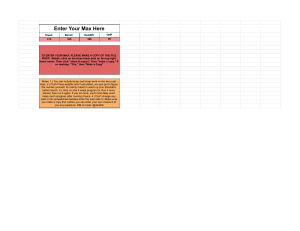
MMA Strength Training Program Monday Deadlift 4x5 Calf raise 4x12 Back extensions 4x10 superset Battle ropes 4x30s Tuesday Bench Press 4x5 Explosive pushups 4x12 Dips 4x10 Bridges 4x10 Wednesday Power cleans 4x5 Kettlebell swings 4x10 Turkish get ups 4x10 (5 for each side) L-sit 4xf Thursday Pendley rows 4x8-10 Pull ups 4x10 Decline sit ups 4x15 Leg Raise 4x15 Friday Squat 4x5 Tibialis raise 4x10 Nordic Curls 4x10 superset Battle ropes 3x30s Saturday Overhead Press 4x5 Lateral raise 4x10 superset face pulls 4x10 Dead hangs 4xf Leg Twists 4x20 Sunday Twists 4x20 The deadlift is a weight training exercise in which a loaded barbell or bar is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting exercises, along with the squat and bench press. Two styles of deadlift are commonly used in competition settings: the sumo deadlift and the standard deadlift. While both of these styles are permitted under the rules of powerlifting competition, only the conventional stance is used in strongman deadlifting contests. A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent and knee joints flex while the ankle joint dorsiflexes; conversely the hip and knee joints extend and the ankle joint plantarflexes when standing up. Squats also help your hip muscles Squats are considered a vital exercise for increasing the strength and size of the lower body muscles as well as developing core strength. The primary agonist muscles used during the squat are the quadriceps femoris, the adductor magnus, and the gluteus maximus. The squat also isometrically uses the erector spinae and the abdominal muscles, among others. The squat is one of the three lifts in the strength sport of powerlifting, together with the deadlift and the bench press. It is also considered a staple exercise in many popular recreational exercise programs. Battling ropes (also known as battle ropes or heavy ropes) are used for fitness training to increase full body strength and conditioning.[1] It was designed by John Brookfield in 2006, who developed the system around his backyard. It can be alternatively used as a resistance training technique. After its development, he taught the system to Special Forces, the Cincinnati Bengals, and the Olympic wrestling team. Since then, the training system has increased in popularity and has expanded to mainstream gyms. Battling ropes have numerous advantages including the fact they are safe, easy to use, and increase power output. With one battle rope per upper extremity, they also work out each arm Independently, overcoming strength imbalances. It also reduces orthopedic load on joints. Rope workouts has benefits. For example, a small study in 2015 showed that a 10-minute workout with the ropes increased heart rate and energy expenditure. Another study showed multiple physical fitness benefits to collegiate basketball players. Battling ropes are thick and heavy and strong end to give significant resistance, and there are numerous types of ropes used. The ropes typically have two common diameters (25 mm and 44 mm) and common standard lengths (5 m, 10 m, and 25 m). Some battle ropes now have a flexible metal core, making them heavier, shorter and allowing the user to move during training without being restricted by an anchor point. The bench press, or chest press, is a weight training exercise in which the trainee presses a weight upwards while lying on a weight training bench. Although the bench press is a full-body exercise, the muscles primarily used are the pectoralis major, the anterior deltoids, and the triceps, among other stabilizing muscles. A barbell is generally used to hold the weight, but a pair of dumbbells can also be used. The barbell bench press is one of three lifts in the sport of powerlifting alongside the deadlift and squat and is the only lift in the sport of Paralympic powerlifting. The bench press is an upper body massbuilding exercise that stresses some of the body’s largest muscles, including chest, triceps, shoulders, front deltoids, and even upper back. It is also used extensively in weight training, bodybuilding, and other types of training to develop the chest muscles. Bench press strength is important in combat sports as it tightly correlates to punching power. Bench press can also help contact athletes increase their performance because it can increase effective mass and functional hypertrophy of the upper body. A pull-up is an upper-body strength exercise. The pull-up is a closedchain movement where the body is suspended by the hands, gripping a bar or other implement at a distance typically wider than shoulderwidth, and pulled up. As this happens, the elbows flex and the shoulders adduct and extend to bring the elbows to the torso. Pull-ups build up several muscles of the upper body, including the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and biceps brachii. A pull-up may be performed with overhand (pronated), underhand (supinated)— sometimes referred to as a chin-up—neutral, or rotating hand position. Pull-ups are used by some organizations as a component of fitness tests, and as a conditioning activity for some sports. In strength training, rowing (or a row, usually preceded by a qualifying adjective — for instance a seated row) is an exercise where the purpose is to strengthen the muscles that draw the rower's arms toward the body (latissimus dorsi) as well as those that retract the scapulae (trapezius and rhomboids) and those that support the spine (erector spinae). When done on a rowing machine, rowing also exercises muscles that extend and support the legs (quadriceps and thigh muscles). In all cases, the abdominal and lower back muscles must be used in order to support the body and prevent back injury. Many other weight-assisted gym exercises mimic the movement of rowing, such as the deadlift, high pull and the bent-over row. An effective off-season training program combines both erg pieces and weight-assisted movements similar to rowing, with an emphasis on improving endurance under high tension rather than maximum strength. The clean and jerk is a composite of two weightlifting movements, most often performed with a barbell: the clean and the jerk. During the clean, the lifter moves the barbell from the floor to a racked position across the deltoids, without resting fully on the clavicles. During the jerk, the lifter raises the barbell to a stationary position above the head, finishing with straight arms and legs, and the feet in the same plane as the torso and barbell. Of the several variants of the lift, the most common is the Olympic clean and jerk, which, with the snatch, is included in Olympic weightlifting events.