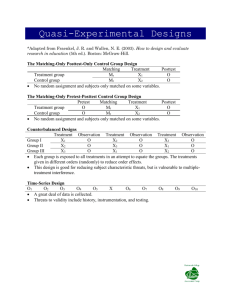
INTRODUCTION • In any profession, research is necessary to invention of new technology and techniques its help to improve the body of knowledge in profession. • Nursing Research nurses need the scientific knowledge required to be a competent nurse practitioner. 2 DEFINITION OF RESEARCH Research is defined as systemic and scientific process to answer question about facts and relationship between facts. It is an activity involved in seeking answers to unanswered questions. - ICN 3 4 Research design is a plan of how, when and where data are to be collected and analyzed. Research design is the research’s overall plan for answering the research questions or testing the research hypotheses. To provide answer to research question. To control the variants. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com Population, sample, and sampling technique. The time, place, and sources of data collection. Tools and methods of data collection and data analysis. The selection of a research design largely depends on the nature of the research problem, the research available, accessible of subjects, and research ethics. Nature of the research problem Purpose of the study Research’s knowledge and experience Researcher’s interest and motivation Research ethics and principles Subjects/participants Resources and Time availability Possible control on extraneous variables There are two important criteria for evaluating the credibility and dependability of the research results Internal validity External validity • Campbell and Stanley used the term internal validity to refer to the extent to which it is possible to make an inference that the independent variable is truly influencing the dependent variables. • The internal validity the independence variable is responsible for variation in dependent variable, internal validity demands a tighter control over study to maximize the effective result. • VARIABLE. • External validity explores the generalization beyond specific experiment’s to check if the result and finding come out to be same with other setting or with other subject population, but related variables. TYPES OF RESEARCH • Research is classified based on either an approach of studying variable or the purpose of conducting the research. • These classification are as follows: 1. Quantitative research, 2. Qualitative research and 3. Mixed method research 13 Egg - Quantity- number, shape, size, color etc. - Quality - smell, taste, aroma etc. Experience of patient about nursing care? 14 QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH • It is an enquiry into an identified problem based on testing a theory composed of variables, measured with numbers and analysed using statistical techniques. • In this types of research data is collected in numerical form and analysed by using descriptive and inferential statistics. • The three major types of quantitative research design are experimental, Nonexperimental and other research design 15 QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH 16 ACCORDING TO RILEY, EXPRIMENTAL RESEARCH DESIGN IS A POWERFUL DESIGN FOR TESTING HYPOTHSESE OF CAUSAL RELATIONSHIP AMONG VARIABLES. EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH DESIGN TRUE EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN QUASIEXPERIMENTAL DESIGN PREEXPERIMENTAL DESIGN TRUE EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH DESIGNS ARE OBSERVED EFFECT ON THE DEPENDABLE VARIABLE IS ONLY DUE TO THE MANIPULATION OF THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE. MANIPULATION, CONTROL, RANDOMIZATION. TRUE EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN CROSSOVER POSTTEST ONLY PRETEST POSTTEST ONLY RANDOMIZED BLOCK SOLOMON 4 GROUP FACTORIAL EXP.GROUP