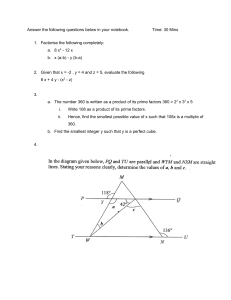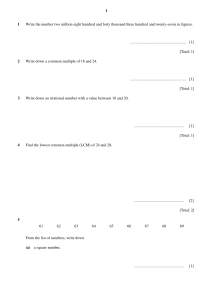
MATHEMATICS OBJECTIVE NOTES CH.1,2,3 Chapter 1: Primes, H.C.F and L.C.M 1. A Prime number has two different factors 1 and itself. Example: 3, 5, 7 2. A composite number has more than two different factors. Example: 8, 10 , 12 3. 0 and 1 are neither Prime numbers nor Composite Numbers. 4. A perfect square is a number whose square root is a whole number. Example: 25 is a perfect square of 5. 2√25 = 5 5. A perfect cube is a umber whose cube root is a whole number. Example : 27 is a perfect cube of 3. 6. The smallest prime number from 1- 100 is 2. 7. The largest prime number from 1-100 is 97. 8. There are 25 prime numbers which are less than 100. 9. The method of finding HCF and LCM is called Listing Method. 10. In order to find HCF, we multiply only common numbers. When you are taking HCF of 3 numbers then only those numbers are common which are present in all numbers. 11. In order to find LCM, you multiply all the numbers common and uncommon. When you are taking LCM of 3 numbers then the numbers which are present in all three and the numbers which are present in even only 2 numbers are taken as common. NOTE: Time related word problems are of LCM Chapter 2: Integers, Rational Numbers and Real Numbers Real Numbers Include both Rational numbers and irrational numbers. Rational Numbers are the real numbers which can be written in the form of fractions 1 and q in not equal to zero. Example: 2 Irrational Numbers Example: п, √2. 𝑝 are the real numbers that cannot be written in the form of 𝑞. 𝑝 𝑞 Integers An integer is a whole number that is not in fractions. An integer is a number zero, positive numbers and all negative numbers. 0 is neither positive integer nor negative integer. Positive Numbers Negative Numbers Are the numbers that are greater than zero. Example: +1, +5, +20 Are the numbers that are less than zero. Example: -1, -3, -8 Number Line NOTE: -1 is greater than -2 because -1 is closer to 0. NOTE: EX 2A questions for objective 1) 4 + (-7) = 4 – 7 = -3 when there is a positive and a negative number, we do subtraction and insert sign of a greater number. 2) -2 – 3 = -5 when there are two negative numbers we add them and insert a minus- sign because we are adding two negative numbers. Positive Numbers * Negative Numbers =Negative Numbers Negative Numbers * Positive Numbers = Negative Numbers Negative Numbers * Negative Numbers= Positive Numbers NOTE: Same rules apply on division. Chapter 3: Approximation and Estimation: NOTE: Nearest dollar or nearest number means whole number not decimals. Significant Figures show the degree of accuracy. A number is more accurate when it is given to a greater number of significant numbers. Rules to identify Significant Figures: i. ii. iii. iv. v. All non-zero digits are significant like 2, 5, 79 All zeros between non-zero digits are significant like 2005, 79.06 In a decimal, all zeros after a non-zero digit are significant like 15.60 In a decimal, all zeros before a non-zero digit are not significant like 0.052 In a whole number, zeros at the end may or may not be significant depending upon how the numbers are approximated.