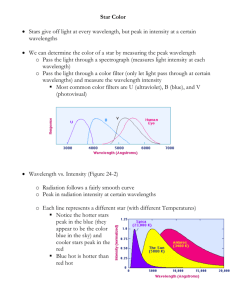
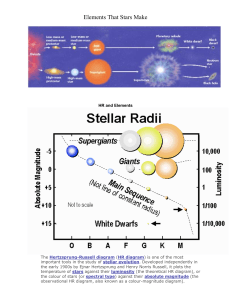
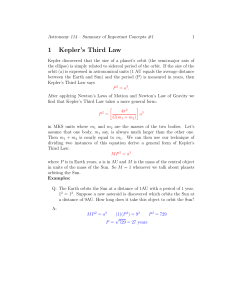
Astrophysics & Cosmology Definitions ➢ Luminosity: total power output by radiation of a star ➢ Radiant flux intensity: The observed amount of intensity transmitted normally through a surface per unit of area, of radiation measured on Earth ➢ Standard candle: An astronomical object which has a known luminosity due to a characteristic quality possessed by that class of object ➢ Wien’s displacement law: The black body radiation curve for different temperatures peaks at a wavelength which is inversely proportional to the temperature ➢ Black body: absorbs all light falling upon it and is a good emitter of radiation ➢ Stefan-Boltzmann Law: The total energy emitted by a black body per unit area per second is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature of the body ➢ Doppler effect: The apparent change in wavelength or frequency of the radiation from a source due to its relative motion away/toward the observer ➢ Redshift: The fractional increase in wavelength (or decrease in frequency) due to the source and observer receding from each other ➢ Hubble’s Law: The recession speed of galaxies moving away from Earth is proportional to their distance from the Earth Equations ❖ 𝐹= 𝐿 4𝜋𝑑2 ➢ F = radiant flux intensity ➢ L = luminosity ➢ d = distance b/w bodies ❖ 𝜆𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑇 = 2.9 × 10−3 ➢ 𝜆𝑚𝑎𝑥 = maximum wavelength emitted by the star at the peak intensity ➢ T = temperature ❖ 𝐿 = 4𝜋𝑟 2 𝜎𝑇 4 L = luminosity of the star (W) r = radius of the star (m) σ = the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10-8 kg s-3 K-4) T = surface temperature of the star (K) ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ ❖ ∆𝜆 𝜆 = ∆𝑓 𝑓 𝑣 =𝑐 ❖ 𝑣 = 𝐻0 𝑑 ➢ v = recessional velocity ➢ H0 = Hubble's constant / the rate of expansion of the universe ➢ d = distance b/w body and Earth 1 ❖ 𝑇0 = 𝐻 0 ➢ H0 = Hubble's constant ➢ T0 = age of universe