Digestive System: Functions, Anatomy, and Processes
advertisement

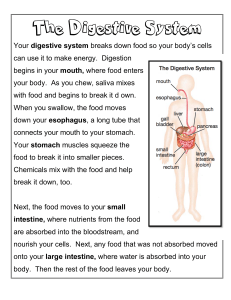
Chapter 25 : The Digestive System Digestive Functions: ○ Digestive System: processes food, extracts nutrients from it, and eliminates the residue. Five stages: ■ Ingestion: selective intake of food ■ Digestion: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into a form usable by body ■ Absorption; intake of nutrient molecules into the epithelial cells of digestive tract and then the blood or lymph ■ Compaction: absorbs water and makes the indigestible residue into feces ■ Defecation: elimination of feces Two anatomical subdivisions: - Digestive tract (alimentary canal): muscular tube extending from mouth to anus. 5m (16 ft) long in living and 9m (30 ft) dead. Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Stomach and intestines = gastrointestinal (GI) tract. - Accessory organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas Layers of the digestive tract wall: Mucosa Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosae Submucosa Muscularis mucosae Inner circular layer Outer longitudinal layer Serosa Areolar tissue Mesothelium Enteric Nervous System - nervous network found in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Composed of two networks of neurons ● Submucosal plexus - found in submucosa ● Myenteric plexus - found in parasympathetic ganglia and nerve fibers between layers of the muscularis externa The stomach and intestines are held up loosely by connective tissue sheets called mesenteries. The lower omentum is seen in the first figure, extending from the liver to the right superior margin of the stomach. It also houses the bile duct and some major blood vessels. The greater omentum is the larger mesentery found in both figures, it hangs from the left inferior margin of the stomach to the small intestine. The mesocolon is the mesentery in the colon. It looks “lacey” due to the undistributed adipose tissue found throughout the mesentery. ● Intraperitoneal - organ found within the peritoneal cavity (enclosed by mesentery) ● Retroperitoneal - organ found outside the peritoneal cavity (against the posterior body wall) The Mouth (aka oral/buccal cavity) Functions: ingestion, taste, chewing and chemical digestion, swallowing, speech, respiration. Stratified squamous epithelium lines the mouth: Keratinized (gums and hard palate) and Nonkeratinized (floor of the mouth, soft palate, and insides of cheeks and lips) Oral fissure - anterior opening between lips Fauces - posterior opening to the throat Cheeks and lips: - Retains food and pushes it between the teeth - Made of muscles (buccinator muscle of the cheek and orbicularis oris of the lips) and subcutaneous fat Three areas of lips: - Cutaneous area - colored like the rest of the face - Red (vermillion) area - hairless region where lips meet - Labial mucosa - the inner surface of the lips facing the gums and teeth Tongue - manipulates food between teeth - Lingual papillae - bumps and projections