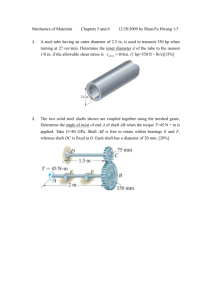
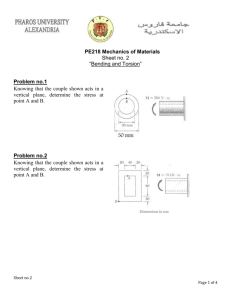
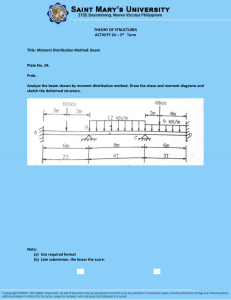
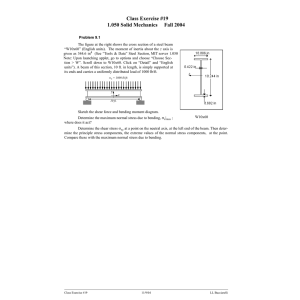
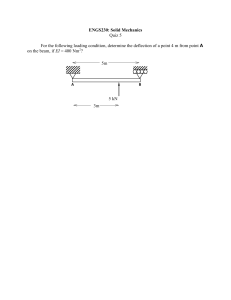
List of HWs EASC2220 Spring 2023 HW#01 (SKIP) Q1 Link AB is to be made of a steel for which the ultimate normal stress is 450 MPa. Determine the cross-sectional area for AB for which the factor of safety will be 3.50. Assume that the link will be adequately reinforced around the pins at A and B. Q2 Knowing that the average normal stress in member BD of the Pratt bridge truss shown must not exceed 21 ksi for the given loading, determine the cross-sectional area of that member that will yield the most economical and safe design. Q3 Link BD consists of a single wooden member 36 mm wide and 18 mm thick. Knowing that each pin has a 12-mm diameter, determine the maximum value of the average normal stress in link BD if ϴ = 90°. Required HW#02 (Due: 9:30am Feb. 6, bring hard copy) Q1 Q2 10” 45° 10” 20” 20” 20” The 1/8 in. diameter cable DG is made of a steel with 29,000 ksi. Knowing that the maximum stress in the cable must not exceed 70 ksi and that the elongation of the cable must not exceed ¼ inch, find the maximum load W that can be applied as shown. The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires of 1/16 -in. diameter (E = 29 × 106 psi) and a pin and bracket at A. Knowing that the wires were initially taut, determine (a) the additional tension in each wire when a 220-lb load P is applied at D, (b) the corresponding deflection of point D. A square was scribed on the side of a large steel pressure vessel. After pressurization the biaxial stress condition at the square is as shown. Knowing that E = 29 × 106 psi and v = 0.30, determine the change in length of (a) side AB, (b) side BC, (c) diagonal AC. Suggesting A rectangular block of material (Structural Steel – ASTM-A36) is bonded to two rigid horizontal plates. The lower plate is fixed, while the upper plate is subjected to a horizontal force P. Knowing that the upper plate moves through 0.03 in. under the action of the force, determine (a) the average shearing strain in the material, and (b) the force P exerted on the plate. Suggesting HW#03 (Due: 02/13/2023) Q1 Q2 A hole is punched at A in a plastic sheet by applying a 1000-N force P to end D of lever CD, which is rigidly attached to the solid cylindrical shaft BC. Design specifications require that the displacement of D should not exceed 20 mm from the time the punch first touches the plastic sheet to the time it actually penetrates it. Determine the required diameter of shaft BC if the shaft is made of a steel with G of 77.2 GPa and τall of 80 MPa. Two solid steel shafts are connected by the gears shown. A torque of magnitude T = 1000 N · m is applied to shaft AB. Knowing that the allowable shearing stress is 100 MPa and considering only stresses due to twisting, determine the required diameter of (a) shaft AB, (b) shaft CD. DO NOT LOOK BEYOND THIS SLIDE • Feb 8 HW#04 (Due: 03/04/2022 – hardcopy) Draw Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams Q1 2 k/ft A 5 ft Q3 Q4 D 10 kips A 3 ft B 5 ft 2 ft 5 ft 2 k/ft 5 ft 10 kips A 10 kips 5 ft C C 2 k/ft B C 3 ft 3 ft 2 k/ft 3 ft B Q2 7 ft 10 kips B 5 ft 10 kips A 3 ft C 2 k/ft C 2 ft 10 kips A 3 ft 7 ft B Q5 HW#05 (Due: 03/23/2022 – hardcopy) Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown and determine the maximum normal stress due to bending. Knowing that the allowable normal stress for the steel used is 36 ksi, select the most economical wide-flange beam to support the loading shown. HW#06 (Due: 03/28/2022 – hardcopy) Q1 Q2 A square box beam is made of two 3 4 3 4 3.5-in. planks and two 5-in. planks nailed together as shown. Knowing that the spacing between the nails is s = 1.5 in. and that the vertical shear in the beam is V = 200 lb, determine (a) the shearing force in each nail, (b) the maximum shearing stress in the beam. Draw Shear and Moment Diagram. Then, For the beam and loading shown, consider section n-n and determine (a) the largest shearing stress in that section, (b) the shearing stress at point a. Q3 Draw Shear and Moment Diagram. Then, For the beam and loading shown, determine the minimum required width b, knowing that for the grade of timber used, σall = 12 MPa and τall = 825 kPa Q4 Draw Shear and Moment Diagram. Then, For the beam and loading shown, determine the largest shearing stress in section n-n. HW#07 (Due: 04/20/2022 – hardcopy) See another file