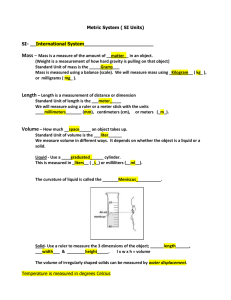
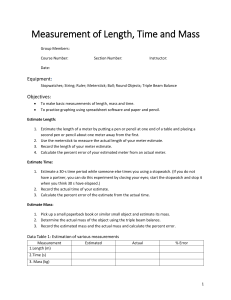
Speed Lab Activity Background Information: Speed is used to describe how fast an object is traveling. It is measured in meters per second. The speed of an object can be found at one point in time (instantaneous speed) or as an average over the entire journey. Average speed considers that an object’s speed changes over its journey. In this lab activity, your group will investigate the motion of toy cars and collect data to analyze the vehicle’s speed between various points (positions) and overall or average rate. Goal: By the end of this lesson, you should be able to: 1. State the variables associated with speed, their relevant symbols, and units. 2. Calculate the speed specification points along a vehicle’s journey and average speed. Pre-lab Questions: 1. State the equation used to calculate speed. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Complete the table to show the units for each variable used to calculate speed. Variable Name Symbol Unit Distance Seconds (s) v 3. Distinguish between instantaneous and average speed. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Lab setup: Time allowance: 45 minutes Grouping: 4-6 students Equipment needed: Meter ruler or measuring tape Masking tape Toy car Stopwatch Method: 1. Place the car on a flat surface (if using a motorized vehicle) and mark the start position with a small piece of tape. If the vehicle is not motorized, place it at the top of the ramp and use this as the start position. 2. Measure and mark each meter along the floor in a straight line using a measuring tape or meter ruler. 3. Turn on or wind up the car, start the stopwatch, and record the time as it crosses each meter mark on the floor. You will need to delegate different people in your group to complete specific roles, e.g., one person watching the stopwatch, one person recording times, and another identifying when the car passes each meter. 4. Repeat the task five times and record the results for each trial in the table below. Results: Distance (m) Time (s) Trial 1 1 2 3 4 5 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5 Average Post-Lab Tasks: 1. Calculate the average time for the car to reach each meter mark and complete the final column in the results table. 2. Using the average times from the results table, calculate the speed using the equation v = d/t Distance (m) Average time (s) Speed (ms-1) 1 2 3 4 5 3. Construct a distance-time graph in the space below. Distance will be on the y-axis, and time on the x-axis.