Community Mining in Virtual Social Networks: Trends & Challenges
advertisement

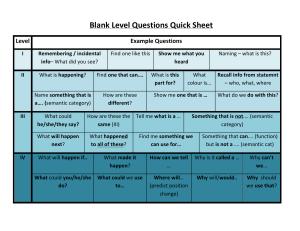
Community Mining in Virtual Social Networks: Trends and Challenges Asmae El Kassiri and Fatima-Zahra Belouadha Siweb research team, Computer Science Department Ecole Mohammadia d’Ingénieurs, Mohammed V- Agdal University Rabat, Morocco asmaekassiri@gmail.com, belouadha@emi.ac.ma A. El Kassiri, PhD student, Research Interest: Semantic community mining F. Belouadha, Habilitated Professor, Research Interests: Semantic Web service composition, BPM, Cloud computing and semantic data mining Data mining in VSN: interest and purposes VSN refers to networks of people interacting online using e.g. social media. Interest: VSN contain a large volume of important information which can be exploited in various areas e.g. marketing and politics. Purposes: Detection of important nodes of the network Opinion mining Community mining based on clustering techniques. etc. Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 1 Clustering: definition and types Clustering is a division of data into groups (clusters) of similar objects. It consists in three iterative stages and leads to hard or fuzzy clusters. Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 2 Structural analysis It is based on the graph theory and calculates similarity according to the VSN topology. It does not consider the semantics of the information included in VSN. Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 3 Semantic analysis It is based on the semantic Web. It uses ontologies to represent the network. It adopts a semantic clustering. Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 4 Related work Specific or generic ontologies are used to represent the VSN. music ontology,event ontology, SCOT, MOAT… Profiles, activities and tags (FOAF, SIOC, semSNI, SKOS) Semantic clustering based on: a two phase-algorithm using both semantic and structural measures semantic structural measures (semantic modularity and centrality). Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 5 VSN Semantic Analysis Issues What semantic model is it appropriate to represent the VSN data? What similarity measure is it adapted to analyse the VSN data? At what level of the clustering algorithm, is it appropriate to integrate the semantic dimension? Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 6 Conclusions Standard-based extended generic ontology Able to describe the contents of different social media Makes easy the aggregation of the contents describing the behavior of a person, from a set of social media of which he is a member. Issues: What semantic model is it appropriate to represent the VSN data? What similarity measure is it adapted to analyse the VSN data? At what level of the clustering algorithm, is it appropriate to integrate the semantic dimension? Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 7 Semantic analysis It is based on the semantic Web. It uses ontologies to represent the network. It adopts a semantic clustering based on: only semantic distance a two phase-algorithm using both semantic and structural measures semantic structural measures. Asmae EL KASSIRI and Fatima-Zahra BELOUADHA. Oracle Presentation. March 2014. 8