed by complete transfer of valence electrons to attain stability + Transfer Of Electron Covalent Compounds + Attraction + Nucleus H A covalent chemical bond between two atoms that is produced when one atom shares a pair of electrons with another atom lacking such a pair. Also called coordinate covalent bond H N + - - - - - - - - - - - + + + + H - sharing of electrons - + + + - Molecule - Metallic Bond + + + + + + + + H + + Shared electrons Negative Ion Positive Ion - atoms Bonds in which two atoms share a pair of electrons - Coordinate Bond - Bond is formed when metals share their electrons Hydrogen Bond Hydrogen bond is the chemical bond between H-atom and electronegative atom Inter Molecular Hydrogen bonding Intra Molecular Hydrogen bonding O HO O N O N HO p- nitrophenol o-nitrophenol O (Intermolecular hydrogen bonding) Intramolecular hydrogen bonding Polarity of Bonds Bond Parameters State of atom or molecule having positive and negative charges in case of magnetic or an electrical poles Bond Length Bond Length Factors affecting A B rB rA Polar bonds/molecules Examples- HCl, NH3 Bond multiplicity H Non-polar bonds/molecules Examples- BF3, CCl4 Cl F Size of the atom Bond Angle A bond angle is the angle formed between three atoms across at least two bonds. Contribute to the shape of a molecule. O H .. N H H B H F H Bond Angle Enthalpy change when one mole of bonds are broken in a substance at 298 K. The higher its value, the stronger the bond and the more energy required to break it. Atomic size Electronegativity Extent of overlapping Cl Bond Order Number of bonds that form between two atoms H H Bond order is 1 O O Bond order is 2 F F Bond Enthalpy Factors affecting H O O Average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. O N C Cl Cl N N Bond order is 3 Cl



