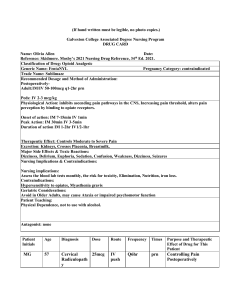
Medication Reference: Furosemide, KCl, Nitroglycerin, Pilocarpine, Insulin
advertisement

FUROSEMIDE/LASIX ANTIHYPERTENSIVES/LOOP DIURETICS USE: Treat edema & hypertension DRUG INDICATION/ACTION: Indication: Acute pulmonary edema, Edema, Hypertension. Action: Inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption at the proximal and distal tubules and the ascending loop of Henle. DOSE: Edema 🡪 PO = 20-80 mg qAM– if response is inadequate, give 2 dose, and each succeeding dose q6-8h, increase in 20-40mg increments (max. 600 mg/daily) HTN 🡪 PO = 20-40 mg bid nd Acute pulmonary edema 🡪 IV = 40 mg injected slowly over 1-2 mins, 80 mg over 1-2 mins after 1hr prn ADMINISTRATION: PO & IM – give in morning to prevent nocturia, give 2 dose (if ordered) 6-8 hrs. after, record injection site for IM nd IV – do not use if discolored yellow, do not infuse @ a rate no greater than 4 mg/min, use prepared infusion within 24 hrs. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Should not be used in pts hypersensitive to drug and anuria. Use cautiously in pts w/ hepatic cirrhosis and sulfonamide allergies. May cause tinnitus and reversible/irreversible hearing loss, ototoxicity. May exacerbate or activate SLE. SIDE EFFECTS: Headache, vertigo, orthostatic hypotension, tinnitus, blurred or yellow vision, anorexia, nausea, frequent urination, anemia, jaundice, hepatic dysfunction, dehydration, muscle spasm, toxic epidermal necrolysis ONSET/PEAK/DURATION: PO = Onset (20-60 min), Peak (1-2 hr), Duration (6-8 hr) IV = Onset (5 min), Peak (30 min), Duration (2 hr) IM = Onset (unknown), Peak (30 min), Duration (2 hr) NURSING IMPLICATIONS: Monitor weight & vitals routinely if long term usage. Drug is a potent diuretic, monitor pt for diuresis (especially older adults). May need to stop drug if oliguria or azotemia develops/increases. Monitor for hypokalemia, muscle weakness. Encourage a high potassium diet. Monitor uric acid level, glucose level, urine retention, renal function. Lab results: May increase cholesterol, glucose, BUN, creatinine, liver enzyme, and uric acid levels. May decrease calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium levels, Hb level and granulocyte, platelet, WBC counts TEACH: Take drug in morning. Pt may need potassium or magnesium supplements. Stand slowly. Limit alcohol intake & strenuous exercise. Report adverse effects (ringing ears, abdominal pain, sore throat, fever). DO NOT store different types of drugs in same container. Consult pharmacists before taking OTC drugs. Avoid direct sunlight, wear protective clothing. Onset – how quickly a medication will work. Peak – when the medication will reach maximum effectiveness. Duration – how long the pain relief will last. POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (KCl) POTASSIUM SUPPLEMENTS/SALTS USE: Prevent or treat hypokalemia (low potassium levels) DRUG INDICATION/ACTION: Indication: Hypokalemia Action: Replaces potassium and maintains potassium level DOSE: PO Prevent hypokalemia = 20 mEq/day. Adjust prn based on pt’s K+ levels. (Max. no more than 20 mEq as a single dose). 40 mEq/L @ infusion rate of 10 mEq/hr (Max. 200 mEq/daily) Hypokalemia = 40-100 mEq in 2-5 divided doses/day. (Max. 20 mEq single dose) IV Severe hypokalemia = 20-40 mEq/L @ no more than 40 mEq/hr (Max. 400 mEq/daily) ADMINISTRATION: PO – powders are completely dissolved before giving. Enteric coated tablets not recommended. Pt should take w/ meals & full glass of water. Use sugar free liquid form tablets for pts w/ esophageal stasis or obstruction. DO NOT crush extended release forms. IV – use only when oral is not feasible or if hypokalemia is life-threatening. Give by infusion only (slow infusion, rapid rate can cause fatal hyperkalemia). Administer high concentrations (300-400 mEq/L) via central route & infusion pump. Decrease rate if burning occurs. Ensure proper needle/catheter placement before and during infusion. Avoid extravasation. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use in pts w/ KCl hypersensitivity, renal failure pts, in pts w/ conditions that causes potassium retention. Use cautiously in pts w/ cardiac disease, renal impairment, acid-base disorders SIDE EFFECTS: Confusion, paresthesia of limbs, arrhythmias, heart block, cardiac arrest, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, hyperkalemia, respiratory paralysis, extravasation ONSET/PEAK/DURATION: PO: Unknown IV: Onset (immediate), Peak (immediate), Duration (unknown) NURSING IMPLICATIONS: Pts w/ scleroderma, diabetes, mitral valve replacement, cardiomegaly, esophageal strictures, immobile older adults = @ risk for GI lesions. Commonly used w/ potassium wasting diuretics. Monitor ECG, electrolyte levels, renal function. Store concentrated IV potassium separately (do not want to mistakenly administer through IV push). Verify potassium preparations. TEACH: Teach pt how to prepare powders & taking drug (take w/ meals and full glass of water/juice). Teach signs & symptoms of hyperkalemia. Report discomfort at IV site. Do not use salt substitutes concurrently. Do not be alarmed if wax matrix appears in stool. NITROGLYCERIN/NITRO-DUR VASODILATORS-ANTIANGINALS/NITRATES USE: Treat the symptoms of angina pectoris (chest pain) due to coronary artery disease DRUG INDICATION/ACTION: Indication: Anginal attacks, acute angina pectoris, hypertension, heart failure, chronic anal fissure pain Action: Reduces cardiac oxygen demand by decreasing left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (preload) and, to a lesser extent, systemic vascular resistance (afterload). Also increases blood flow through the collateral coronary vessels. DOSE: Preventing anginal attacks = transdermal patch 🡪 0.2-0.4 mg/hr once daily for 12-14 hrs., patch off for 10-12 hrs. ADMINISTRATION: Transdermal = apply to non-hairy area, remove after 12-14 hrs. and clean skin w/ soap & water. Rotate patch sites. Other ADM methods can be IV, topical, sublingual, buccal, translingual CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use in pts who are hypersensitive to nitrates, taking PDE5 inhibitors, early MI, severe anemia, acute circulatory failure/shock, increased ICP, glaucoma, orthostatic hypotension, transdermal allergy Use cautiously in pts w/ hypotension or volume depletion SIDE EFFECTS: Headache, dizziness, hypotension, bradycardia, palpitations, pharyngitis, nausea, dyspnea, rash ONSET/PEAK/DURATION: Transdermal = Onset (30 min), Peak (2 hr), Duration (10-12 hr) NURSING IMPLICATIONS: Monitor vital signs during infusion, especially in MI pts. Monitor BP and intensity during duration of drug response. Can cause headaches (treat w/ NSAIDS or acetaminophen). Assess blood pressure and oxygen saturation prior to applying patch. Lab results: IV nitroglycerin may falsely elevate triglyceride assay results with some tests. TEACH: Stopping drug abruptly can cause coronary artery spasm. Teach pt how to give prescribed form of nitroglycerin. Dispose of skin patches carefully. Notify MRI if wearing patch. Avoid alcohol. Do not use avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil w/ any nitrate 🡪 cause life threatening hypotension PILOCARPINE 1%, 2%, 4% MIOTICS Isopto Carpine, Vuity Use: Primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular HTN, Management of acute angle-closure glaucoma, Prevention of postoperative elevated IOP associated with laser surgery, Induction of miosis, Induction of miosis before goniotomy or trabeculotomy Action: A direct-acting cholinergic that causes contraction of iris sphincter muscles, resulting in miosis, and that produces ciliary spasm, deepening of the anterior chamber, and vasodilation of conjunctival vessels of the outflow tract. Route/Dose: Ophthalmic-instill 1 drop in the eye(s) up to four times daily; adjust concentration and frequency to control intraocular pressure (IOP). Start patients with 1% SE: EENT: blurred vision, brow pain, myopia, changes in visual field, conjunctival irritation, periorbital or supraorbital headache, transient stinging and burning, visual impairment (dim, dark, or “jumping” vision), eye pain. Contra: Hypersensitive to drugs and in those with anuria. Caution in patients with preexisting retinal disease, acute cardiac failure, bronchial asthma, hyperthyroidism, GI spasm, urinary tract obstruction, and parkinson's. ADM: Without touching tip of dropper to eye/surrounding tissue, apply light pressure on lacrimal sac for 2 mins after instilling to minimize systemic absorption. OPD: Onset= 10-30 min, peak= 30-60 min, duration= 4-8 hrs Nursing Implications: Drug may be used in combination with beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sympathomimetics, or hyperosmotic agents. If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least 5 minutes apart. ensure eye is clean, do it in correct eye, finger pressure on lacrimal duct of eye to prevent from going systemic and causing decrease BP. Teach: Advise patient to wash hands before and after installation, to apply light finger pressure on lacrimal sac for 2 minutes after drops are instilled, and not to touch applicator tip to eye or surrounding tissue. Have patient remove lenses before and wait 10 mins after to reinsert. Warn patients that transient brow pain and nearsightedness are common at first but usually disappear in 10 to 14 days. GENERIC NAME - Insulin (regular, short acting) Trade name - HumuLIN R Classification Antidiabetic USE - Regulate blood sugar levels ACTION - Lowers blood glucose level by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by binding to insulin receptors on skeletal muscle and in fat cells and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; also inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis. ROUTE/DOSE - Subcutaneous and IV. Individualized dosage & varies according to pt’s blood glucose and health status, 100units/ml in 3ml (10ml vial); 500 units/ml in 3ml pens and 20ml vial SIDE EFFECTS - Sweating, dizziness or lightheadedness, shakiness, hunger, fast heart rate, tingling in your hands, feet, lips, or tongue, trouble concentrating or confusion. blurred vision. CONTRADICTIONS - Contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia. Contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to drug or its components. Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products. ADMINISTRATION - Subcu - Administer by subcut injection in abdominal region, buttocks, thigh, or upper arm | IV - Don’t use if solution is viscous or cloudy; use only if clear and colorless. OPD - IV - Onset 10 to 15 min | Peak 15 to 30 min | Duration 2 to 6 h Subcu - Onset 30 min | peak 1.5 to 3.5 h | Duration 4 to 12h NURSING IMPLICATIONS - Monitor blood glucose level + adjust insulin dosage as needed for pt specific goals, monitor pt carefully for signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia (sweating, shaking, confusion, trembling), monitor K+ levels in pts at risk for hypokalemia PATIENT TEACHING - Instruct patient in self-management, including glucose management, injection technique, proper storage of insulin, and recognition and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Teach patient to eat within 30 minutes of injecting short-acting insulin. Instruct patient to only use syringes calibrated for their particular concentration of insulin. Albuterol Bronchodilators/Adrenergics USE: To prevent or treat bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease ACTION: Relaxes bronchial, uterine, and vascular smooth muscle by stimulating beta2 receptors ADMINISTRATION: If more than 1 inhalation is ordered, wait at least 2 minutes between inhalations. Shake the aerosol inhaler well to prime according to the manufacturer's instructions before first use. ROUTE: Oral/inhalation OPD: Inhalation (aerosol) Onset 5-15min Inhalation (powder) Onset rapid tablet and syrup form also available Peak 30-120min Peak 30min Duration 3-4hr Duration 3-4hr DOSE: Inhalation aerosol Adults and children age 4 and older: 1 to 2 inhalations every 4 to 6 hours as needed. Regular use for maintenance therapy to control asthma symptoms isn’t recommended. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Use cautiously in patients with CV disorders, hyperthyroidism, or diabetes mellitus and in those who are unusually responsive to adrenergics. Overdose Signs & Symptoms: Exaggeration of adverse reactions, seizures, angina, hypotension, HTN, tachycardia, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, dry mouth, palpitations, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, sleeplessness, hypokalemia, cardiac arrest. IMPLICATIONS: Monitor patient for effectiveness. Long-term control medications may be needed. In patients with COVID-19 who require a bronchodilator for asthma or COPD symptoms, use of pressurized metered-dose inhalers as opposed to nebulized delivery is preferred. Nebulized delivery may increase transmission of particles (SARS-CoV2) into the environment. Alert: Drug may cause paradoxical bronchospasm. Monitor patient closely; discontinue drug immediately and use alternative therapy if paradoxical bronchospasm occurs PATIENT TEACHING: Warn patient about risk of paradoxical bronchospasm and advise patient to stop drug immediately if it occurs. Teach patient to perform oral inhalation correctly. If prescriber orders more than 1 inhalation, tell patient to wait at least 2 minutes before repeating procedure. Tell patient that use of a spacer device with appropriate inhaler may improve drug delivery to lungs. GENERIC NAME- NPH Insulin (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) *Intermediate acting insulin Trade Name- HumuLin N, NovoLin ge NPH Classification- Antidiabetic USE - lower & assist in regulation of blood sugar levels ACTION - Increases cellular intake of glucose in the liver, adipose tissue & skeletal muscles, stimulating hepatic glycogen synthesis (to suppress glucose production). ROUTE- Subcutaneous injection DOSE- Individualized dosage per glucose levels; 100 units/mL (3 mL) or 100units/mL (10 mL) **NPH IS CLOUDY IN APPEARANCE** SIDE EFFECTS - Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar-dizziness, blurred eyesight, mood changes), weight gain, swelling of hands & feet, itching, mild skin rash, redness or thickening of skin at injection site, low potassiummuscle pain, cramps or weakness, abnormal heartrate. CONTRADICTIONS- In hypersensitivity reactions, allergic reactions, in instances of hypoglycemia ADMINISTRATION - Subcutaneous injection in upper arm, thigh, buttocks or stomach. TIME- 30-45 minutes before a meal OPD- Onset: 1-2 hours, Peak: 4-6 Hours, Duration: 12 hours or more depdending on dosage NURSING IMPLICATIONS - Monitor blood glucose levels & food intake. Monitor injection site for reactions, any swelling, monitor patient for signs