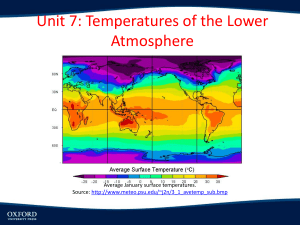
Module 8- Adiabatic Processes and Clouds Adiabatic process- air expands at high altitude due to lower atmospheric pressure, uses heat energy to expand parcel, it is thus cold at high temperature, doesn’t interchange with heat Sinking, compressed, and warms Dry adiabatic lapse rate DALR- warming and cooling remains constant, applies only to unsaturated air Moist adiabatic lapse rate- less than DALR, varies with temperature as water condenses into clouds past the dew point as air cools Absolutely stable atmosphere- environmental lapse rate is less than saturated adiabatic, parcel is cooler than environment, tendency to go down Absolutely unstable- environmental lapse rate is greater, parcel is warmer than environment, tendency to go up conditional instability- unsaturated air lifted to saturation where we don’t know where it goes, environmental lapse rate in between How do clouds form Orographic uplift- air deflect over a mountain, adiabatic cooling and promotes cloud Radiation fog, valley fog Advection fog Upslope fog Evaporation fog