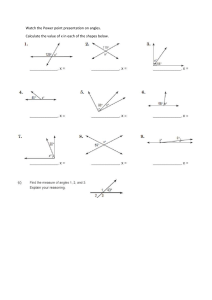
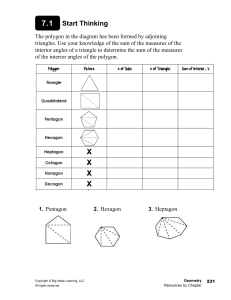
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Unit 7 Chapter 6 Test Review - GEOMETRY 1. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 23-gon? 2. The sum of the angle measures of a polygon with s sides is 3240. Find s. 3. A road sign is in the shape of a regular hexagon. What is the measure of each angle on the sign? Round to the nearest tenth. 4. Find the missing values of the variables. The diagram is not to scale. 5. Find the value of x. The diagram is not to scale. 6. The sum of the measures of two exterior angles of a triangle is 278. What is the measure of the third exterior angle? 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A 7. Find the values of the variables in the parallelogram. The diagram is not to scale. 8. In the parallelogram, mKLO 78 and mMLO 23. Find mKJM. The diagram is not to scale. 9. In the parallelogram, mQRP 11 and mPRS 93. Find mPQR. The diagram is not to scale. 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A 10. For the parallelogram, if m2 4x 27 and m4 3x 13, find m3. The diagram is not to scale. 11. LMNO is a parallelogram. If NM = x + 14 and OL = 2x + 6, find the value of x and then find NM and OL. 12. In the figure, the horizontal lines are parallel and AB BC CD. Find JM. The diagram is not to scale. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A 13. Find values of x and y for which ABCD must be a parallelogram. The diagram is not to scale. 14. Based on the information in the diagram, can you prove that the figure is a parallelogram? Explain. 15. In the rhombus, m1 30x, m2 x y, and m3 3z. Find the value of each variable. The diagram is not to scale. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A 16. In the rhombus, m1 148. What are m2 and m3? The diagram is not to scale. 17. Find the measure of the numbered angles in the rhombus. The diagram is not to scale. 18. DEFG is a rectangle. DF = 6x – 1 and EG = x + 59. Find the value of x and the length of each diagonal. 19. In rectangle KLMN, KM = 6x 11 and LN = 68. Find the value of x. 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A 20. In quadrilateral ABCD, AE x 22 and BE 3x 18 . For what value of x is ABCD a rectangle? 21. Find the values of a and b. The diagram is not to scale. 22. J and M are base angles of isosceles trapezoid JKLM. If mJ 15x 9, and mM 13x 13, find mK. 23. LM is the midsegment of ABCD. AB 44 and DC 118. What is LM? 6 Name: ________________________ 24. LM is the midsegment of ID: A ABCD. AB x 8, LM 4x 3, and DC 306. What is the value of x? 25. Find m1 and m3 in the kite. The diagram is not to scale. 26. mR 150 and mS 100. Find mT. The diagram is not to scale. 7 ID: A Unit 7 Chapter 6 Test Review - GEOMETRY Answer Section 1. ANS: 3780 PTS: OBJ: NAT: KEY: 2. ANS: 20 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 6-1.1 To find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 1 Finding a Polygon Angle Sum Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: OBJ: NAT: KEY: 3. ANS: 120 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 6-1.1 To find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 1 Finding a Polygon Angle Sum Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 6-1.1 To find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon NAT: CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 2 Using the Polygon Angle-Sum KEY: Corollary to the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem | regular polygon 4. ANS: x = 128, y = 58 PTS: OBJ: NAT: KEY: 5. ANS: 45 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 6-1.1 To find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 3 Using the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem exterior angle | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: OBJ: NAT: KEY: 6. ANS: 82 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 6-1.1 To find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 3 Using the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: OBJ: NAT: KEY: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 6-1.2 To find the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon CC G.SRT.5| M.1.d| G.3.f TOP: 6-1 Problem 4 Finding an Exterior Angle Measure exterior angle | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem 1 ID: A 7. ANS: x 25, y 51, z 104 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: 8. ANS: 101 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-2 Problem 1 Using Consecutive Angles parallelogram | opposite angles | consecutive angles | transversal PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 9. ANS: 76 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-2 Problem 1 Using Consecutive Angles KEY: parallelogram | opposite angles PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 10. ANS: 151 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-2 Problem 1 Using Consecutive Angles KEY: parallelogram | consecutive angles PTS: 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms OBJ: 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-2 Problem 1 Using Consecutive Angles KEY: algebra | parallelogram | opposite angles | consecutive angles 11. ANS: x = 8, NM = 22, OL = 22 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 12. ANS: 15 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-2 Problem 3 Using Algebra to Find Lengths KEY: parallelogram | algebra 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms 6-2.1 To use relationships among sides and angles of parallelograms CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-2 Problem 4 Using Parallel Lines and Transversals KEY: transversal | parallel lines 2 ID: A 13. ANS: x = 5, y = 8 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-3 Proving That a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram OBJ: 6-3.1 To determine whether a quadrilateral is a parallelogram NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-3 Problem 1 Finding Values for Parallelograms KEY: algebra | parallelogram 14. ANS: Yes; both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-3 Proving That a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram OBJ: 6-3.1 To determine whether a quadrilateral is a parallelogram NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-3 Problem 2 Deciding Whether a Quadrilateral Is a Parallelogram KEY: opposite angles | parallelogram 15. ANS: x = 3, y = 87, z = 30 PTS: 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares OBJ: 6-4.2 To use properties of diagonals of rhombuses and rectangles NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-4 Problem 2 Finding Angle Measures KEY: algebra | diagonal | rhombus 16. ANS: m2 = 148, m3 16 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares OBJ: 6-4.2 To use properties of diagonals of rhombuses and rectangles NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-4 Problem 2 Finding Angle Measures KEY: diagonal | rhombus 17. ANS: m1 90, m2 = 35, and m3 55 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares OBJ: 6-4.2 To use properties of diagonals of rhombuses and rectangles NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-4 Problem 2 Finding Angle Measures KEY: diagonal | rhombus 18. ANS: x = 12, DF = 71, EG = 71 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares 6-4.2 To use properties of diagonals of rhombuses and rectangles CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-4 Problem 3 Finding Diagonal Length KEY: rectangle | algebra | diagonal 3 ID: A 19. ANS: 9.5 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 20. ANS: 20 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-4 Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares 6-4.2 To use properties of diagonals of rhombuses and rectangles CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-4 Problem 3 Finding Diagonal Length KEY: rectangle | algebra | diagonal PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-5 Conditions for Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares OBJ: 6-5.1 To determine whether a parallelogram is a rhombus or rectangle NAT: CC G.CO.11| CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-5 Problem 2 Using Properties of Special Parallelograms KEY: parallelogram | rectangle | reasoning 21. ANS: a 137, b 71 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites OBJ: 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-6 Problem 1 Finding Angle Measures in Trapezoids KEY: trapezoid | base angles 22. ANS: 141 PTS: OBJ: TOP: KEY: 23. ANS: 81 1 DIF: L4 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-6 Problem 2 Finding Angle Measures in Isosceles Trapezoids algebra | isosceles trapezoid | base angles | trapezoid PTS: OBJ: TOP: KEY: 24. ANS: 44 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f 6-6 Problem 3 Using the Midsegment of a Trapezoid trapezoid | base angles | midsegment of a trapezoid PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites OBJ: 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-6 Problem 3 Using the Midsegment of a Trapezoid KEY: trapezoid | base angles | midsegment of a trapezoid 25. ANS: m 1 26, m3 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites OBJ: 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-6 Problem 4 Finding Angle Measures in Kites KEY: kite | diagonal 4 ID: A 26. ANS: 10 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites OBJ: 6-6.1 To verify and use properties of trapezoids and kites NAT: CC G.SRT.5| G.1.c| G.3.f TOP: 6-6 Problem 4 Finding Angle Measures in Kites KEY: kite | sum of interior angles 5