of hypoglycemia (sweating, dizziness, skaking/trembling, tiredness, palpitations), monitor Postassium levels. PATIENT TEACHING - Instruct patient on administration of proper injection and in site rotating pattern, monitoring blood glucose, proper insulin storage, inspection of insulin prior to use, recognition and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, recognizing signs of reactions and hypokalemia GENERIC NAME- Acetaminophen and Codeine TRADE NAME- Tylenol with Codeine No. 3 Classification-Narcotic Analgesic USE - To relieve mild to moderate pain ACTION - Acetaminophen acts on CNS by upping pain threshold by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, inhibiting creation of prostagladins, reduces fever by direct action hypothalamus heat regulating center w/ consequent peripheral vasodilation, sweating and dissipation of heat. Codeine is an optiate narcotic used to reduce pain by directly working on opioid receptors in CNS to reduce feelings of pain. ROUTE- Orally by tablet, capsule or liquid DOSE- Adults, 15 mL every 4 hours as needed. Children (ages 7-12)-10 mL, 3-4 times per day. Children (ages 36) 5 mL, 3-4 times per day. Children younger than 3 years of age, use & dose must be determined by doctor. SIDE EFFECTS - minor side effects: dizziness, tiredness, constipation, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain & upset stomach, dry mouth, excessive sweating, headache, flushing. Rare/dangerous side effects: allergic reactions like hives, swelling. Liver problems seen by dark urine, upset stomach, yellow skin/eyes, vomiting. Bad dizziness, passing out, fever, chills, shallow breathing, seizures, confusion. CONTRADICTIONS - In patiens with significant respiratory depression or those with acute asthma. Those on other benzodiazepine medications (due to increase in risk of breathing problems) ADMINISTRATION - Orally by tablet, capsule or liquid. OPD - Tylenol Onset: 20-45 min, Peak: 0.5-2 hours, Duration: 3-4 hours Codeine Onset: 15-30 min, Peak: 0.5-1 hour, Duration: 4-6 hours NURSING IMPLICATIONS - Priority: Monitor for life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression especially during initial dosing. Monitor for any additional side effects PATIENT TEACHING - Instruct on importance of monitoring for respiratory depression. Instruct on correct dosage administration. Relay information regarding addictive qualities of narcotics and risks of overuse or misuse that can lead to overdose or death. Enoxaparin/Lovenox Anticoagulant/Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins USE: Thrombosis, unstable angina, prophylaxis of AMI, prophylaxis and treatment of PE and DVT ACTION: Accelerates development of antithrombin III-thrombin complex and deactivates thrombin, preventing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Drug has increased antifactor-Xa-to-antifactor-IIa activity ratio in comparison to heparin ROUTE/DOSE: Prevent PE & DVT after abdominal surgery: subcut=40 mg qd w/initial dose 2 hr before surgery Prevent PE & DVT after hip or knee replacement: subcut=30 mg q12h for 7-10 days Prevent PE & DVT in pt w/ acute illness who are at high risk due to lack of mobility: subcut=40 mg qd for 6-11 days Prevent ischemic complications of unstable angina and non-Q-wave MI w/ oral aspirin therapy: subcut 1mg/kg q12h until clinical stabilization (min 2 days) w/ aspirin 100-325 mg PO once daily Acute ST-segment elevation MI: age <75 30 mg single IV bolus & 1 mg/kg subcut followed by 1 mg/kg subcut q12h w/ aspirin 75 to 325 mg PO once a day Inpatient treatment of acute DVT w/ and w/o PE when given w/ warfarin sodium: 1 mg/kg subcut q12h or 1.5 kg/mg one daily for 5-7 days until therapeutic oral anticoagulant effect is achieved Outpatient treatment of acute DVT w/o PE when given warfarin sodium: subtcut=1 mg/kg q12h for 5-7 days until therapeutic oral anticoagulant effect is achieved Prevent PE & DVT in pts undergoing general surgery: 40 mg once daily w/ initial dose 2hr before surgery w/ usual duration of admin of up to 7-10 days Contraindication: Contraindicated in pts that are hypersensitive to drug, heparin, pork products, benzyl alcohol. Pts with active major bleeding. Pts with hx of immune-mediated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia w/in past 100 days or w/in the presence of circulating antibodies Side Effects: Confusion, fever, pain, edema, peripheral edema, nausea, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, ecchymoses, bleeding complications, hypochromic anemia, dyspnea, angioedema, anaphylaxis, irritation, rash, urticaria, pain, hematoma, erythema (at injection site), elevated liver enzymes Administration: Subcut - Pt must lay down, administer by deep subcut injection, alternating doses between left and right anterolateral and posterolateral abdominal walls. Do not expel bubbles of air from the prefilled syringe prior to injection. Insert entire length of needle while grasping onto skin with thumb and forefinger. Push the plunger to the lowest level of the syringe. After administering medication, do not rub injection site. Check and identify for any indication of bleeding at the site. Alternate site of injection and maintain a record of it. Onset/Peak/Duration: Subcut=Onset (unknown), Peak (4 hr), Duration (unknown) Nursing Implications: ✓ anti-Xa levels in pregnant pt w/ mechanical heart valves & in pts w/ notable renal impairment; Reach hemostasis at puncture site after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI); delay placement or removal of spinal catheter for a min. of 12 hrs after prophylactic doses; do not ever administer drug IM; TEACH: Teach pt and family to identify and look for sings of bleeding or abnormal bruising. If present notify healthcare provider immediately. Pt to avoid OTC drugs which include aspirin or salicylates unless Metoclopramide Hydrochloride GI Stimulants/Dopamine Antagonists USE: Prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting from emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, prevent or reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting, facilitate small-bowel intubation, aid in radiologic exam, delayed gastric emptying secondary to diabetic gastroparesis, GERD. ACTION: Stimulates motility of upper GI tract, increases lower esophageal sphincter tone, and blocks dopamine receptors at the chemoreceptor trigger zone. ROUTE/DOSE: To Prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting from emetogenic cancer chemotherapy o Adults: 1 to 2 mg/kg IV 30 minutes before chemotherapy; repeat every 2 hours for two doses, then every 3 hours for three doses. To prevent or reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting o Adults: 10 to 20 mg IM near end of surgical procedure. To facilitate small-bowel intubation o Adults and children older than age 14: 10 mg IV as a single dose over 1 to 2 minutes. o Children ages 6 to 14: 2.5 to 5 mg IV as a single dose slowly over 1 to 2 minutes. o Children younger than age 6: 0.1 mg/kg IV as a single dose slowly over 1 to 2 minutes. To aid in radiologic exam o Adults: 10 mg IV as a single dose over 1 to 2 minutes. Delayed gastric emptying secondary to diabetic gastroparesis o Adults: 10 mg PO 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime for mild symptoms. Maximum daily dosage is 40 mg. Or, give 10 mg IM or by slow IV push over 1 to 2 minutes 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime for up to 10 days for severe symptoms; then PO dose may be started and continued for 2 to 8 weeks. GERD o Adults: 10 to 15 mg PO q.i.d., as needed, 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime. Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with pheochromocytoma or other catecholamine-releasing paragangliomas, tardive dyskinesia, or seizure disorders. Contraindicated in patients for whom stimulation of GI motility might be dangerous (those with hemorrhage, obstruction, or perforation). Side Effects: anxiety, drowsiness, dystonic reactions, fatigue, lassitude, restlessness, seizures, suicidal ideation, akathisia, confusion, depression, dizziness, extrapyramidal symptoms, fever, hallucinations, headache, insomnia, tardive dyskinesia, NMS, bradycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, hypotension, fluid retention, transient HTN, HF, bowel disorders, diarrhea, nausea, incontinence, urinary frequency, erectile dysfunction, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, rash, urticaria, loss of libido, prolactin secretion, gynecomastia, amenorrhea. Administration PO: Give drug 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime when used for gastroparesis and GERD. PO (ODT):Give drug at least 30 minutes before eating and at bedtime.Give immediately after opening sealed blister. If the tablet breaks or crumbles, throw it away and obtain a new one.Place tablet on patient’s tongue. Tell patient to let it melt for approximately 1 minute and then swallow. IV: Drug is compatible with D5W, NSS for injection, dextrose 5% in half-NSS, Ringer injection, and lactated Ringer injection. NSS is the preferred diluent; drug is most stable in this solution. Give doses of 10 mg or less by direct injection over 1 to 2 minutes. Dilute doses larger than 10 mg in 50 mL of compatible diluent, and infuse over at least 15 minutes. Monitor BP closely. There is no need to protect drug from light if infusion mixture is given within 24 hours. If protected from light and refrigerated, it’s stable for 48 hours. Incompatibilities: Cephalothin, chloramphenicol, sodium bicarbonate. IM: Inspect for particulate matter and discoloration. If either is present, don’t use. Inject into a large muscle. Onset/Peak/Duration PO: Onset (30-60mins). Peak (1-2hr). Duration (1-2hr) IV: Onset (1-3mins). Peak (unknown). Duration (1-2hr) IM: Onset (10-15mins). Peak (Unknown). Duration (1-2hr) Nursing Implications: Monitor bowel sounds. Safety and effectiveness of drug haven’t been established for therapy lasting longer than 12 weeks. Drug may cause tardive dyskinesia, parkinsonian symptoms, and motor restlessness. Monitor patient for involuntary movements of face, tongue, and extremities, which may indicate tardive dyskinesia or other extrapyramidal adverse effects.Monitor patient for fever, CNS symptoms, irregular pulse, cardiac arrhythmias, or abnormal BP, which may indicate NMS. Monitor patient for dizziness, headache, or nervousness after metoclopramide is stopped; these may indicate withdrawal. Diphenhydramine or benztropine may be used to counteract extrapyramidal adverse effects from high doses. TEACH:Instruct patient to take ODTs 30 minutes before food and at bedtime and not to repeat dose if inadvertently taken with food. Teach patient proper drug administration for prescribed formulation. Tell patient to avoid activities that require alertness for 2 hours after doses. Urge patient to report persistent or serious adverse reactions promptly. Teach patient signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia, other extrapyramidal signs and symptoms, and NMS. Advise patient to discontinue drug and to seek immediate medical attention if such signs and symptoms occur. Advise patient not to drink alcohol during therapy. GENERIC NAME: Docusate sodium Trade Name: Colace Classification: Stool Softener USE - prevention of dry, hard stool ACTION - increases water, fat penetration in intestine; allows for easier passage of stool ROUTE/DOSE Adult PO 50-400mg/day in divided doses or 240 mg q day (rectal enema 4 mL) Child > 12 yr: enema 2 mL Child 6-12 yr PO: 40-150mg/day Child 3-6 yr PO: 20-60mg/day Child <3 yr PO: 10-40mg/day Infant PO: 5mg/kg/day SIDE EFFECTSEENT: bitter taste, throat irritation GI: nausea, anorexia, cramps, diarrhea INTEG: rash OTHER: laxative dependence with long-term or excessive use CONTRADICTIONS- hypersensitivity, obstruction, fecal impaction, nausea/ vomiting PRECAUTIONS- pregnancy, breastfeeding ADMINISTRATION Swallow tabs whole; do not break crush or chew Oral Sol: diluted in milk, fruit juice to decrease bitter taste In morning or evening (oral dose) Store in cool environment, do not freeze Onset PO: 12-72hr Rectal: 2-15min Peak Unknown Duration Unknown NURSING IMPLICATIONS Assess: cause of constipation; identify whether fluids, bulk or exercise is missing from lifestyle; constipating products’ cramping, rectal bleeding, nausea, vomiting; if these occur product should be D/C Pregnancy/breastfeeding: low risk of fetal harm in pregnancy, breastfeeding Evaluate: Therapeutic response: decrease in constipation TEACH PATIENT/FAMILY: That normal BM do not always occur daily Not to use in presence of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting To notify prescriber if constipation is unrelieved or if symptoms of electrolyte imbalance occur: muscle cramps, pain, weakness, dizziness, excessive thirst That product may take up to 3 days to soften stools To take oral temp w/ a full glass of water (unless on fluid restrictions) & to increase fluid intake Generic Name: Sodium Chloride, Normal saline Classification: Crystalloid Fluid Use: Injection is indicated for diluting/dissolving drugs for Intravenous, Intramuscular, or Subcutaneous injections. Maintenance for fluid and electrolyte status in situations in which losses may be excessive. 0.9% is used for replacement, treatment of metabolic alkalosis, a primary fluid for hemodialysis to beginning/end blood transfusions. Action: Sodium is a major cation in extracellular fluid and helps maintain water distribution, fluid and electrolyte in balance, acidbase equilibrium, and osmotic pressure. Chloride is the major anion in extracellular fluid and is involved in maintaining acid-base balance. Solutions of NaCl resemble extracellular fluid. Reduces corneal edema by osmotic effect. Route/Dose: 0.9% NaCl 0.5mL IM before discharge SE: Febrile response, infection or irritation at injection site, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasating and hypervolemia. Hypernatremia may be associated with edema and exacerbation of CHF due to water retention. Cerebral edema and myelinolysis have been reported. Contra: These solutions are contraindicated where the administration of sodium or chloride could be clinically detrimental. Use with great care, if at all in patients with congestive heart failure. Patients with cardiac disease, sodium chloride administration and subsequent sodium retention may exacerbate hypertension, edema, and heart failure. During fluid resuscitation, rapid infusion of a large volume of fluid in patients with hypoxia and/or compromised cardiac or renal function may result in decreased cardiac output and pulmonary edema. Additionally, patients with diabetic ketoacidosis may be at risk for cerebral edema after rapid administration of a crystalloid (e.g., normal saline). In such incidences, smaller fluid boluses and/or longer administration times are appropriate. Monitor fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid base balance during prolonged therapy or whenever the patient or dosage and/or rate of administration warrants such evaluation. In patients with organ dysfunction, monitor respiratory status and tissue perfusion, as well as changes in clinical condition. ADM: Fluid administration should be based on calculated maintenance or replacement fluid requirements for each patient. 