CONTROL GROUP TREATMENT POST-TEST POST-TEST EXP.GROUP CONTROL GROUP PRE TEST PRE TEST TREATMENT o POSTTEST o POSTTEST EXP.GROUP.1 CONTROL GROUP.1 EXP.GROUP.2 CONTROL GROUP.2 PRE TEST TREATMENT PRE TEST TREATMENT o POSTTEST o POSTTEST o POSTTEST o POSTTEST TYPE OF ANTIHYPERTEN SIVE DRUGS BLOCK PATIENTS WITH PRIMARY HYPERTENSION (I) DIABETIC PATIENTS WITH HYPERTENSION (II) RENAL PATIENTS WITH HYPERTENSION (III) A A,I A,II A,III B B,I B,II B,III C C,I C,II C,III GROUPS PROTOCOLS OF THE MOUTH CARE GROUP1 CHLORHEXIDINE(A1) SALINE(A2 GROUP2 SALINE(A2) CHLOHEXIDINE(A1) IT INVOLVES THE MANIPULATION OF INDEPENDENT VARIABLE TO OBSERVE THE EFFECT ON DEPENDENT VARIABLE. LACK OF AT LEAST ONE OF THE TWO OTHER ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE TRUE EXPERIMENT NON RANDOMIZED CONTROL GROUP DESIGN EXP.GROUP CONTROL GROUP PRE TEST PRE TEST TREATMENT o POSTTEST o POSTTEST EXP.GROUP O1 O2 O3 O3 O2 TREATMENT O1 THIS RESEARCH DESIGN IS CONSIDERED VERY WEAK, BECAUSE THE RESEARCH HAS VERY LITTLE CONTROL OVER THE EXPERIMENT. MANIPULATION OF INDEPENDENCE VARIABLE BUT LIMITED CONTROL OVER THE EXTRANEOUS VARIABLE AND NO RANDOMISATION AND CONTROL GROUP. ONE SHOT CASE DESIGN; EXP.GROUP TREATMENT o POST-TEST ONE- GROUP PRETEST- POSTTEST DESIGN o EXP.GROUP PRE TEST TREATMENT o POSTTEST IT IS ONE OF THE BROAD CATEGORIES OF RESEARCH DESIGNS IN WHICH THE RESEARCH OBSERVES THE PHENOMENA AS THEY OCCUR NATURALLY, AND NO EXTERNAL VARIABLES ARE INTRODUCED. THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLES CANNOT BE MANIPULATED. THE RESEARCH SITUATIONS WHERE IT IS NOT PRACTICALLY POSSIBLE TO CONDUCT EXPERIMENTS. DESCRIPTIVE-TYPE STUDIES THAT DO NOT REQUIRE ANY EXPERIMENTALAPPROACHES. DESCRIPTIVE DESIGN UNIVARIANT DESCRIPTIVE DESIGN EXPLORATORY DESCRIPTIVE DESIGN COMPARATIVE DESCRIPTIVE DESIGN CORRELATION/EX-POST FACTO DESIGN PROSPECTIVE DESIGN RETROSPECTIVE DESIGN DEVELOPMENTAL RESEARCH DESIGN CROSS-SECTIONAL DESIGN LONGITUDINAL DESIGN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DESIGNS CASE- CONTROL STUDIES COHORT STUDIES SURVEY RESEARCH DESIGN IT IS USED TO OBSERVE, DESCRIBE, AND DOCUMENT ASPECT OF A SITUATION AS IT NATURALLY OCCURS, AND SOMETIMES TO SERVE AS A STARTING POINT FOR HYPOTHESIS GENERATION OR THEORY DEVELOPMENT. USED TO OBSERVE, DOCUMENT,AND DESCRIBE A PHENOMENON OCCURING IN NATURAL SETTING. TO GAIN MORE INFORMATION ABOUT CHARACTERISTICS WITHIN A PARTICULAR FIELD OF INQUIRY. USED TO DEVELOP THEORIES, IDENTIFY PROBLEMS WITH CURRENT PRACTIS, MAKE JUDGEMENTS, OR DETERMINE OTHER PRACTICES IN SIMILAR SITUATIONS. THIS DESIGN DOES NOT FOCUS ON THE STUDY OF A SINGLE VARIABLE; THERE MAY BE ONE OR MORE VARIABLES INVOLVED IN THE STUDY. IT IS USED TO IDENTIFY, EXPLORE , AND DESCRIBE EXISITING PHENOMENON AND ITS RELATED FACTORS. IT INVOLVES COMPARING AND CONTRASTING TWO OR MORE SAMPLE OF STUDY SUBJECT ON ONE OR MORE VARIABLES OFTEN AT A SINGLE POINT OF TIME. THIS IS A NON EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN, WHERE RESEARCHER EXAMINES THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TWO OR MORE VARIABLES IN A NATURAL SETTING WITH OUT MANIPULATION OF CONTROL. THE RESEARCHER FIND THE STRENGTH OF RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE VARIABLES. GENERALLY IT HAS INDEPENDENT AND DEPENDENT VARIABLES EFFECT OF INDEPENDENT VARIABLE IS OBSERVE WITH OUT MANIPULATING THE DEPENDENT VARIABLE. HERE THE RESEARCHER RELATES THE PRESENT TO THE FUTURE IS A PROSPECTIVE RESEARCH DESIGN. RETROSPECTIVE RESEARCH DESIGN HERE THE RESEARCHER STUDIES THE CURRENT PHENOMENON BY SEEKING INFORMATION FROM PAST. IT EXAMINES THE PHENOMENON WITH REFERANCE TO TIME. CROSS SECTION DESIGN IN WHICH RESEARCHER COLLECT DATA AT PARTICULAR TIME (ONE PERIOD OF DATA COLLECTION) IT IS MORE CONVENIENT. LONGITUDINAL DESIGN