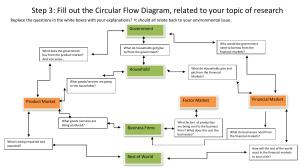
ECONOMIC AND MANGEMENT SCIENCE TOPIC: GOVERNMENT Government is the system by which a country is controlled. Or A group of people that govern the country. In a democratic country the people of the country elect the government. Since 1994 South Africa has operated as a democratic government. The constitution of South Africa lays down the rules of how the South African government functions. Government is responsible for: Making law under which all its citizens are forced to follow. Ruling the country Creating policies and law about the rights and responsibilities of their citizens/people. Collecting taxes so that they can deliver government services and provide infrastructure. Government services include: Education, health , defence force , policing, grants to the poor .etc Infrastructure provided by government include: Road, airports , harbour, hospitals , schools , police stations ,RDP .etc The different levels of Government National government – is responsible for ruling the country. Provincial government – is responsible for ruling the province. Local government – is responsible for ruling the city and towns. Local government o o o o o The whole of south Africa is divided into local municipalities. Each municipality has a council where decisions are made. The municipal council is made up of members who are elected by the residents of the ward, town, or city. Each municipal council must prepare a budget every year. They must also decide on the development plan and services delivery for the area. They must ensure that services are provided to communities. They must promote social and economic development. Examples of municipal service delivery include: o o o o o Municipal health services Decisions about the use of land Supply of electricity and water Sewage and sanitation Refuse/garbage removal o o o o Firefighting services Maintenance of municipal roads Municipal public transport Storm water systems o o o o o o o Provincial government To make national government’s job easier, each of the nine provinces has its own government. The government in each of the provinces is called the provincial government. Each province has its own Premier to lead its government. Provincial government is responsible for a particular province. It deals with economic issues that are specific to a given province. Provincial government develop its own laws and policies within the framework that suit its specific needs. Each province has its plan for developing the economy of the province and improve services. Provincial department includes: o o o Finance Economic Development Tourism o Housing o Education o Health National government The national government is responsible for the overall running of the country. It deals with issues such as safety and security, foreign affairs and international trade. Parliament consists of two houses: • National Assembly • National Council of Provinces. National government branches Legislative branch: Describes a body that has the power to make laws. Makes the laws of the country. It consists of the South African Parliament Executive Branch: Describes a body that has the power to execute or carry out laws. It leads the country. It consists of the President, Deputy President, and ministers. Judicial branch Describes a body that has the power to make sure justice is served. It ensures that justice is served if people break the laws that Parliament makes. It consists of the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court, the High Court, and the Magistrate’s Courts. Legislative branch Executive branch Judicial branch Parliament National Assembly National Council of provinces Cabinet President Deputy president Ministers The law court Constitutional Court Supreme Court of Appeal High Court Magistrates Court Roles of the different levels of government in households’ use of resources and services For a country to work properly, people need to be able to access resources and services. These people can be households or businesses. Government is a consumer as it purchases: Labour, goods and pays for services by members of households. Government is also producer as it produces: Electricity, builds hospitals, police stations and courts for households. Households provide labour and capital for the government, and they consume electricity and water and use the infrastructure, such as roads. Money moves through the economy when households sell their labour to businesses and businesses pay money to households in the form of salaries and wages. Households and businesses are producers and consumers. HOUSEHOLDS: Households are producers because they “sell” their labour as a product to businesses. Households are consumers because they buy the products that businesses produce. BUSINESSES: Businesses are producers because they make or produce goods or services to sell. Businesses are consumers because they buy or use households’ labour to make their products or services. Roles of the different levels of government in business’s use of resources and services There are several ways in which the government interacts with businesses in the economy. Businesses are also called firms. The government can be both a producer and a consumer concerning its relationship with business ➢ Businesses sell services and products to the government. For example, if the national government needs uniforms for the soldiers in the army, it buys these uniforms from a business that makes military uniforms. ➢ Businesses also pay for services that are provided by the government on all levels. For example, every vehicle needs to have a licence that is paid to the government for the use of the roads and the services of the traffic departments. The government uses many of the same resources as it does for households. Industries require large quantities of natural resources like water and coal for electricity. It also needs human-built resources like good road transport networks, railways and harbours. Businesses employ members of households and pay for their labour. In this way, they give households the means to pay taxes to the national government. Businesses also pay taxes to the national government. Businesses use or consume the services that the provincial and local government provides, such as electricity and water. TOPIC: The National Budget National budget: A National Budget is a summary of the government’s expected income and their planned expenditure. The money to pay for countries need comes mostly from taxes. The government may borrow money locally or internationally if it does not have money. Most taxes are collected for the National government by the SARS.(South African Reserve Services). Government revenue : Is the government income obtained from taxes, property that it rents, Interest on investment and government borrowings. This is the money available to render services to the country and to pay government workers. The government generate revenue from direct and indirect taxes. Direct tax: is tax on earning (income tax or PAYE- Pay As You Earn) Indirect tax: is a tax that you do not pay directly from your earnings, it is a consumption tax (VAT). Government expenditure on services ➢ The government uses the revenue it raises to provide public goods and services. ➢ Government spending focuses on providing citizens with education, health care, safety and security, and the necessary infrastructure (roads, airports, railways, harbours, hospitals and schools) Education Education is an important national priority. The government spends large sums of money providing schools, educators, and textbooks to learners, teachers, and furniture. Health The South African constitution guarantees all individuals the right to health. The government’s health department provides primary health care in the form of local clinics. The Department is committed to the following: ➢ Increasing life expectancy. ➢ Lowering levels of mother and child death. ➢ Combatting HIV and AIDS and decreasing the burden of diseases from tuberculosis (TB). ➢ Strengthening the effectiveness of the health system. Housing The government makes money available to provide housing and social grants to the poor citizens of the country. This is one way of reducing poverty and raising the standard of living for economically vulnerable individuals. Social grants Social grants play an important role in protecting the poorest households against poverty. ➢ The old-age pensions; disability; war veterans; child support; foster care; care dependency and grants in aid. ➢ Child support grants. ➢ Foster care grants. Transport The Department of Transport is responsible for the regulation of public transport, rail transportation, civil aviation, shipping, freight and motor vehicles. The department is also responsible for providing the infrastructure – roads, bridges, rail links, airports and harbours that are needed to move people and goods around the country as part of its economic activity. Security Government is responsible for keeping the peace and enforcing law and order in the country. The rights and safety of all citizens must be protected, and peace and stability attract business investments, which help the economy to grow. The impact of the National Budget on economic growth ➢ The national Budget is the most important instrument of fiscal policy that the government can use to shape or stimulate economic growth. ➢ To achieve this, the government has to make sure more goods and services are produced. ➢ To stimulate economic growth, the government has to spend its money in such a way that it encourages new businesses to be established and existing businesses to expand their profits. Economic Growth is an increase in the capacity of an economy to produce goods and services, compared from one period of time to another. Economic growth can be measured in nominal terms, which include inflation, or in real terms, which are adjusted for inflation. Inflation is a substantial rise in the general level of prices related to an increase in the volume of money and resulting in the loss of value of the currency.