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP may also be administered intravascularly as a priming fluid in hemodialysis procedures. When Sodium Chloride Injections USP are used as diluents for infusion of compatible drug additives, refer to dosage and administration information accompanying additive drugs. Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store. OPD: I.V. Onset: rapid, Peak: end of fusion, Duration: unknown NSE: High Alert: Accidental administration of hypertonic sodium chloride solutions (greater than 0.9% have resulted in serious electrolyte imbalances. Do not confuse vials of concentrated sodium chloride (23.4%) with vials of sodium chloride flush solutions (0.9%). Dose of NaCl depends on patients age, weight, condition, fluid and electrolyte balance, and acid-base balance. Do not administer bacteriostatic NaCl containing benzoyl alcohol as a preservative to neonates. This should not be used to reconstitute or to dilute solutions or to flush intravascular catheters in neonates. TEACH: The NaCl is used to replenish lost water and salt in your body due to certain conditions. Contact your doctor if you have any serious side effects. Get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including rash, itching/swelling, severe dizziness or trouble breathing. benazepril Action hypertensive/ace inhibitors Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. lowering the blood pressure side effects: CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, headache. Resp: cough. CV: hypotension. GI: nausea. GU: impaired renal function. Derm: rashes. F and E: hyperkalemia. Misc: ANGIOEDEMA. implications: Monitor signs of angioedema, including rashes, raised patches of red or white skin (welts), burning/itching skin, swelling in the face, and difficulty breathing. Notify physician of these signs immediately. Assess blood pressure periodically and compare to normal values (See Appendix F) to help determine antihypertensive effects. Report low blood pressure (hypotension) Assess dizziness and drowsiness that might affect gait, balance, and other functional activities (See Appendix C). Be alert for signs of high plasma potassium levels (hyperkalemia), Patient/Client-Related Instruction Remind patients to take medication as directed to control hypertension and other cardiac conditions even if they are asymptomatic. Counsel patients about additional interventions to help control blood pressure, including regular exercise, weight loss, sodium restriction, stress reduction, moderation of alcohol consumption, and smoking cessation. Instruct patient to report signs of impaired renal function, including decreased urine output, cloudy urine, or sudden weight gain due to fluid retention. Instruct patient to notify physician of a prolonged dry cough; drug therapy may need to be altered to resolve this side effect. Instruct patient or family/caregivers to report other troublesome side effects such as severe or prolonged headache, nausea, or skin rash. ROUTE: oral onset: 1h peak: 1-2hr duration: 24hr Contraindications & Cautions Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to ACE inhibitors and in those with a history of angioedema regardless of prior ACE inhibitor use. Use cautiously in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. If jaundice develops or liver enzyme levels are markedly elevated, discontinue drug. Trade Name: Tylenol Generic Name: Acetaminophen Drug Classification: Nonopioid analgesic Usual Dose: 2 tablets (325 mg) q 4-6 hours Indications: mild to moderate pain/fever, arthralgia, dental pain, dysmenorrhea, headache, myalgia, osteoarthritis. Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatotoxicity, hepatic seizure (overdose), GI bleed. Nursing Considerations/Pt. Education/ Lab Data: Monitor liver function studies: AST, ALT, bilirubin, creatine before therapy if long-term therapy is anticipated. Inform the patient that toxicity may occur when used with other combination products. Pregnancy Category: B Trade Name: Gocovri Generic Name: Amantadine Drug Classification: Antiviral, Antiparkisonian agent Usual Dose: 100 mg BID Indications: Prophylaxis or treatment of influenza type A, EPS, parkinsonism, Parkison’s disease. Side Effects: psychosis, depression, hallucinations, tremors, seizures, insomnia, blurred vision, urinary retention, dermatitis. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Monitor mental status may cause increased psychiatric disorders especially in the elderly, giat, tremors, akinesia, rigidity, may be effective if anticholinergics have not been effective. Pregnancy Category: C Trade Name: Enalapril Generic Name: Enalapril Maleate Drug Classification: Antihypertensive, Ace inhibitor Usual Dose: 2.5-5mg/day Indications: Hypertension, heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction. Side Effects: chest pain, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, syncope, angina, orthostatic hypotension, double vision, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, proteinuria. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Monitor blood pressure, peak/trough level orthostatic hypotension, syncope when used with diuretic, pulse; note rate, rhythm, quality. Those with impaired renal function should be monitored for hyperkalemia. Pregnancy Category: D Trade Name: Zyprexa Generic Name: Olanzapine Drug Classification: Antipsychotic (typical) Usual Dose: 5-10mg/day Indications: Schizophrenia, acute manic episodes with bipolar disorder, acute agitation. Side Effects: Tachycardia, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, urinary retention, hyperlipidemia, peripheral edema. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Assess sleep pattern disturbances, mood,. Behavior, presence of hallucinations, suicidal thoughts/behaviors. Asses for slurred speech, altered gait, aggression, dizziness, weakness, hypertension, and seizures. Pregnancy Category: C Generic name: warfarin Brand name: Jantoven Classification: anticoagulants Drug Indication/Action: Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thromboembolic disorders (DVT, PE) and embolic complications from atrial fibrillation or cardiac valve replacement; adjunct to reduce risk of systemic embolism after MI/Inhibits vitamin K–dependent activation of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, formed in the liver. Also inhibits anticoagulant proteins C and S. ONSET: Within 24 hrs Duration: 2-5 days Half-life: 20-60 hours Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: 2 to 5 mg PO daily for 2 to 4 days; then dosage based on daily PT and INR until stable in the therapeutic range. Usual maintenance dosage is 2 to 10 mg PO daily. Base dosages on INR target goals and other clinical factors. Individualize duration of treatment as clinically indicated. Contraindications: Uncontrolled bleeding; Open wounds; Active ulcer disease; Recent brain, eye, or spinal cord injury or surgery; Severe liver or kidney disease; Uncontrolled hypertension; OB: Pregnancy (may cause fetal harm). Side Effects: CNS: taste perversion. CV: vasculitis.GI: abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, nausea, vomiting.Hematologic: hemorrhage. Hepatic: hepatitis.Respiratory: tracheal or tracheobronchial calcification. Skin: alopecia, pruritus, rash, dermatitis.Other: chills, hypersensitivity or allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and urticaria. Nursing Implications: Boxed Warning: Warfarin can cause major or fatal bleeding, which is more likely to occur during the starting period and with a higher dose. Regularly monitor INR in all patients. Consider more frequent INR monitoring in those at high risk for bleeding. Obtain daily INR determinations upon initiation until stable in the therapeutic range; then, every 1 to 4 weeks. Avoid IM injections when possible. Regularly inspect patient for bleeding gums, bruises on arms or legs, petechiae, nosebleeds, melena, tarry stools, hematuria, and hematemesis Patient Education: Instruct patient to take medication as directed. Take missed doses as soon as remembered that day; do not double doses. Inform health care professional of missed doses at time of checkup or lab tests. Inform patients that anticoagulant effect may persist for 2–5 days following discontinuation. Review foods high in vitamin K (see food sources for specific nutrients). Patient should have consistent limited intake of these foods, as vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin, and alternating intake of these foods will cause PT levels to fluctuate. Advise patient to avoid cranberry juice or products during therapy. Generic Name/Trade Name: Cinnamon Classification: Anticoagulant Drug Indication/Action: used as a treatment for bronchitis, GI problems, anorexia, and diabetes. Both species of cinnamon contain coumarin, however, cassia cinnamon contains much larger amounts and may decrease blood clotting ONSET: Duration: Half-life: Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Safe if taken in amounts of no more than 6g per day. Contraindications: People who are allergic to cinnamon or Peru balsam. Side Effects: Heavy exposure may cause skin irritation, GI problems, or allergic reactions. Nursing Implications: watch for toxicity, stop use at least three weeks before any surgical procedures, do not use if pregnant, may cause liver disease with long term use Patient Education: Cinnamon should not be used in place of conventional medical care or to delay seeking care if you have health problems. This is particularly true if you have diabetes. Generic Name/Trade Name: Turmeric (Curcuma longa) supplement Classification: Herbal: Anti-Inflammatory/ Dietary Drug Indication/Action: Used as a dietary supplement to treat heartburn, stomach ulcers, gallstones, inflammation & cancer. May also treat symptoms of conditions such as arthritis, digestive disorders, respiratory infections, allergies, liver disease, depression or skin conditions. ONSET: N/A Duration: N/A Half-life: N/A Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Some research indicates dosages of 500-2,000mg PO capsule Daily. Can be used in cooking moderately as an individual prefers. Long term usage in high dosages is not recommended. Contraindications: In those with gallbladder disease as it may worsen condition. Used with caution in those pregnant or breastfeeding. Side Effects: Generally safe. High doses may cause nausea or diarrhea. Nursing Implications: Be aware of patients potential usage of Turmeric supplements and monitor for signs of nausea or diarrhea. Patient Education: Inform patients of use in caution if pregnant or breastfeeding. To monitor for any signs of nausea/ diarrhea. Consult with a doctor prior to using herbal supplements such as turmeric. Generic Name/Trade Name: Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Classification: Herbal: Anti-Inflammatory Drug Indication/Action: Used to treat Nausea, pain, including menstrual cramps and headache, swelling and Arthritis joint stiffness ONSET: N/A Duration: N/A Half-life: N/A Recommended Doses: Can be consumed in foods and drinks, including teas, capsules, syrups & liquid extracts. Consumption in natural form in foods is generally safe and dosage is dependent on the individual. Capsules can vary in dosage, generally capsules come in the form of 550mg taken PO 2x daily or single dose capsules of 1,500mg taken daily. Contraindications: Not recommended/ Use caution in those taking blood thinners such as Warfarin (Coumadin), blood pressure medication, those taking diabetic medication as ginger may lower blood sugar, patients with gallstones, or in Children under 2. Side Effects: gas, bloating, heartburn, nausea Nursing Implications: The nurse needs to be aware when doing the initial assessment for patient medications of any herbal supplements/ vitamins the patient is taking. Nurses should be aware of the contraindications between ginger/ herbal supplements that can cause reactions with other medications. Patient Education: Patients should be informed of risk of bleeding and other side effects of taking ginger as an herbal supplement & be informed of precautions when used with other medications. Patient should be informed of contraindicated use of taking with anti-coagulants and diabetic medication. Patients should consult their doctor before beginning any herbal regiment, especially those taking prescription medications and those who are pregnant or breastfeeding or have risk for bleeding. Generic Name/Trade Name: Garlic Classification: Herbal supplement Drug Indication/Action: Garlic may be used for atherosclerosis prevention, cholesterol and triglyceride levels reduction, to treat colds, coughs, fever, and sore throat, GI tract and colon cancers prevention, Ml and stroke prevention, antimicrobial use (inhibits bacterial and fungal infection). ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: PO - 2 to 5 g of fresh raw garlic; 0.4 to 1.2 g of dried garlic powder, 2 to 5 mg garlic oil: 300 to 1,000 mg of garlic extract (solid material); 2,400 Contraindications: Patients should not take garlic if they have a bleeding disorder or if they are taking the drug saquinavir. Garlic reduces the effectiveness of saquinavir. Garlic should also be avoided prior to having surgery or dental work because it reduces blood clotting. Side Effects: May cause heartburn and upset stomach, and has also been associated with breath and body odor. Nursing Implications: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Carefully monitor PT, PTT, and INR in patients taking anticoagulants. Herb may lower glucose level, if a patient is taking an antidiabetic, watch for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, and monitor their glucose level. Advise parents not to use oil to treat inner ear infection in children. Patient Education: Consume herb in moderation, to minimize the risk of adverse reactions. Heavy use of herb 1 to 2 weeks before surgery is discouraged. If a patient is using herb to lower cholesterol levels, notify health care provider to have cholesterol levels monitored. Using herb with anticoagulants may increase the risk of bleeding. If using herb as a topical antiseptic, avoid prolonged exposure to the skin because burns can occur. Take with food to prevent Gl adverse reactions. Generic Name/Trade Name: Echinacea (Echinacea purpurea) Classification: Herbal supplement Drug Indication/Action: Echinacea is commonly used as an immune booster. It is believed to increase the body's number of white blood cells allowing the prevention of common colds and flu. It is also believed to shorten your length of symptoms by days. In women, it is known to reduce the amount of reoccurring yeast infections. ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Oral: Dry powdered extract: 300-500 mg, three times. Liquid extract tinctures: 2.5 ml, three times daily. Do not exceed 10 ml daily. Tea: 2-3 servings daily Contraindications: patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, leukosis, multiple sclerosis, tuberculosis, and HIV infection. Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, sore throat, skin rash, drowsiness, headache disorder, abdominal pain with cramps Nursing Implications: Monitor skin for rashes, change in appetite due to nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain with cramps. Monitor VS and additional pain. Patient Education: Consult with your doctor before beginning to take Echinacea, especially if pregnant. Discontinue use if side effects persist. Do not take Echinacea for more that 14 consecutive days. Do not take if hypertensive to ragweed allergies MATRICARIA/CHAMOMILE HERBAL SUPPLEMENT Drug Indication/Action: Commonly used for many human ailments such as hay fever, inflammation, muscle spasms, menstrual disorders, insomnia, ulcers, wounds, gastrointestinal disorders, rheumatic pain, and hemorrhoids. ONSET: 30-40 min Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Chamomile has been used as a tea for various conditions and as a topical cream, gel, or oil. Typical oral doses are 1.1 to 15 g/day. No more than 8g of dried flower heads Contraindications: Contraindicated in persons with hypersensitivity to ragweed pollens. Contraindicated for patients taking anticoagulants, NSAIDs, or salicylate Side Effects: Nausea, dizziness, and allergic reactions Nursing Implications: Patients who are sensitive to ragweed and chrysanthemums can be at risk for anaphylaxis. Patients with hay fever or bronchial asthma can also be at risk for anaphylactic reactions. Patient Education: Do not consume chamomile during pregnancy. Do not use with anticoagulants, NSAIDs, or salicylates. Inform about allergic reactions and ingesting too much dried flower can cause vomiting. Do not give Chamomile to a child without consulting an HCP first. Inform HCP about use of chamomile if asked about herbal remedies. ASTRAGALUS HERBAL SUPPLEMENT Drug Indication/Action: Used for upper respiratory infections, allergic rhinitis (hay fever), asthma, chronic fatigue syndrome, and chronic kidney disease ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Powder: 1-30 g/day orally. Doses greater than 28 g/day are not recommended. Decoction: 0.5-1 Liter per day (maximum of 120 grams of whole root per liter of water) Contraindications: Avoid using astragalus if you are taking immune-suppressing drugs. Pregnant or nursing women should not use astragalus root. If you have an immune system disease such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or another autoimmune disease, you should not use astragalus root. Side Effects: Rash, itching, nasal symptoms, or stomach discomfort Nursing Implications: Always notify HCP or RN if taking. Patient Education: Do not take with prescription drugs without checking with health care provider. Do not take if pregnant or nursing. Do not give to infants/young children. Discontinue if side effects are disturbing and contact health care provider Ginkgo/Ginkgo Biloba Classification: Plant; Herb asthma, bronchitis, fatigue, and tinnitus, improve memory, prevent Alzheimer disease and other dementias, decrease intermittent claudication, and as a treatment for sexual dysfunction and multiple sclerosis. May decrease phenytoin, carbamazepine and valproate effectiveness Drug Indication/Action • Duration: • Half-life: Onset: • N/A Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: 80 mg b.i.d Contraindications: People taking blood can increase bleeding Ibuprofen slows blood clotting Diabetes- can cause hypoglycemia Warfarin •Side Effects: headache, nausea, GI upset, dizziness, and allergic reactions that include severe reactions leading to death. In patients taking blood thinners, ginkgo has been shown to increase bleeding risk. •Nursing Implications: Taking increase ginkgo with ibuprofen the might chance HX Not pregnant, of approved blood of Ginkgo can increase glucose levels- check blood sugar levels Taking ginkgo along with warfarin might •Patient Teaching/Education: Don’t take if slow clotting bruising increase the breast-feeding, seizures, chances on much and of bruising blood and thinners recent by too the and bleeding. serious bleeding medications, surgery FDA All herbal of the ingredients may not be known; what is on the label may not be what is in the bottle and not approved by FDA Ginseng Classification:HERBAL SUPPLEMENT Drug Indication/Action: Used to lower blood sugar after a meal in patients with diabetes type 2, and for respiratory infections, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), breast cancer, cancer related fatigue, menopausal symptoms, memory loss, anemia, insomnia, bleeding disorders, digestive disorders and other conditions. ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Crude preparations of dried root powder 1 to 2 g can be taken daily for up to 3 months. In numerous clinical trials, the dosage of crude root has ranged from 0.5 to 3 g/day and the dose of extracts has generally ranged from 100 to 800 mg. Contraindications: Contraindicated in persons with history of heart problems, high or low BP, rheumatic heart disease, bleeding/clotting problems, mental/mood disorders, overactive immune system disorders such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or cancer of the breasts, ovaries, or uterus. Do not take if on warfarin or diabetic medications. DO not take if currently taking immunosuppressants. Side Effects: Diarrhea, insomnia, headache, rapid heartbeat, increased or decreased BP, agitation, upset stomach, menstrual problems (vaginal bleeding), breast pain, dizziness Nursing Implications: Monitor BP for increased or decreased levels. Monitor vital signs for heart problems, such as abnormal heart rhythm. Monitor for purple skin rash that causes blisters and peeling. Patient Education: Do not consume Ginseng if taking warfarin or other blood thinning medications. Do not take if there is a history of heart conditions. Inform patients about BP and heart rate levels. Patients should also be instructed to consult their primary care providers before initiating any supplement use. Generic Name/Trade Name: Kava Kava/Piper Methysticum Classification: Herbal Remedy/ Dietary Supplement Drug Indication/Action: Kava is used to aid in relaxation, insomnia and treat anxiety Use: An herbal remedy that functions in accordance with other treatments or as a primary method of treating insomnia or anxiety ONSET: 30min Duration: 4-6 hours Half-life: 2 hours Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Oral: 300 mg Capsules PO 3 tablespoons diluted in water, approximately 8 to 12 oz In the form of tea consumed PO Contraindications: contraindicated in patients taking the following drugs or with the following conditions: CNS depressant/sedative medication Contraindicated in those with liver disease, it can progress or worsen liver damage. Opioids Antiparkinsonian drugs Analgesics (Ex. tramadol due to drug-herb interactions) Pretomanid Antihistamines Anticonvulsants Consumption of alcohol use excessively Side Effects: Dry scaly yellowing skin, eye irritation, heart problems, liver damage especially with use of alcohol, headache, fatigue, depression, diarrhea Nursing Implications: Observe patient for increased CNS depression, observe and watch patient’s function of the liver to avoid toxicity due to decreased metabolization of drugs. Patient Education/Teaching: Patients should be advised that a drug-herb interaction could take place upon taking medications such as antiretroviral medicines, benzodiazepines, bartiturates, Parkinson’s disease treatment medications. These would include medications that treat conditions such as HIV or AIDS, anxiety, Parkinson’s disese. Other medications to avoid would be opioids, analgesics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, CNS depressants, sedative medications, and pretomanid. Furthermore, patient’s should be advised to refrain from usage of Kava if they have mental health conditions such as depression or bipolar disorder, diseases of the liver, or are currently pregnant or breastfeeding. Interactions of these drugs or conditions could minimize the effectivness of current treatment or worsen conditions. Licorice Generic/Trade Name: Licorice/Glycyrrhiza Glabra Classification: Herbal Drug Action: licorice has anti inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Aiding skin conditions, acid reflux and indigestion, anti cancer properties and respiratory infections Drug Onset: Unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: unknown Route and Dose Range: Oral no more than 100 mg per day. Contraindication: Avoid in pregnant women, can cause abnormal brain development in babies. Do not take with blood thinners, BP medications, cholesterol medications, diuretics, NSAIDs. Side Effects: overdose increases stress hormone, cortisol. Can trigger low potassium levels, high BP, muscle weakness and abnormal heart rhythms. Nursing Implications: observe for potassium and heart rhythms for patients who say they are taking licorice supplements. Patient Teaching: Teach patients about drug-herb interaction, to avoid taking supplements with blood pressure medications, blood thinners, diuretics, NSAIDs. Advise patients to tell their HCP about consuming licorice as a herbal supplement. Advise patients of the side effects, and teach pregnant patients to avoid licorice teas, and supplements. Name: Valerian Generic Name: Valeriana officinalis Drug Classification: Herbal product Usual Dose: (capsule or liquid dosage) For insomnia, PO 300-600 mg q 30 min-2 hr before bedtime. For anxiety, PO 120-200 mg, t.i.d. Action: GABA receptor agonist Indications: tx insomnia, stress, anxiety, depression, ADHD. Onset: 30 min Peak: 30 min-2hr Duration: Unknown Half-life: 1.1 hr Capsule/Liquid Side Effects: CNS: headache, drowsiness GI: upset stomach, dry mouth. Capsule/Liquid Adverse reactions: GI: abdominal pain, hepatotoxicity, CV: chest tightness, MS: tremors. Contraindications: avoid combining it with sedative drugs, sleep aids, antidepressants, and/or alcohol. Nursing interventions (capsule or liquid): 4-8 weeks use is a safe period for consumption. Pt with liver disease avoid use may cause hepatotoxicity, monitor ALT, AST levels. Pt. Education (capsule or liquid): Avoid operating heavy machinery or vehicles. It is not recommended for pregnant women or breastfeeding women, it may pose potential harm. Pregnancy Category: C Saw Palmetto Herbal remedy Route: Oral Dose: 320mg Use: Treat urinary symptoms related to benign prostatic hypertrophy, chronic pelvic pain, decreased libido, migraine, and hair loss. Action: Include antiandrogenic effects such as inhibition of 5a-reductase I and II and inhibition of binding of dihydrotestosterone to the cytosolic androgen receptors, anti-proliferative effects and anti- inflammatory effects. Side effects: Digestive issues and headache. No drug interactions are reported. Contraindications: May interact with bleeding or blood clotting disorder. Likely to not be safe during pregnancy. Can make birth control pills less effective Nursing intervention: have liquid available to chase with if needed. Patient teaching: stop taking if nose begins to bleed, avoid if pregnant. St. John Wort Herbal Remedy Route: oral Dose: 300mg Use: treat mental disorder, nerve pain, malaria and sleep disorder. Action: Reduce the uptake of serotonin at the neuronal synapses, as well as dopamine and norepinephrine. Contraindications: Drug interactions include antidepressants (which can lead to serotonin syndrome), birth control pills, cyclosporine, digoxin, indinavir, irinotecan, drugs for seizure control, and anticoagulants. Side effects: sensitivity to sunlight, anxiety, dry mouth, dizziness, GI problems, fatigue, headache, and sexual dysfunction. Nursing intervention: monitor patient’s use of drug and note drug interactions before administration. Patient teaching: teach patient to avoid sunlight while on medication, stop medication of onset of dizziness and headache. Trade Name: Tylenol Generic Name: Acetaminophen Drug Classification: Nonopioid analgesic Usual Dose: 2 tablets (325 mg) q 4-6 hours Indications: mild to moderate pain/fever, arthralgia, dental pain, dysmenorrhea, headache, myalgia, osteoarthritis. Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatotoxicity, hepatic seizure (overdose), GI bleed. Nursing Considerations/Pt. Education/ Lab Data: Monitor liver function studies: AST, ALT, bilirubin, creatine before therapy if long-term therapy is anticipated. Inform the patient that toxicity may occur when used with other combination products. Pregnancy Category: B Trade Name: Flomax Generic Name: Tamsulosin Drug Classification: Alpha-1 blocker Usual Dose: 0.4 mg/day increasing to 0.8 mg/day if required after 2-4 wk Indications: symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) Side Effects: Dizziness, headache, asthenia, insomnia, chest pain, orthostatic hypotension, nausea, diarrhea, pruritus, urticaria, back pain, rhinitis, pharyngitis, cough, angioedema. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Prostatic hyperplasia; change in urinary patterns at baseline and throughout treatment, I&O ratios, weight daily; edema, report weight gain or edema. Pregnancy Category: B Trade Name: Synthroid Generic Name: Levothyroxine Sodium Drug Classification: Thyroid hormone Usual Dose: 12.5-25 mcg/day, titrate by12.5-25mcg q 6-8wk (adult >50 yr w/ heart disease) Indications: hypothyroidism, myxedema coma, thyroid hormone replacement, thyrotoxicosis, congenital hypothyroidism, some types of thyroid cancer, pituitary TSH suppression. Side Effects: Anxiety, insomnia, tremors, headache, thyroid storm, tachycardia, palpitations, angina, dysrhythmia, cardiac arrest,nausea, diarrhea, weight loss, sweating, heat intolerance, fever, decreased bone mineral density. