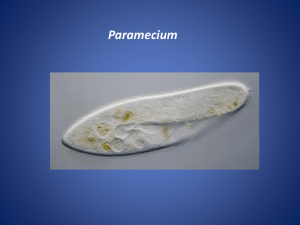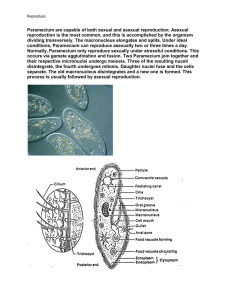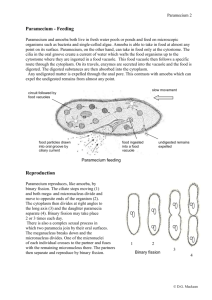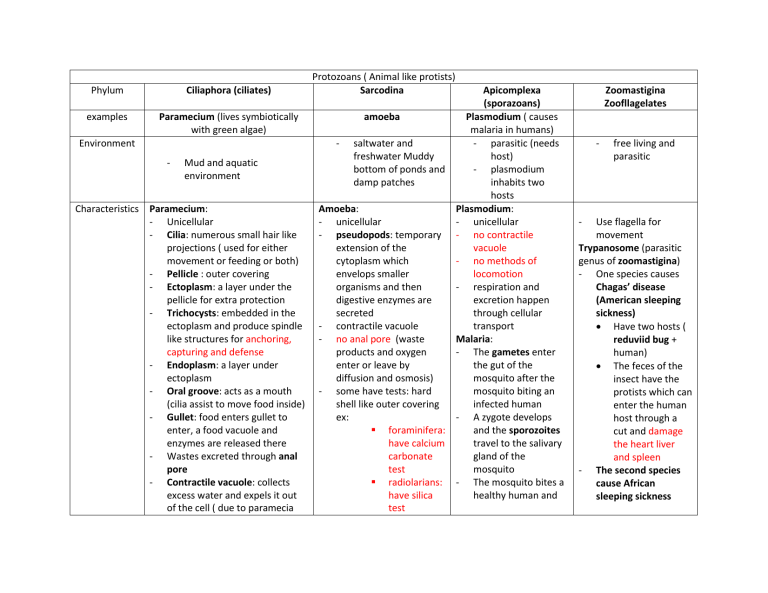
Phylum Ciliaphora (ciliates) examples Paramecium (lives symbiotically with green algae) Environment - Mud and aquatic environment Characteristics Paramecium: - Unicellular - Cilia: numerous small hair like projections ( used for either movement or feeding or both) - Pellicle : outer covering - Ectoplasm: a layer under the pellicle for extra protection - Trichocysts: embedded in the ectoplasm and produce spindle like structures for anchoring, capturing and defense - Endoplasm: a layer under ectoplasm - Oral groove: acts as a mouth (cilia assist to move food inside) - Gullet: food enters gullet to enter, a food vacuole and enzymes are released there - Wastes excreted through anal pore - Contractile vacuole: collects excess water and expels it out of the cell ( due to paramecia Protozoans ( Animal like protists) Sarcodina Apicomplexa (sporazoans) amoeba Plasmodium ( causes malaria in humans) - saltwater and - parasitic (needs freshwater Muddy host) bottom of ponds and - plasmodium damp patches inhabits two hosts Amoeba: Plasmodium: - unicellular - unicellular - pseudopods: temporary - no contractile extension of the vacuole cytoplasm which - no methods of envelops smaller locomotion organisms and then - respiration and digestive enzymes are excretion happen secreted through cellular - contractile vacuole transport - no anal pore (waste Malaria: products and oxygen - The gametes enter enter or leave by the gut of the diffusion and osmosis) mosquito after the - some have tests: hard mosquito biting an shell like outer covering infected human ex: - A zygote develops foraminifera: and the sporozoites have calcium travel to the salivary carbonate gland of the test mosquito radiolarians: - The mosquito bites a have silica healthy human and test Zoomastigina Zoofllagelates - - free living and parasitic Use flagella for movement Trypanosome (parasitic genus of zoomastigina) - One species causes Chagas’ disease (American sleeping sickness) Have two hosts ( reduviid bug + human) The feces of the insect have the protists which can enter the human host through a cut and damage the heart liver and spleen - The second species cause African sleeping sickness - living in hypotonic solution environment) usually have 2 or 3 to maintain homeostasis Micronucleus: assist in conjugation macronucleus: main nuclease that controls organism - transfer the sporozoites Sporozoites travel to liver Merozoites exit the liver to enter the blood and break down RBCs Reproduction and sexual process - - Conjugation in paramecium: exchange of the micronucleus through cytoplasmic bridge - reproduction through mitosis - Reproduce by Mitosis Some become cysts during harsh environments - Through host - Passed thrugh tsetse fly The fly feed on an infected mammal or human and transfers by a bite Causes fever, inflammation of lymph nodes and damage to nervous system Through host