Protista/Fungi/Cell Respiration Remediation Guide
advertisement
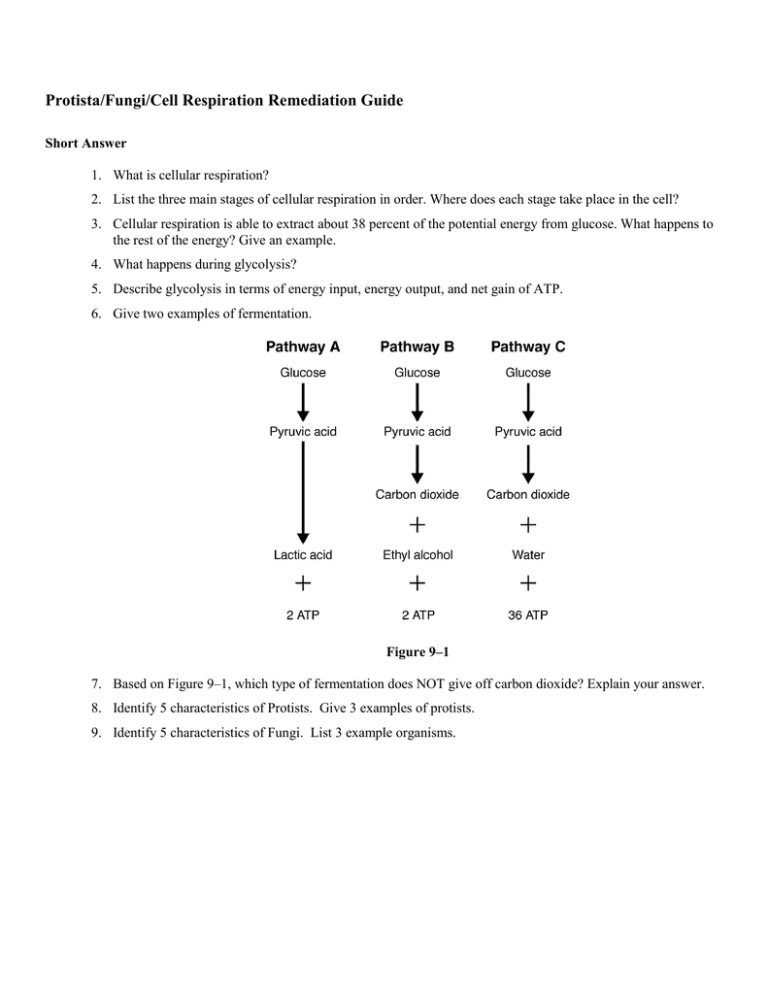
Protista/Fungi/Cell Respiration Remediation Guide Short Answer 1. What is cellular respiration? 2. List the three main stages of cellular respiration in order. Where does each stage take place in the cell? 3. Cellular respiration is able to extract about 38 percent of the potential energy from glucose. What happens to the rest of the energy? Give an example. 4. What happens during glycolysis? 5. Describe glycolysis in terms of energy input, energy output, and net gain of ATP. 6. Give two examples of fermentation. Figure 9–1 7. Based on Figure 9–1, which type of fermentation does NOT give off carbon dioxide? Explain your answer. 8. Identify 5 characteristics of Protists. Give 3 examples of protists. 9. Identify 5 characteristics of Fungi. List 3 example organisms. Protista/Fungi/Cell Respiration Remediation Guide Answer Section SHORT ANSWER 1. ANS: Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen. PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 222 OBJ: 9.1.1 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.a STA: SC.HS.3.4.2| SC.HS.4.6.5| SC.HS.4.6.10 KEY: knowledge 2. ANS: The three stages are as follows: glycolysis (which occurs in the cytoplasm), the Krebs cycle (which occurs in the mitochondria), and electron transport (which occurs in the mitochondria). PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 222 OBJ: 9.1.1 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.a STA: SC.HS.3.4.2| SC.HS.4.6.5| SC.HS.4.6.10 KEY: application 3. ANS: The rest of the energy is released as heat, as indicated by the fact that you feel warmer after exercising and are able to maintain a constant temperature even in cold weather. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 229 OBJ: 9.1.1 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.a STA: SC.HS.3.4.2| SC.HS.4.6.5| SC.HS.4.6.10 KEY: synthesis 4. ANS: During glycolysis one molecule of glucose is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid. PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 223 OBJ: 9.1.2 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.a STA: SC.HS.3.4.2| SC.HS.4.6.5| SC.HS.4.6.10 KEY: knowledge 5. ANS: Glycolysis requires an initial input of 2 ATPs and produces 4 ATPs, for a net gain of 2 ATPs. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 223 OBJ: 9.1.2 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.a STA: SC.HS.3.4.2| SC.HS.4.6.5| SC.HS.4.6.10 KEY: synthesis 6. ANS: Students should list two fermentation reactions, such as those that occur in the muscles and in rising bread dough. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 224 | p. 225 OBJ: 9.1.3 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.c STA: SC.HS.3.4.2 KEY: application 7. ANS: Sample answer: Lactic acid fermentation does not give off carbon dioxide, as shown by pathway A in the figure. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 NAT: C.1.a | C.1.b | C.5.c 8. ANS: d PTS: 1 9. ANS: s PTS: 1 REF: p. 225 STA: SC.HS.3.4.2 OBJ: 9.1.3 KEY: application