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Pt may require decreased anticoagulant; check for bleeding, bruising. Assess cardiac status for angina, palpitation, chest pain, change in VS. Monitor for coronary insufficiency; also watch for cardiac changes in those receiving high, rapid dosing. Assess bone density baseline; bone loss may occur with long term therapy. To avoid iodine-rich food, iodine salt, soybeans, tofu, turnips, high iodine seafood, and some bread products. Pregnancy Category: A Trade Name: Zyprexa Generic Name: Olanzapine Drug Classification: Antipsychotic (typical) Usual Dose: 5-10mg/day Indications: Schizophrenia, acute manic episodes with bipolar disorder, acute agitation. Side Effects: Tachycardia, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, urinary retention, hyperlipidemia, peripheral edema. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Assess sleep pattern disturbances, mood,. Behavior, presence of hallucinations, suicidal thoughts/behaviors. Asses for slurred speech, altered gait, aggression, dizziness, weakness, hypertension, and seizures. Pregnancy Category: C Trade Name: Oxtellar XR Generic Name: OXcarbazepine Drug Classification: Anticonvulsant Usual Dose: 300 mg bid, may be increased by 600mg/day bid at at weekly intervals Indications: partial seizures, (unlabeled uses) trigeminal neuralgia, atypical panic disorder, bipolar disorder. Side Effects: confusion, fatigue, tremors, anxiety, suicidal thoughts/behaviors, hypotension, chest pain, edema, bradycardia, blurred vision, rhinitis, hypothyroidism, vomiting, abdominal pain, urinary frequency, purpura, rash, hyponatremia, angioedema. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Hyponatremia; headache, nausea, confusion, usually within the first 3 mo of treatment, but may occur ≤ 1yr, if this product is being used with other products that decrease sodium, monitor sodium levels. Note to not discontinue medication quickly after long-term use as seizures may increase. Treatment of overdose; give 0.9% NaCl (hypotensive state), atropine (bradycardia), use benzodiazepine, barbiturates for seizures. Pregnancy Category: C Trade Name: Nitrostat Generic Name: Nitroglycerin Drug Classification: Coronary vasodilator, antianginal Usual Dose: SL; take ≤ 3 tabs/15min; use 1 tab prophylactically 5-10min before activities. Indications: Chronic stable angina pectoris, prophylaxis of angina pain, HF, acute MI, controlled hypotension for surgical procedures, anal fissures. Side Effects: Headache, flushing, dizziness, postural hypotension, tachycardia, collapse, syncope, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, pallor, sweating, rash. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Chest pain/angina; orthostatic BP, pulse before & after administration. Tolerance if taken over long period. Teach; that product may cause headache; that tolerance usually develops; to use nonopioid analgesic. Pregnancy Category: C Trade Name: Consta Generic Name: RisperiDONE Drug Classification: Antipsychotic Usual Dose: 0.5mg daily BID increase by 1mg/wk Indications: Irritability associated with autism, bipolar disorder, mania, schizophrenia, (unlabeled uses) acute psychosis, agitation, ADHD, dementia, psychotic depression, Tourette’s syndrome. Side Effects: seizures, suicidal ideation, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, HF, sudden death (geriatric pt), AV block, constipation, weight gain, dysuria, renal artery occlusion, rhinitis, upper respiratory infection. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Thyroid function test, blood glucose, serum electrolyte/prolactin/lipid profile, bilirubin, creatine, weight, pregnancy test, CBC, LFT’s, AIMS assessment, baseline & periodically. Affect, orientation, LOC, reflexes, gait, coordination, sleep pattern disturbances. Serious reactions in geriatric pt; fatal pneumonia, HF, sudden death, dementia. Pregnancy Category: C Trade Name: Atrovent HFA Generic Name: Ipratropium Drug Classification:Anticholinergic, bronchodilator Usual Dose: INH 2 sprays (17mcg/spray) 3-4x/day, max 12 INH/24hr Indications: Bronchospasms, COPD, rhinorrhea (nasal spray) Side Effects: dizziness, headache, nervousness, palpitation, dry mouth, blurred vision, nasal congestion, nausea, vomiting, cramps, rash, cough, worsening of symptoms, bronchospasms. Nursing considerations/Pt. Education/Lab Data: Tolerance can be developed over long term therapy; dosage may have to be increased or changed. Note; do not exceed 12 doses within 24hr, notify health care professional if symptoms do not improve within 30 min after administration of medication or if condition worsens. Pregnancy Category: B Generic Name/Trade Name: Sulfasalazine Derivative Group of NSAIDs Classification: NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug) Salicylate Use: to relieve inflammation associated with Rheumatoid arthritis & ulcerative colitis. Drug Indication/Action: May be related to observed anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory properties. Onset: Unknown Peak: 3-12 hours Duration: Unknown Recommended Doses/ Administration: For Rheumatoid arthritis, PO: Initially 0.5-1 g/d (500mg-1000mg); maintaining dose: 2g/d in 2-3 divided doses; max: 3 g/d. Give WITH food to decrease GI irritation. Do not crush, chew or split tablets. Contraindications: In pts. hypersensitive to drug, its metabolites, sulfonamides or salicylates & in those with porphyria or intestinal & urinary obstruction. Side Effects: May cause headache, dizziness, rash, anorexia, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, dyspepsia (indigestion), oligospermia (decreased/low sperm count). Nursing Implications: ALERT: stop drug immediately & notify prescriber if patient shows signs & symptoms of hypersensitivity. Maintain adequate fluid intake to prevent crystalluria and stone formation. Obtain CBCs including differential WBC count and LFT values before starting Tx & every 2nd week during first 3 months of therapy & monthly during second 3 months. Serum sulfapyridine levels greater than 50 mcg/mL appear to be associated with an increased incidence of adverse reactions. Drug may cause urine discoloration. Patient Education: Instruct patient to take drug after eating & to space doses evenly. Advise patient, that drug may produce orange/yellow skin & urine discoloration. Teach pt. signs of adverse reactions & to report them. A sore throat, fever, pallor, purpura or jaundice may indicate serious blood disorder. Tell the patient to drink plenty of water & to swallow tablets whole without crushing or chewing. Advise patients about continuous blood/urine tests needed to monitor treatment. Generic Name/Trade Name: Oxaprozin/ Daypro Inflammatory Drug) Propionic Acid Group of NSAIDs Classification: NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti- Use: to Tx/ reduce inflammation associated with Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in adults & juveniles Onset/Peak/Duration: May take up to 1-2 weeks for anti-inflammatory effects Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 600-1200 mg/d based upon weigh; max: 1800 mg/d Contraindications: Pts. allergic to this drug, allergy to aspirin or NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen. Side Effects: May cause edema, dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, headache, tinnitus, abdominal pain, dyspepsia (indigestion), nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, GI bleeding/ perforation or ulcer. Nursing Implications: Monitor for side effects/ adverse reactions. This drug may raise the risk for heart attack or stroke. May raise the risk of severe stomach or bowel problems, like ulcers or bleeding. Patient Education: Teach patients to be aware of side effects symptoms & to report them to HCP immediately. Advise patients to inform the doctor prior to use of any heart disease or GI disease. Generic Name/Trade Name: Meloxicam/ Anjeso, Mobic Drug) Oxicam Group of NSAIDs Classification: NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Use: To relieve signs & symptoms or osteoarthritis or RA, juvenile RA, pauciarticular or polyarticular (other types of arthritis), management of moderate-severe pain, alone or in combo with non-NSAID analgesics. Drug Indication/Action: May inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, to produce anti-inflammatory, analgesic & antipyretic effects (fever). Onset/Peak/ Duration: PO: ONSET: unknown, PEAK: 2-5 Hours, DURATION: unknown/ IV: ONSET: unknown, PEAK: 8 min, DURATION: unknown. HALF LIFE= 15-26 Hours. Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: tablets 7.5-15 mg/d; max: 15 mg/d. Capsules: 5-10 mg/ Injection: 30 mg/mL. May be taken without meals. Contraindications: Pts. hypersensitive to drug & in those that have had asthma, urticaria (hives), or allergic reactions after taking Aspirin. Use cautiously in pts w/ ulcers, GI bleeding, MI or asthma, dehydration, anemia, hepatic disease, renal disease, HTN, fluid retention, HF. Pts. with diabetes or renal disease should be monitored closely as drug may increase risk for hyperkalemia. Pregnant women should not take this drug after 20 weeks. Side Effects: May cause dizziness, headache, edema, dyspepsia (indigestion), nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, eructation (excessive burping), arthralgia (joint pain), GI bleeding/ perforation Nursing Implications: NSAIDs may increase risk for bleeding/ allergic reactions, thrombotic events such as stroke or MI. Watch for GI adverse effects. Monitor for bleeding, bruising OR any and all side effects. Make sure pt. is hydrated before starting this drug. Monitor pt. analgesic response when given through IV. Monitor for fluid retention. MONITOR: potassium & LFT values. (Liver Function Test) Patient Education: Warn pt. to avoid NSAIDs @ 20 weeks pregnant or later unless instructed by HCP due to high fetal risk. Tell pt. to report any side effects or allergic reactions to aspirin or other NSAIDs BEFORE starting therapy. Instruct pt. to take drug w/ out regard to meals. Advise patient of signs to look out for GI complications like black, tarry stools, vomiting. Report for signs of Liver damage: nausea, jaundice, fatigue, Rt. upper Abd. quadrant pain. Warn pt. w/ history of asthma that drug may trigger attack. Inform pt. it may take several days to achieve consistent pain relief. Generic Name/Trade Name: Etanercept/ Enbrel, Enbrel SureClick Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Classification: Anti-Inflammatory Drug: Disease- Use: To relieve inflammation and associated pain caused by Rheumatoid Arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis. Drug Indication/Action: TNF Blocker (tumor necrosis factor- causes inflammation in body). Binds specifically to TNF & Blocks its action with cell-surface TNF receptors, reducing inflammatory & immune responses found in RA. Onset: unknown Peak: 72 hours Duration: unknown HALF-LIFE: about 5 days Recommended Doses/ Administration: For Psoriasis- SUBCUTANEOUS: 50 mg twice weekly for 3 months, then 50 mg/wk; max: 100 mg/wk./ INJECTION: 25 mg multi use vial. Contraindications: In those hypersensitive to drug or components or those receiving a live-virus vaccine. Use cautiously in patients 65 years or older & in patients with underlying diseases that predispose them to infection (diabetes, HF, or history of active or chronic infections). DON’T start drug in patients with active infection. Children should be up to date with all immunizations before the start of therapy. Side Effects: May cause injection site reaction, antibody formation, diarrhea, pharyngitis, rash, sinusitis, influenza & infection. headache, fever, dizziness, peripheral edema, mouth ulcers, abdominal pain, urticaria (hives) Nursing Implications: Monitor for signs of adverse effects. Patients with anti-TNF therapies are at increased risk for developing serious & fatal infections, monitor patients for signs of infections before & after starting therapy. Patient Education: Teach patient how to self-administer drug & how to mix correctly. Teach on injection site reactions & redness. Inform pt. about avoiding live-virus vaccine during therapy. Advise patient to report signs of pancytopenia (deficiency of all 3 blood cell components-red, white & platelets)= bruising, bleeding, persistent fever, or pallor. Stress importance of letting their other HCP’s about current anti-TNF therapy. Advise patient to stop breastfeeding when using this drug. Generic Name/Trade Name: Acetaminophen/ Tylenol Classification: Analgesic/ Antipyretic Use: Fever reducer & temporary relief of mild-moderate pain. Substitute to Aspirin when pt. does not tolerate it or it is contraindicated. Drug Indication/Action: Acts on CNS by increasing pain threshold by inhibition cyclooxygenase (inhibits creation of prostaglandins), reduces fever by direct action on hypothalamus heat regulating center w/ consequent peripheral vasodilation, sweating & dissipation of heat. Onset: 20-45 min Peak: 0.5-2 hours Duration: 3-4 hours …. Distribution: in all body fluids, crosses placenta. Elimination: 90-100% of drug excreted as urine, excreted in breast milk. Metabolized in liver. Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 325-650 mg Q4H (max 4g/day)/ IV: 1000 mg Q4-6H PRN. DO NOT crush extended release tablets. Entire pill needs to be swallowed whole. Chewable tabs need to be chewed thoroughly. Do not give with high carb meals as it will delay absorption. RECTAL: insert suppositories beyond rectal sphincter. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to acetaminophen or phenacetin, acute renal failure associated w/ doses exceeding 4000 mg/day. Pt’s. that suffer from alcoholism, malnutrition, bone marrow depression, immunosuppression. Side Effects: Rash, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis (excessive sweating), abdominal pain, diarrhea, elevation of serum transaminases (ALT, AST) & bilirubin, hepatotoxicity (liver damage), hepatic coma, acute renal failure. Nursing Implications: Check for signs of hepatotoxicity (liver damage), even w/ pts. on moderate doses, especially in individuals w/ poor nutrition who have ingested alcohol (3+ drinks daily). Patient Education: DO NOT TAKE with other meds containing Acetaminophen. DO NOT self-medicate adults more than 10 days w/o consulting a HCP. Do not use med. w/o medical direction for fever persisting longer than 3 days, fever over 103.F Generic Name/Trade Name: Morphine Sulfate/ Arymo ER, Duramorph PF II Controlled substance Classification: Opioid analgesic, SCHEDULE Use: Moderate-Severe pain relief Drug Indication/Action: Depression of the CNS; depression of pain impulses by binding with opiate receptors in the CNS Onset: PO: 30 min/ PO (extended release): 1-2 hrs/ IV: 5-10 min/ IM: 10-30 min, PR (rectal): 20-60 min Peak: PO: 1-2 hrs/ PO (extender release): 3-4 hrs/ IV: 20 min/ IM: 30-60 min, PR (rectal): 20-60 min Duration: PO: 3-5 hrs/ PO (ER): 8-24 hours/ IV: 4-5 hours/ IM: 4-5 hours/ PR (rectal): 3-7 hours 24 hours HALF-LIFE: Immediate release, 2-4 hours; extended release: 11- Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO (immediate release): 15-30 mg initially Q4H PRN/ PO (extended release): 15 mg Q8-12H PRN or 30 mg/d/ IV/ IM/ Subcut: 2-10 mg/ 70kg Q3-4H PRN Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, CNS/ Respiratory depression, status asthmaticus, increased intracranial pressure, shock, alcohol use disorder, ileus, hypovolemia, dysrhythmias, shock. CAUTION: respiratory insufficiency, seizures, renal or hepatic disorders, urinary retention, sleep apnea, older adults. Side Effects: Anorexia, dry mouth, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, fever, drowsiness, dizziness, agitation, anxiety, dysgeusia (altered sense of taste), confusion, depression, urinary retention, rash, blurred vision, miosis, weakness, flushing, euphoria, peripheral edema, paresthesia (pins & needles), diaphoresis (excessive sweating), pruritus (itchy skin), infection, back pain, insomnia, erectile dysfunction. Nursing Implications: Assess patients risk for addiction/ abuse, monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of ER or Long acting dosage or after dosage increase. Monitor for all other side effects/ allergic reactions. Monitor circulatory, respiratory, bladder & bowel function carefully. Drug may cause hypotension, urine retention, nausea, vomiting or altered LOC (level of consciousness). KEEP OPIOID ANTAGONIST (NALOXONE) & RESUSCITATION EQUIPMENT AVAILABLE Patient Education: Caution pt. or caregiver of pt. taking opioid w/ benzodiazepine, CNS depressant or alcohol & to seek immediate medical care for dizziness, light-headedness, extreme sleepiness, slowed or difficult breathing, or unresponsiveness. Counsel pt. on the importance of sticking to prescribed dosage & dosing schedule. Generic Name/Trade Name: Fentanyl/ Fentanyl citrate substance Classification: Opioid Analgesic, SCHEDULE II controlled Use: For moderate-severe pain & anesthesia induction & maintenance. Drug Indication/Action: Binds with opioid receptors in the CNS, altering perception & emotional response to pain. Onset: IV: 1-2 min/ IM 7-15 min LIFE: 3.5 HOURS Peak: IV: 3-5 min/ IM: 20-30 min Duration: IV: 30-60 min/ IM: 1-2 hours HALF- Recommended Doses/ Administration: IM/ IV: 50-100 mcg/ 30-60 min before surgery (slow IV over 1-2 min); may repeat in 1-2 hours for post op. pain. CAN ALSO BE ADMIN: intranasal, transdermal & transmucosal. Contraindications: Assess risk of drug abuse before drug is prescribed. Opioids should only be prescribed w/ benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants to pts. for whom alternative Tx options are inadequate. Side Effects: May cause drowsiness, dizziness, euphoria, headache, confusion, fatigue, weakness, hypokalemia, vomiting, nausea, constipation, rash & tolerance. Nursing Implications: BOXED WARNING: Respiratory depression or death can occur even when used as recommended & not misused. Monitor closely & frequently for any signs. Monitor for signs of addiction, abuse or misuse. Don’t stop drug abruptly, withdraw slowly & individualize gradual taper. Patient Education: Caution pt. on taking opioid w/ benzodiazepines or CNS depressants. Avoid alcohol & to seek immediate medical attention for dizziness, light-headedness, extreme sleepiness, slowed or difficult breathing or unresponsiveness. Advise patient that drug increases risk of opioid addiction, abuse & misuse & to use as prescribed. Generic Name/Trade Name: Oxycodone- Naloxone/ OxyCONTIN (oxycodone) SCHEDULE II controlled substance Classification: Opioid Analgesic, Use: To ease severe pain. Only to be used when around-the-clock (continuous) care is needed for a long time or when other pain drugs do not treat pain well enough. Drug Indication/Action: Binds with opioid receptors in the CNS, altering perception of and emotional response to pain. Onset: PO Immediate release: 10-15 min, PO Extended-release: unknown Peak: PO IR: 0.5-1 HR, PO ER: 4-5 hours Duration: PO IR: 3-6 hours, PO ER: 12 hours/ HALF-LIFE: 3-4 hours. Extended release tab: 4-5 hours, extended release capsules: 5.6 hours. Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: Oxy: 10 mg, Naloxone: 5 mg Q12H; max; Oxy 80mg, naloxone 40 mg Contraindications: Those with sleep apnea as usage causes increased risk for respiratory depression & oversedation. Use cautiously in older adults. Those with known drug abuse Side Effects: May cause abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, diarrhea, anxiety, weakness, confusion, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), orthostatic hypotension & withdrawal. Nursing Implications: Monitor patient closely for serious, life-threatening/ fatal respiratory depression. Monitor vitals closely & frequently. Monitor for signs/symptoms of abuse, misuse & addiction. Reassess pt. pain level 15-30 min after administration. Give drug before pt. has intense pain for full analgesic effect. KEEP OPIOID ANTAGONIST (NALOXONE) & RESUSCITATION EQUIPMENT READILY AVAILABLE. Patient Education: Caution pt. on taking opioid w/ benzodiazepines or CNS depressants. Avoid alcohol & to seek immediate medical attention for dizziness, light-headedness, extreme sleepiness, slowed or difficult breathing or unresponsiveness. Advise patient that drug increases risk of opioid addiction, abuse & misuse & to use as prescribed. ADALIMUMAB/HUMIRA TNF BLOCKERS Drug Indication/Action: Reduces the signs and symptoms of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA), such as joint swelling, pain, and fatigue. It is also approved for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, uveitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. ONSET: Variable Duration: unknown Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Half-life: 10-20 days RA; psoriatic arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis - 40 mg subcut every other week Crohn’s disease - 160 mg subcut on day 1 given in 1 day or split over 2 consecutive days; then 80 mg 2 weeks later (day 15), followed by a maintenance dose of 40 mg every other week starting at week 4 (day 29) Contraindications: Contraindicated in pts. with immunosuppression or active chronic or localized infection. At increased risk of hospitalization or death. Side Effects: Headache, syncope, HTN, arrythmia, abdominal pain, nausea, hematuria, leukopenia, back pain, dyspnea Nursing Implications: Give first dose under supervision of prescriber. Patient should be evaluated and treated, if necessary, for latent TB before start of adalimumab therapy. Serious infections and sepsis, including TB and invasive fungal infections, may occur. If patient develops new infection during treatment, monitor closely; if infection becomes serious, stop drug. Patient Education: Report all adverse reactions and any evidence of TB or other infection. Warn patient to seek immediate medical attention for symptoms of blood dyscrasias or infection, including fever, bruising, bleeding, and pallor. Tell patient to rotate injection sites and to avoid tender, bruised, red, or hard skin. Teach patient to dispose of used needles and syringes properly and not in the household trash or recyclables. Tell patient to refrigerate drug in its original container before use. If necessary, drug may be stored at room temperature up to maximum of 77° F (25° C) for up to 14 days, protected from light. LEFLUNOMIDE/ARAVA PYRIMIDINE SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS Drug Indication/Action: Used to relieve symptoms caused by active rheumatoid arthritis, such as inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain. This medicine works by stopping the body from producing too many of the immune cells that are responsible for the swelling and inflammation. ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: 18-19 days Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Adults: 100 mg PO loading dose every 24 hours for 3 days; then 20 mg (maximum daily dose) PO every 24 hours. Eliminating loading dose may decrease risk of adverse reactions, especially in patients at risk for hematologic or hepatic toxicity. Dose may be decreased to 10 mg daily if higher dose isn’t well tolerated. Contraindications: Contraindicated in pts. hypersensitive to the drug or have severe hepatic impairment. Not recommended for pts. with HBV or HBC infection, severe immunodeficiency, bone marrow dysplasia, severe uncontrolled infections. Contraindicated in pregnant women. Side Effects: Dizziness, headache, HTN, palpitations, blurred vision, diarrhea, abdominal pain, thrombocytopenia, dyspnea, alopecia Nursing Implications: Evaluate patient for active TB and screen for latent TB infection, check BP, and obtain blood for lab tests, including serum ALT and Hb levels, hematocrit, and WBC and platelet counts. Vaccination with live-virus vaccines isn’t recommended. Consider the long half-life of drug when contemplating giving a live-virus vaccine after stopping drug treatment. Risk of malignancy. Monitor platelet and WBC counts and Hb level or hematocrit at baseline and monthly for 6 months after starting therapy and every 6 to 8 weeks thereafter. Continue monitoring AST, ALT, and serum albumin levels monthly if treatment includes methotrexate or other potential immunosuppressants. Patient Education: Explain need for and frequency of required blood tests and monitoring. Instruct patient to use birth control during course of treatment and until it’s been determined that drug is no longer active. Warn patient to notify prescriber if signs or symptoms of pregnancy (such as late menstrual periods or breast tenderness) occur because of risk of fetal birth defects. Advise female patient to stop breastfeeding. Report all adverse reactions. ABATACEPT/ORENCIA SELECTIVE COSTIMULATION MODULATORS Drug Indication/Action: Used to treat psoriatic arthritis (condition that causes joint pain and swelling and scales on the skin) in adults. ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: IV, 13 days; subcut, 14.3 days Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Adults weighing more than 100 kg: 1 g IV over 30 minutes. Repeat 2 and 4 weeks after initial infusion and then every 4 weeks thereafter. Adults weighing 60 to 100 kg: 750 mg IV over 30 minutes. Repeat 2 and 4 weeks after initial infusion and then every 4 weeks thereafter. Adults weighing less than 60 kg: 500 mg IV over 30 minutes. Repeat 2 and 4 weeks after initial infusion and then every 4 weeks thereafter. Adults (subcut): 125 mg subcut once weekly with or without IV loading dose. For patients receiving loading dose, give single IV dose based on weight. Then give 125 mg subcut within a day, followed by 125 mg subcut once weekly. Patients transferring from IV to subcut form should receive the first subcut dose instead of the next scheduled IV dose. Contraindications: Use cautiously in patients with active infection, history of chronic infections, or underlying conditions that may predispose patient to infection; scheduled elective surgery; or COPD. Patients should be screened for viral hepatitis before starting therapy. Patients who test positive for TB should be treated before receiving drug. Side Effects: Dizziness, headache, HTN, sinusitis, nausea, diverticulitis, UTI, back pain, bronchitis, cough, cellulitis Nursing Implications: Make sure patient has been screened for TB and viral hepatitis before giving drug. Monitor pts. for infection and malignancies. If pt. develops severe infection, notify prescriber, may need to stop drug therapy. Check for worsening respiratory status in COPD patients. Patient Education: TB and viral hepatitis screening is necessary before therapy. Continue taking prescribed arthritis drugs. Avoid exposure to infections. Report signs and symptoms of infections. Avoid live-virus vaccines during and for 3 months after therapy. TOFACITINIB/XELJANZ JANUS KINASE INHIBITORS Drug Indication/Action: Used to treat moderate to severely active rheumatoid arthritis, active psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, ankylosing spondylitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis. ONSET: unknown Duration: unknown Half-life: Immediate-release, 3 hours; extended-release, 6 to 8 hours. Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: RA - Adults: 5 mg (immediate-release) PO b.i.d. Or, 11 mg (extended-release) once daily. Psoriatic arthritis - 5 mg (immediate-release) PO b.i.d. Or, 11 mg (extended-release) once daily. Active ulcerative colitis - 10 mg (immediate-release) PO b.i.d. or 22 mg (extended-release) for at least 8 weeks followed by 5 or 10 mg (immediate-release) b.i.d. or 11 or 22 mg (extended-release) once daily depending on therapeutic response. Use lowest effective dose to maintain response. Discontinue after 16 weeks of treatment with 10 mg b.i.d. (immediate-release) or 22 mg once daily (extended-release) if adequate therapeutic benefit isn’t achieved. Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Use cautiously in patients at risk for infection. Serious infections can lead to hospitalization or death. Lymphoma or other malignancies can happen. Should not receive livevirus infections. Side Effects: Headache, paresthesia, HTN, peripheral edema, diarrhea, UTI, anemia, dehydration, dyspnea, muscle or bone pain, rash Nursing Implications: Make sure the patient has been screened for TB and viral hepatitis before giving the drug. Monitor pts. for infection and malignancies. If pt. develops severe infection, notify prescriber, may need to stop drug therapy. Check for worsening respiratory status in COPD patients. Patient Education: Pts. should be tested for latent TB. Monitor pts. for thrombosis. Monitor lymphocyte count. Interrupt treatment if infection occurs. Monitor neutrophil count, platelet, and Hb level at baseline, after 4 to 8 weeks of treatment, and every 3 months thereafter. Don’t initiate therapy if lymphocyte count is less than 500/mm , ANC is less than 1,000/mm , or Hb level is less than 9 g/dL. 3 Dihydroergotamine mesylate 3 ergot derivative Action: treat the symptoms of Migraine Headache. route: intranasal spray dose: 1 spray in each nostril followed by another spray in each nostril after 15 minutes for a total of 4 spray (2.0mg) onset: 15mins duration: 2 hours half-life: 1 hour side effects: coronary artery vasospasm, transient myocardial ischemia, myocardial infraction, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation. contraindications: contraindicated in patients with known peripheral arterial disease. fetal harm in pregnant women. patient teaching: do not try to use it to prevent headache, it is to treat an active migraine headache. should no exceed dose, not use for chronic daily administration. Generic: sumatriptan brand: alsuma antimigraine agents action: Sumatriptan binds with high affinity to human cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. route: subcutaneous dose: 6mg onset: 6 minutes duration: 10 hours half-life: 2 hours side effect: hypertension, increase heart rate, myocardial, arrhythmia, serotonin syndrome contraindications: contraindicated in patients with ischemic, wolff-parkinson syndrome, history of stroke, uncontrolled hypertension patient teaching: check blood pressure before administration, find a site on the body with significant body fat, do not administered in vein Generic Name: Nalbuphine hydrochloride Classification: Opioid analgesics Drug Indication/Action: Binds with opioid receptors in the CNS, altering perception of and emotional response to pain. Drug is an agonist at kappa opioid receptors and an antagonist at mu opioid receptors. ONSET: 2-3 min Duration: 2-3 min Half-life: 3-6 hr Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: Adults: For patient weighing about 70 kg, 10 to 20 mg subcut, IM, or IV every 3 to 6 hours PRN. Maximum, 160 mg daily. Adjust dosage according to the severity of pain, physical status, and other drugs patient is receiving. Contraindications: in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components and in those with significant respiratory depression, known or suspected GI obstruction (including paralytic ileus), and acute or severe asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment. Side Effects: Dizziness, headache, sedation, vertigo, bradycardia, hypotension, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression, clamminess, and diaphoresis. Nursing Implications: Reassess pain level at least 15 and 30 minutes after parenteral administration. Carefully monitor vital signs, pain level, respiratory status, and sedation level in all patients receiving opioids, especially those receiving IV drugs, even those given postoperatively. Drug can cause life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression. Monitor patient for respiratory depression, especially within first 24 to 72 hours of the start of therapy and after dosage increase. Before starting drug, assess patient’s risk of opioid abuse, misuse, and addiction. Regularly monitor patients for development of these behaviors or conditions Patient Education: Encourage patient to report all medications being taken, including prescription and OTC medications and supplements. Counsel patient not to discontinue opioids without first discussing with prescriber the need for a gradual tapering regimen. Caution patient to immediately report signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, and decreased sex hormone levels. Explain assessment and monitoring process to patient and family. Instruct them to immediately report difficulty breathing or other signs and symptoms of a potential adverse opioid-related reaction. Caution patient who is ambulatory about getting out of bed or walking. Warn outpatient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities that require mental. Teach patient that naloxone is prescribed in conjunction with the opioid when treatment is started or renewed as a preventive measure to reduce opioid overdose and death. Ensure someone close to patient knows how to administer naloxone. Teach patient how to manage troublesome adverse effects such as constipation. Tell patient to inform prescriber if she is pregnant or plans to become pregnant. Generic Name/Trade Name: Dextroamphetamine sulfate/ Dexedrine, ProCentra, Zenzedi Amphetamines, Controlled Substance Schedule II Classification: Use: CNS Stimulant, to treat ADHD & Narcolespsy. Drug Indication/Action: Promotes release of dopamine and norepinephrine from nerve terminals in the brain and, to a lesser extent, the reuptake of catecholamines. Onset: unknown Peak: PO: 3 hours, PO: extended release: 8 hours 10-12 hours Duration: PO: 4-6 hours, PO ER: 8 hours HALF-LIFE: Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 5, 10 or 15 mg. 5 mg qd/bid; max 60 mg. Capsules, oral solutions: 5mg/5mL or tablets, 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg. Contraindications: in pts. hypersensitive or with previous reactions to sympathomimetic amines, those with hyperthyroidism, moderate to severe HTN, CV disease, glaucoma, history of drug abuse, arteriosclerosis (thickening or hardening of artery walls). Side Effects: Headache, euphoria, anorexia, abdominal pain, weight loss, growth suppression, insomnia, irritability, palpitations, blurred vision, nervousness, restlessness, tremor, chills, overstimulation, aggressive behavior, dry mouth, urticaria (hives). Nursing Implications: obtain detailed patient history, monitor patients beginning tx for ADHD aggressive behavior or hostility. BOXED WARNING: drug has high abuse potential. ALERT: monitor pt. for changes in HR or BP. Patient Education: warn patient about the miuse of amphetamines and effects of misuse. Instruct patient to immediately report chest pain, shortness of breath or fainting. warn patient of potential fatigue side effect. Inform patient to report signs & symptoms of excessive stimulation. Tell patient not to drink fruit juice at same time as oral solution. Generic Name/Trade Name: Lorazepam/ Ativan Classification: Benzodiazepines, CSS IV Use: used for sedation induction and to reduce anxiety, insomnia and seizures Drug Indication/Action: Potentiates the effects of GABA, depresses the CNS, and suppresses the spread of seizure activity. Onset: PO: 1 hr, IV: 5 min, IM: 15-30 min Peak: PO: 2 hr, IV: 60-90 min, IM: 60-90 min Duration: PO: 12-24 hours, IV: 6-8 hours, IM: 6-8 hours HALF-LIFE: 10-20 hours Recommended Doses/ Administration: 2-6 mg PO daily for anxiety, 2-4 mg PO at bedtime for insomnia. Available forms: IM: 2 mg/mL; 4mg/mL, Oral solution: 2 mg/mL; Tablets: 0.5 mg; 1 mg; 2 mg. IV: 2 mg Contraindications: in patients hypersensitive to drug or other benzodiazepines. In patients with abuse history Side Effects: tolerance, drowsiness, dizziness, hypotension, blurred vision, anterograde amnesia, memory impairment, agitation, nightmares, dependence, injection site reaction & suicial ideation. hypotension, visual disturbances, nasal congestion, abdominal discomfort, change in appetite, respiratory failure or depression. Nursing Implications: Monitor hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically in patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy. To reduce risk of withdrawal symptoms, gradually taper down drug, do not abrupt discontinue. Monitor pt. for all signs and symptoms of side effects. Patient Education: inform patient or caregiver to NOT take an benzodiazepine with an opioid, CNS depressant or alcohol & to seek immediate medical attention for dizziness, light-headedness, extreme sleepiness, slowed or difficult breathing or unresponsiveness. Caution patient about risk of abuse & misues. Armodafinil Stimulant Use: for narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder and sleep apnea Action: promotes wakefulness is unknown. Armodafinil (R-modafinil) has pharmacological properties similar to those of modafinil (a mixture of R- and Smodafinil), to the extent tested in animal and in vitro studies. Route and dose: PO, 150-250 mg/d in the morning onset: 20 minutes peak: 2 hours half-life: 13 hours Side Effects: may cause headaches, anxiety, dizziness, insomnia, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth, insomnia, back pain Contraindications: contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to modafinil or armodafinil or its inactive ingredients nursing implications: Assess for psychiatric symptoms (mania, delusions, hallucinations, suicidal ideation, aggression) periodically during therapy; may require discontinuation, Monitor BP periodically during therapy. patient teaching: take medication 20 minutes before driving or a work shift to prevent the urge of falling asleep. stop taking medications immediately if experiencing side effects and consult with a doctor Generic Name/Trade Name: Oxaprozin/ Daypro Classification: NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug) Propionic Acid Group of NSAIDs Use: reduce inflammation associated with Osteoarthritis and RA Onset/Peak/Duration: Can take up to 1-2 weeks for anti-inflammatory effects Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 600-1200 mg/d based upon weigh; max: 1800 mg/d Contraindications: Allergies ,allergy to aspirin or NSAIDs (ibuprofen) Side Effects: May cause edema, dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, headache, tinnitus, abdominal pain, dyspepsia (indigestion), N/V,, constipation, diarrhea, GI bleeding/ perforation or ulcer. Nursing Implications: Monitor for side effects/ adverse reactions. This drug may raise the risk for heart attack or stroke. Risk for GI issues, can cause ulcers or bleeding. Patient Education: Teach patients to be aware of side effects symptoms & to report them to HCP immediately. Advise patients to inform the doctor prior to use of any heart disease or GI disease. Generic Name/Trade Name: Diflunisal Classification: NSAIDs Salicylate Drug Indication/Action: A form of treatment for individuals with osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, or those experiencing mild to moderate pain. The action is not entirely known. However, it is attributed to the relation of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. ONSET: 1 hour Duration: Unknown Half-Life: 8-12 hours Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: PO: 250-500 mg bid; max: 1500 mg/d Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients taking the following medications or treatments due to drug-drug interactions: ACE inhibitors angiotensin II antagonists acetaminophen, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, indomethacin are all medications contraindicated with NSAIDS because they heighten the toxicity risk Antacids and aspirin will minimize the diflunisal level Use for perioperative pain treatment after CABG surgery Patients that have peptic ulcer disease, mild-moderate renal impairment, limited cardiac function, hypertension, and predisposition to fluid retention should be cautious upon taking diflunisal Patients that are hypersensitive to drugs and those who experience a rapid onset of asthmatic attacks, urticaria, rhinitis, or allergy reactions from aspirin or NSAIDs. Side Effects: dizziness, fatigue, headache, insomnia, tinnitus, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, GI pain, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia Nursing Implications: Fatality could occur when patients take NSAIDs as they heighten the risk of cardiovascular thrombotic occurrences such as stroke or myocardial infarction. Diflunisal is contraindicated for perioperative pain treatment after Children or teenagers that have flu-like symptoms that include fever or not, or chicken box should refrain from taking salicylates due to the risk of Reye syndrome. Patient Education: Patient should be advised of medications to terminate at the administration of diflunisal due to contraindications. Patients should be advised to completely avoid taking acetaminophen, aspirin, or over-the-counter NSAIDs as they are on diflunisal. Furthermore, they should be advised of medications to monitor when taking simultaneously with Diflunisal. Teach patient to take medication along with meals, water, or milk. Generic Name/Trade Name: Naproxen Classification: NSAIDs Use: Acute gout, Acute tendinitis, bursitis, pain, primary dysmenorrhea, Ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, RA, Juvenile arthritis Drug Indication/Action: May inhibit prostaglandin synthesis to produce anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects. Onset: 30–60 min Peak: 2–4 hr Duration: <12 hr HALF-LIFE: 12 to 17 hours. Recommended Doses/ Administration: Acute gout: 750 mg naproxen PO; then 250 mg every 8 hours until attack subsides. Acute tendinitis, bursitis, pain, primary dysmenorrhea: 550 mg naproxen sodium PO, then 550 mg PO every 12 hours or 275 mg every 6 to 8 hours. Ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, RA: 275 to 550 mg naproxen sodium PO b.i.d. Or 250 to 500 mg naproxen tablet or suspension PO b.i.d. Or 375 or 500 mg naproxen delayed-release tablet PO b.i.d. Or 750 to 1,000 mg extended-release tablets PO once daily, Juvenile arthritis: Children aged 2 and older: 10 mg/kg naproxen suspension PO daily in two divided doses. Don’t exceed 15 mg/kg/day. Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those with the syndrome of aspirinsensitive asthma, rhinitis, and nasal polyps. Side Effects: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, vertigo. edema, palpitations. visual disturbances, tinnitus, auditory disturbances. abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, epigastric pain, heartburn, nausea, occult blood loss, peptic ulceration, stomatitis, thirst. dyspnea. diaphoresis, pruritus, purpura Nursing Implications: Monitor CBC and renal and hepatic function every 4 to 6 months during long-term therapy. Monitor patients for neurologic effects (drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision), which may impair physical or mental abilities. ALERT: Watch for and immediately evaluate signs and symptoms of heart attack (chest pain, shortness of breath or trouble breathing), or stroke (weakness in one part or side of the body, slurred speech). BOXED WARNING: NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious GI adverse events, including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. Older adults are at greater risk. These events may occur at any time during therapy without warning. BOXED WARNING: NSAIDs may increase the risk of serious thrombotic events, MI, or stroke, which can be fatal. The risk may be greater with longer use or in patients with CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. Patient Education: Instruct adult not to take more than 440 mg of naproxen sodium in any 8- to 12-hour period or 660 mg of naproxen sodium in a 24-hour period. Advise patient to take drug with food or milk to minimize GI upset and to drink a full glass of water or other liquid with each dose. Tell patients taking prescription doses for arthritis that full therapeutic effect may be delayed 2 to 4 weeks. Warn patients against taking naproxen and naproxen sodium at the same time. Advise patients to seek medical attention immediately if chest pain, shortness of breath or trouble breathing, weakness in one part or side of the body, or slurred speech occurs. Teach patient signs and symptoms of GI bleeding (including blood in vomit, urine, or stool; coffee-ground vomit; and black, tarry stools) and to notify prescriber immediately if any of these occurs. Warn patient who is pregnant not to take NSAIDs at 20 weeks’ gestation or later unless instructed to do so by prescriber due to fetal risk. Trade Name: Cosentyx Generic Name: Secukinumab Drug Classification: Immunosuppressant, antiinflammatory Use: used to treat autoimmune conditions