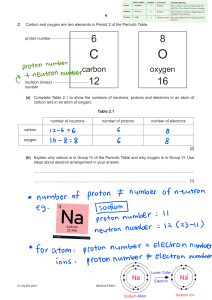
Part of the nucleus of an atom is made up of protons. Each proton has a positive electrical charge and attracts electrons; neutrons form the remainder of the nucleus. Neutrons are electrically neutral. They can neither attract nor repel other electrical charges Name Charge Mass (kg) Proton Positive Charge 1.672 𝑥 10−27 Electron Negative Charge 9.107 𝑥 10−31 Neutron No charge 1.672 𝑥 10−27 One or more electrons revolve continuously around the nucleus of an atom (just as the planets revolve about the sun). Electrons possess a negative electrical charge and are very much lighter in weight than protons. All electrons are alike regardless of the atoms of which they are a part. An atom contains the same number of electrons as protons. For example, the aluminum atom has thirteen electrons and thirteen protons. Element No. of electrons No. of Protons Number of Neutrons Valence Electrons Copper 29 29 34 1 Aluminum 13 13 14 3 Germanium 32 32 41 4 𝑸 𝑰= 𝒕 • 𝐼 = 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑓𝑙𝑜𝑤, 𝑖𝑛 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠 (𝐴) 𝑄 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 𝑚𝑜𝑣𝑖𝑛𝑔, 𝑖𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑠 𝐶 𝑡 = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑛 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠 (𝑠) • 𝟔. 𝟐𝟓 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟖 𝒆𝒍𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒓𝒐𝒏𝒔 𝒐𝒓 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒕𝒐𝒏𝒔 𝑾 𝑬= 𝑸 𝐸 = 𝐸𝑀𝐹 𝑜𝑟 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑜𝑟 𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒, 𝑖𝑛 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑠 (𝑉) 𝑊 = 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 , 𝑖𝑛 𝐽𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑒𝑠 (𝐽) Q = 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒, 𝑖𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑠 (𝐶) • • Current Types • Direct current (DC) is the movement of electrons in one direction in a conductor. • Pulsating direct current is a current in one direction that varies in intensity at a regular interval of time. • Alternating current (AC) is a current that changes in direction and intensity at a regular interval of time. • Ω 𝑷 = 𝑬𝑰 𝑾 = 𝑷𝒕 𝑊 = 𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑐 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦, 𝑖𝑛 𝑗𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝐽 𝑃 = 𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑐 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟, 𝑖𝑛 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑡𝑠 𝑊 𝐼 = 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡, 𝑖𝑛 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠 𝐴 , 𝐸 = 𝑒𝑚𝑓 𝑜𝑟 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒, 𝑖𝑛 𝑉 𝑡 = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒, 𝑖𝑛 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠 (𝑠) • • • • • • An electric circuit contains a closed path for providing a flow of electrons from a voltage source or current source. The elements present in an electric circuit will be in series connection, parallel connection, or in any combination of series and parallel connections. BASIC PARTS OF A CIRCUIT: 1.SOURCE An electric circuit contains a closed path for 2.WIRES/CONDUCTORS providing a flow of electrons from a voltage 3.LOAD source or current source. The elements present in an electric circuit will be in series 4.SWITCH connection, parallel connection, or in any combination of series and parallel connections. All DC sources of electrical pressure have two terminals to which electrical devices are connected. These terminals have electrical polarity. One terminal is the positive terminal, whereas the other is the negative terminal. Active Elements deliver power to other elements, which are present in an electric circuit. Sometimes, they may absorb the power like passive elements. That means active elements have the capability of both delivering and absorbing power. Passive Elements can’t deliver power (energy) to other elements, however they can absorb power. That means these elements either dissipate power in the form of heat or store energy in the form of either magnetic field or electric field. Examples: Voltage sources and current sources. Examples: Resistors, Inductors, and capacitors If a current of 2A flows through a point in a wire for 30 seconds, how many coulombs pass through the point in the wire? What quantity of charge must be delivered by a battery with a potential difference of 100 V to do 500 J of work? A radio receiver draws 0.9 A at 110 V. If the set is used 3 hours per day, how much energy does it consume in 10 days?