Research Inquiry & Problem Statement: High School Guide
advertisement

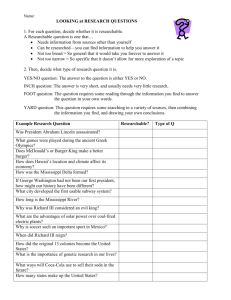
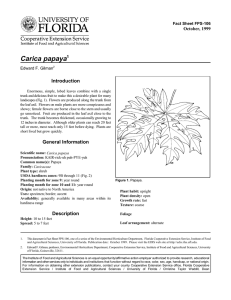
Identifying the Inquiry and Stating the Problem OBJECTIVES 1. design a research useful in daily life (CS_RS12-Id-e-1); 2. write research title (CS_RS12-Id-e-2); 3. describe background of research (CS_RS12-Id-e-3); 4. state research questions (CS_RS12-Id-e-4); 5. indicate scope and delimitation of study (CS_RS12-Id-e-5); 6. present written statement of the problem (CS_RS12-Id-e-7); • Directions: Take time to identify the things that matters most to you by filling out the following information: • My chosen SHS track is: ____________________________________. • The top three things that I excel doing are ________ , _____and _________. • The top five (5) things that make me happy are ______ , ___________, ____________, ________________, and ___________________. • The three things that I find interesting are _____________, ______________ and ________________. Designing Research Topic •Research topic serves as the groundwork for any succeeding actions, it must be defined appropriately at the beginning of the research work. Important Things to Consider in Choosing a Topic (1) Your school’s requirements (2) Your areas of knowledge and interest (3) The scientific, social or practical relevance (4) The availability of data and sources (5) The length and timeframe of your research Sources of Research Topics/Problems (1) Prevailing theories/philosophy (2) Observations, intuitions or a combination of both (3) Different subjects taken and from them identify a problem that interests a studentresearcher most 4. Fields of interest or specialization or event from related fields 5. Existing problems in the classroom/school which one may want to solve 6. Existing needs of the community or society 7. Repetition or extension of investigations already conducted or may be an offshoot of studies underway (Angels, 1966, p. 6) 8. Related studies and literatures 9. Advice authorities or experts from funding agencies. 10. Offshoot of friendly conversations 11. Incidental from interesting topics of teachers/students during meeting /session Four Basic Steps in Designing a Research Topic (1) choose a broad topic (2) do preliminary research, (3)define the problem (4) refine the question (1)CHOOSE A BROAD TOPIC A. Choose an interesting topic B. Select a significant topic A topic that is worth researching must be able to answer or solve problems in the community C. Choose a topic relevant to your field i. Department of Science and Technology (DOST) Harmonized National R & D Agenda for 2017-2022. Early in 2017, DOST, together with researchers from the health, agriculture, industry, and academe, released research priorities for 2017 to 2022 that are relevant for the economic growth of the country. Visit this link https://bit.ly/3hHTf2Y for a list of suggested studies. ii. Review of Literature iii. Field of Experts iv. Brainstorming Example: HUMSS Twentieth-century Literature Economic History Health Policy The body image and the Filipino Culture Example: HUMSS Politics Governance Example: ABM Online Marketing Micro-business Management Sales Financial Literacy Example:TVL Food preparation Food consumption Eating disorders Food marketing (2) DO A PRELIMINARY RESEARCH You need to have a better understanding of it by reading some more articles, journals, and related research studies (3) DEFINE THE PROBLEM After getting enough information, you may be able to list some questions or problems that you want to research. narrow down broad topic into feasible and manageable research questions. A very narrow research question can be developed by doing a comparative study or expanding the scope of the study. (4) REFINE THE QUESTION This step lets you evaluate the questions formulated. What specific questions should you ask? How should you gather your data sufficient to answer the questions? Are the questions too narrow, or does it need to be trimmed down? How much time are you given to finish the research? What resources do you need and are they available? Are the questions too narrow, or does it need to be trimmed down? How much time are you given to finish the research? What resources do you need and are they available? ACTIVITY: DO THIS 1. Choose one broad topic related to your track that interests you. (1 each member) Explain why did you choose that topic. ACTIVITY: DO THIS 1. Choose one broad topic related to your track that interests you. Do preliminary research on this topic. 2. Take note of at least five related studies with its corresponding author/s 3. List three (3) quantitative research questions related to the topic. References: Title:___________________________________ Author/s: ____________________________ Year of Publication:______________________ Name of Journal/Publication: _________ Link: ________________________ Notes/ Important information: ______________ RESEARCH PROBLEM It is a specific issue, difficulty, contradiction, or gap in knowledge that you will aim to address in your research. 