HERE THE DATACOLLECT AT LONG TIME( LONG TIME STUDY). IT INVOLVES INVESTIGATE THE DISTRIBUTION AND CAUSES OF THE DISEASES IN POPULATION. THE PROSPECTIVE STUDIES ARE KNOW AS COHORT STUDY AND RETROSPETIVE STUDIES ARE KNOW AS CASE- CONTROL STUDIES. COHORT STUDIES HERE THE LONGITUDINAL APPROACH IS USED TO INVESTICATE THE DISEASES AND CAUSES. CASE CONTROL STUDIES IN THIS DESIGN, CAUSES OF A DISEASE ARE INVESTIGATED AFTER THE OCCURRENCE OF A DISEASE. IF THE SURVEY IS CONDUCTED ON A SAMPLE OF POPULATION, IT IS CALLED SAMPLE SURVEY. IF THE ENTIRE POPULATION IS INVOVLED, IT IS CALLED A POPULATION SURVEY SUCH AS CENSUSES, ECT., DEPENDING ON THE NATURE OF PHENOMENON UNDER STUDY. BASED ON METHODS OF DATA COLLECTION. ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES IT IS A CONVENIENT THE RELATIONSHIP METHOD. SUITABLE FOR NURSING RESEARCH. IT IS SIMPLE. LOW COST COMPARE TO EXPERIMENT. BETWEEN VARIABLES FINDING IS NEVER CLEAR. IT HAS MORE ERROR NON RANDOMIZED METHOD WILL RESULTING IN ERROR. METHODOLOGICAL STUDIES META –ANALYSIS SECONDARY DATA ANALYSIS OUTCOME RESEARCH EVALUATION STUDIES OPERATIONAL RESEARCH QUALITATIVE RESEARCH QUALITATIVE RESEARCH • Qualitative research is a field of enquiry that crosscuts disciplines and subject matter. It involves an in depth understanding of human behaviours, • it concerned with the opinions, experiences, and feeling of individuals producing subject data, Here data is collected in descriptive form rather than numerical form • The five major types of qualitative research design are phenomenology, ethnography, grounded theory, case study, and historical research. 54 QUALITATIVE 1) CASE STUDY RESEARCH- This research attempts to shed light on a phenomena by studying in depth a single case. The case can be an individual person, an event, a group or an institution. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com QUALITATIVE 1) CASE STUDY RESEARCH- This research attempts to shed light on a phenomena by studying in depth a single case. The case can be an individual person, an event, a group or an institution. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com QUALITATIVE 3) PHENOMENOLOGICAL RESEARCH an inductive, descriptive research approach developed from phenomenological philosophy; its aim is to describe an experience as it is actually lived by the person. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com QUALITATIVE 4) ETHENOGRAPHIC RESEARCHIt refer to the investigation of a culture through an in-depth study of the members of the culture; it involves the systematic collection, description, and analysis of data for development of theories of cultural behaviour. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com QUALITATIVE 5) HISTORICAL RESEARCHThis research involving analysis of events that occurred in the remote or recent past. Application • Historical research can show patterns that occurred in the past and over time which can help us to see where we came from and what kinds of solutions we have used in the past. • Understanding this can add perspective on how we examine current events and educational practices. www.vipinpatidar.wordpress.com MIXED METRHOD RESEARCH • Nursing research study deals with a complex phenomenon, which cannot be answered completely by qualitative or quantitative research method alone so mixed method is considered as a better alternative to answer a research question. • Mixed method research approach involved in numerical and descriptive narrations in a study. • The four types of mixed method research design are convergent research, explanatory sequential research, exploratory sequential research, embedded research design • ( E.g.) A researcher use convergent design to understand the nurses attitude about care of HIV patients 60 THANK YOU 61