1. Practical problems aimed at contributing to change 2. Theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge How is a problem researchable? The problem is researchable when: 1. There is no known answer or solution to it such that a gap in knowledge exists 2. There are possible solutions the effectivity of which is untested or unknown yet 3. There are answers or solutions the possible result of which may seem or may be factually contradictory 4. There are several possible and plausible explanations for the undesirable condition 5. When the existence of a phenomenon requires explanation Sources of a Research Problem •Personal experience •Symposia,dialogues and ordinary meetings •Journals, books, theses, dissertations and the mass media – radio, television, newspapers and magazines •Thoeries – a tentative or hypothesized statement of relationship of things Criteria of a Good Research Problem: 1. A problem should be of great interest to the researcher 2. A problem should be relevant and useful to a specific group of people 3. A good problem is novel in that it possesses the element of newness or freshness 4. A problem should be well-defined or specified 5. A problem should be measurable 6. A problem is time-bounded 7. A problem is good if the study of it will contribute to the refinement of certain important concepts, creation of improvement of research instruments and analytical system and will permit generalizations 8. A problem is good and researchable on the basis of the investigator’s capability to meet what it requires; expertise, manpower money and time. Defining the Research Problem: 1st Step: major concepts or terms are clearly defined. The concepts must be such that they can be represented by some evidence which can be obtained through direct or indirect activities which are feasible towards carrying out such an observation 2nd Step: To limit the scope of the study in terms of: 1. Issues or concerns 2. Area coverage 3. Subjects/respondents 4. Period of time 5. Type of data – qualitative, quantitative or a combination of the two RESEARCH TITLE Directions: Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is incorrect. __1. Inserting humor on the research title makes it more interesting to the reader. __2. Abbreviations are a must to make the research title shorter. __3. Proper punctuation and correct grammar must be observed in writing the title. __4. All types of quantitative research design must include the independent and dependent variables in the title. __5. Jargons make a research title more sophisticated. __6. Only the first letter of nouns and pronouns are capitalized. __7. To minimize the number of characters in the title, only use the chemical formula than generic names. __8. Use declarative format in writing the research title. __9. To make it more specific, the year must be included in the title. __10. Using obsolete terms do not matter in writing the title. Basic Guidelines in Make Research Title 1. Use an accurate description of the subject and scope of the study instead of using general terms. 2. Do not use abbreviations except for commonly known ones like DNA and ICT. 3. Do not include words like “The study of,” “analysis of,” “an investigation of” or similar construction as these would only lengthen the title. 4. Include the main dependent and independent variables. 5. Be mindful of the proper use of grammar and punctuation. 6. Capitalize all nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs as well as the first letter of the first and last words. 7. State in a declarative form, although you may also see titles in question form from time to time. 9. The year the study has been conducted should not be indicated unless it is a historical study. 10. Use current terminology. 11. Depending on the institutional requirements, 5 to15 words are sufficient to describe the research study. 12.Use the common name instead of chemical formula (e.g., NH4) 13. Write and italicize the full scientific names. 14. Must reflect the tone of the paper. An academic research paper has title which is not casual, or informal, or does not contain humor. Directions: Evaluate the following erroneous research title and justify what makes it wrong. Example: Phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of S. trifasciata leaves Answer: The scientific name was abbreviated and not italicized. Directions: Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is incorrect. __1. Inserting humor on the research title makes it more interesting to the reader. FALSE __2. Abbreviations are a must to make the research title shorter. FALSE __3. Proper punctuation and correct grammar must be observed in writing the title. TRUE __4. All types of quantitative research design must include the independent and dependent variables in the title. __5. Jargons make a research title more sophisticated. __6. Only the first letter of nouns and pronouns are capitalized. __7. To minimize the number of characters in the title, only use the chemical formula than generic names. __8. Use declarative format in writing the research title. __9. To make it more specific, the year must be included in the title. __10. Using obsolete terms do not matter in writing the title. 1. An investigation of the effects of electronics uses on Interpersonal Relationship in adults. Ans: Don’t use the word “an investigation” The effects of electronics uses on Interpersonal Relationship in adults. 2. The Effects of Arts-Integrated Instruction on Arithmetic Skills of Students for S.Y. 2022-2023. Answer: Year must not be included The Effects of Arts-Integrated Instruction on Arithmetic Skills of Students . 3. Antibacterial effects of C2H5OH extract of Carica papaya leaves. Answer: Don’t use chemical formula Antibacterial effects of C2H5OH extract of Carica papaya leaves. 3. Antibacterial effects of C2H5OH extract of Carica papaya leaves. Answer: Don’t use chemical formula Antibacterial effects of C2H5OH extract of Carica papaya leaves.