i.e. plaque psoriasis, active ankylosing spondylitis, nr-axSpA, ERA Action: reduces effects that cause inflammation Dose: A) weekly loading dose on weeks 0,1,2,3,4 and then injections every 4 weeks B) Non-loading dose, injections every 4 weeks Dosage may range between 75, 150, 300 mg prefilled SQ syringes Onset: 3 weeks Peak: 31-34 days Duration: Unk ½ Life: 27 days Contraindications: patients with high risk for infection should use caution when using this medication, avoid use with antihypertensives, live vaccines, anticonvulsant, and ACE inhibitors Side Effects: GI: in severe cases may cause inflammatory bowel disease, diarrhea Resp: difficulty breathing Integ: hives, skin rash, swelling of face, throat, mouth Neuro: dizziness, feeling faint Cardiac: chest tightness, chest pain Nursing interventions: children, adolescents (under 18 years), and 65 years of age and older should avoid use of Cosentyx. Avoid administration to active TB patients. Ensure the site is clean, rotate SQ injection site each time. Pt Teaching: Medication should be stored between 36F-46F. If pt experiences any severe allergic reaction to discontinue and seek medical attention immediately. Pregnancy Category: B Generic Name/Trade Name: Phentermine-topiramate/Qsymia Classification: Anorexiant-anticonvulsants/Sympathomimetic amines-sulfamate-substituted monosaccharides Drug Indication/Action: Phentermine: A sympathomimetic amine with pharmacologic properties similar to amphetamines. CNS effects are secondary in the purpose of suppressing one’s appetite which also stimulates hypothalamus to let out norepinephrine. ONSET: Unknown Duration: Unknown Half-Life: Phentermine, 20 hours; topiramate, 65 hours Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: PO 3.75 mg phentermine/23 mg topiramate/d for 14 d in the morning, then 7.5 mg phentermine / 46 mg topiramate/d; max: 15 mg phentermine / 92 mg topiramate/d Contraindications: Contraindicated in pts with hyperthyroidism or glaucoma, during or in the time frame of 14 days following administration of MAO inhibitors, in pts hypersensitive to drug or the parts of the drug or with indiosyncrasy to the sympathomimetic amines; Contraindicated in pts that have severe hepatic impairment or ESRD and in individuals with current suicidal ideation or history or suicidal ideations; Caution using in pts with depression and those with increased resting heart rate and those with cardiac or cerebrovascular disease, in pts at risk for progression of metabolic acidosis or kidney stones; Contraindicated throughout pregnancy and while breastfeeding Side Effects: Pharyngitis, dry mouth, constipation, headache, dizziness, dysgeusia, tachycardia, hypertension, paresthesia, insomnia, infection, suicidal ideation, hypokalemia. Nursing Implications: Ensure that patient is not pregnant or potential for childbearing prior to therapy and during monthly time periods; Doses should be decreased slowly when discontinuing usage of drug to minimize the risk of seizures, pt should be monitored closely if it’s necessary to abruptly stop; Monitor fluid loss, BP, ocular changes, potential for abuse of the drug, sustained tachycardia, resting heart rate, electrolyte, glucose, bicarbonate levels prior to and throughout treatment. Patient Education: Pt should be advised to avoid consumption of meds at night due to insomnia, pt should take medication once daily in the morning; Effective use of contraceptives must be utilized while taking these medications; use of combined oral contraceptives and use of phentermine-topiramate may lead to irregular bleeding; Report severe and persistant eye pain or vision changes, tachycardia or heart pounding/racing, mood changes, depression, prolonged diarrhea, suicidal ideation, seizure history; Teach pt to advise all healthcare providers about any medications, supplements, or vitamins that are taken with therapy; Fluid intake should be increased to prevent kidney stones, reports of severe side or back pain and blood in urine should be reported immediately in addition to changes in behavior, memory, attention, or concentration. OBILTOXAXIMAB/ANTHIM MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY USE: Used for prophylaxis or treatment of inhalational anthrax. ACTION: A monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits the protective antigen of anthrax (B. anthracis), preventing the entry of anthrax toxins (lethal factor and edema factor) into healthy cells. Drug doesn’t have direct antibacterial activity. DOSE: Adults weighing more than 40 kg: 16 mg/kg/dose IV over 90 minutes as a single dose. Adults and children weighing more than 15 to 40 kg: 24 mg/kg/dose IV over 90 minutes as a single dose. Children weighing 15 kg or less: 32 mg/kg/dose IV over 90 minutes as a single dose. SIDE EFFECTS: Dizziness, headache, fatigue, chest discomfort, vomiting, dry mouth, lymphopenia, leukopenia, extremity pain, cough, urticaria CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity. Drugs should only be used for prophylaxis when its benefit for prevention of inhalational anthrax outweighs risk of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis. Drugs should be used in combination with appropriate antibacterial drugs. Drug doesn’t prevent or treat meningitis and isn’t expected to cross the blood-brain barrier. NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Administer drug in appropriately monitored settings equipped to manage anaphylaxis. Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity (rash, urticaria, pruritus, cough, throat irritation, dysphonia, dyspnea, cyanosis, postural dizziness, chest discomfort) throughout infusion and after administration. If hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis occurs, stop infusion immediately and treat appropriately. PT TEACHING: Notify prescriber for itching, hives, rash, throat irritation, cough, dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest discomfort that occurs during or after drug administration. Determine if patient is allergic to or has contraindications for diphenhydramine, and explain that this drug will be given before infusion. Caution patients that diphenhydramine may cause sleepiness. METHYLPHENIDATE HCL/ADHANSIA XR CNS STIMULANTS USE: To control hyperactive disorder caused by ADHD, increase attention span, and control narcolepsy. ACTION: Releases nerve terminal stores of norepinephrine, promoting nerve impulse transmission. At high doses, effects are mediated by dopamine. DOSE: Adults: 20 to 30 mg (immediate-release) PO b.i.d. or t.i.d. Dosage varies; maximum dosage is 60 mg daily. Children age 6 and older: Initially, 5 mg PO b.i.d. immediate-release form before breakfast and lunch, increasing by 5 to 10 mg at weekly intervals, as needed, until an optimum daily dose of 2 mg/kg is reached, not to exceed 60 mg/day. SIDE EFFECTS: Anorexia, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, insomnia, irritability, restlessness, anxiety, confusion, depression, euphoria, hyperhidrosis, tremors, blurred vision, headache, abdominal pain, weight loss, constipation, and anemia. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the drug. Some formulations are contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, motor tics, family history or diagnosis of Tourette syndrome, or history of marked anxiety, tension, or agitation. NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Don’t use drug to prevent fatigue or treat severe depression. Before starting drug, assess for the presence of cardiac disease by performing a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam. Assess risk of abuse before prescribing. PT TEACHING: Teach how to properly administer.Avoid alcohol and caffeine during therapy. Advise patients with phenylketonuria that the chewable tablets contain phenylalanine. Alert: Inform male patients about possible risk of priapism. Seek medical attention if priapism or erection last longer than 4 hours. Watch for signs of chemical leukoderma, especially under skin patch site, and to report any skin changes to prescriber. Do not stop treatment abruptly. Avoid activities that require alertness or good psychomotor coordination until CNS effects of the drug are known. Warn patients with seizure disorder that the drug may decrease seizure threshold; notify prescriber if seizure occurs. Generic/Trade Name: Dextroamphetamine/Adderall Classification: Amphetamine (Stimulant) Use: To treat ADHD, helps control behavioral problems, stay focused on an activity and increases ability to pay attention. Mechanism of Action: block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine in the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of monoamines. Onset (IR) 20-30 mins (ER) 30 mins Peak: (IR) 1-2 hours (ER) 7 hours Duration: (IR) 4-6 hours (ER) 8-12 hours Half-life: (IR) 9-14 hours (ER) 12 hours Recommended Dose: 5mg-40mg daily Contraindication: overactive thyroid gland, manic behavior, manic depression, suicidal thoughts. psychotic disorder, aggressive behavior. Side Effects: loss of appetite, weight loss, dry mouth, upset stomach, N/V, dizziness, diarrhea, HA, nervousness, trouble sleeping Nursing Implication: watch out for high heart rate and high blood pressure, assess for insomnia and undesired weight loss, assess for manic symptoms. Patient Education: advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery on adderall, can impair judgment, talk about drug abuse, avoid alcohol while taking adderall. Notify the physician if there is numbness/tingling/wounds in fingers or toes. Notify physicians for skin color changes. Generic Name/Trade Name: Amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium/ Augmentin Antibacterials- Penicillins Classification: Use: For treating otitis media, sinusitis, respiratory, skin & urinary tract infections. Drug Indication/Action: Amoxicillin prevents bacterial cell-wall synthesis during replication & clavulanic acid increases amoxicillin’s effectiveness by inactivating beta-lactamases, which typically destroy amoxicillin. Onset: PO: unknown Peak: PO: 1-2.5 hours Duration: PO: 6-8 hours For patients w/ severe renal impairment- 7.5 hours for amox. & 4.5 hours for clavulanate. HALF-LIFE: 1-1.5 hours, Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 500-875 mg amox & 125 mg clavulanate, Q8H for at least 5 days. Extended release: 2000 mg amox & 125 mg clavulanate Q12H for at least 5 days. Contraindications: In those allergic to penicillins & those w/ a history of amox-related cholestatic jaundice or hepatic dysfunction. Use cautiously in pts. with other drug allergies (especially to cephalosporins) because of possible cross-sensitivity. Side Effects: May cause dermatitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, urticaria (hives), tooth/ tongue discoloration, superinfection, candidiasis, and CDAD (c. diff. assoc. diarrhea/ disease). Nursing Implications: Alert: Ratios of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid aren’t consistent from product to product. Therefore, formulations aren’t equivalent. For example, don’t substitute two 250-mg tablets for one 500-mg tablet or substitute one 250-mg film-coated tablet for one 250-mg chewable tablet. Monitor for side effects or complications such as C.Diff. Patient Education: Tell patient to take the entire quantity of drug exactly as prescribed, even after feeling better. Instruct patient to take drug with food to prevent GI upset. Tell patient to report all adverse reactions & to call prescriber if rash occurs (may indicate allergic reaction) Generic Name/Trade Name: Azithromycin/ Zithromax Classification: Antibacterial: Macrolides Use: For treating bacterial conjunctivitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis, PID, STI’s and skin & respiratory infections. Typically given to patients that are allergic to penicillins. Drug Indication/Action: Inhibits the steps of protein synthesis; bacteriostatic (inhibits) or bactericidal (kills) effects depending on concentration. Binds to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes which blocks the protein synthesis. Onset: PO: unknown, IV/ Ophthalmic: unknown Peak: PO: 2-5 hours, IV/ Op: unknown Duration: PO, IV & Oph: unknown HALF-LIFE: About 3 days Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 500 mg for 1 day OR 500 mg/d for 3 days (loading doses); then follow with 250 mg/d for 4 days; max: 500 mg/day Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to macrolides, hepatitis, jaundice. CAUTION: bradycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, dysrhythmias, hepatic/ renal dysfunction, diarrhea, CDAD (c.diff), hypocalcemia, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiac disease, myasthenia gracis, thyroid disorders, breastfeeding, older adults. Side Effects: fatigue, headache, somnolence, dizziness, chest pain, palpitations, eye irritation (ophthalmic administration), abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, candidiasis, vaginitis, cholestatic jaundice, photosensitivity reactions, rash, pain at injection site, angioedema (swelling under skin, similar to hives). Nursing Implications: Monitor closely for superinfection. May cause overgrowth of nonsusceptible bacteria or fungi. Monitor for C. Diff. Patient Education: Inform patient to take drug as prescribed, even after feeling better. Advise patient to avoid excessive sunlight and to wear protective clothing & use sunscreen when outside. Tell patient to report adverse reactions promptly. Teach patient of serious side effects to watch for. Tell pt. that tables & suspension can be taken with or without food but food may reduce GI upset. Generic Name/Trade Name: Ciprofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride/ Cipro/ Cetraxel (otic)/ Ciloxan (ophthalmic) Classification: Antibacterials: Fluoroquinolones (Quinolones) Use: For treating sinusitis, plague, anthrax prophylaxis, typhoid fever, STI’s, prostatis, respiratory, enteric, intraabdominal, bone/joint, urinary tract & skin infections. Drug Indication/Action: Inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase, an enzyme needed for bacterial replication. bactericidal. Onset: PO: 0.5-1 H, ER: unknown, Ophthalmic & Otic: unknown Peak: PO: 1-2 hours, ER: 1-4 hours, Ophthalmic & Otic: unknown Duration: PO: unknown, ER: unknown, Ophthalmic & Otic: unknown HALF-LIFE: PO: 4 hours; ER: 6 hours in adults with normal renal function. Ophthalmic & Otic: unknown Recommended Doses/ Administration: PO: 250 mg Q12H for 3/d; max 1.5g/d, Extended release: 500 mg/d for 3/d; max: 1g/d, IV: 200-400 mg Q12H for 7-14 days; max: 1.2 g/d, Ophthalmic: 0.3% at 1-2 drops into conjunctival sac Q2H while awake. Otic: 0.2% solution at 0.5 mg into affected ear BID for 7 days Contraindications: In patients sensitive to fluoroquinolones. Caution: renal/ hepatic dysfunction, children, stroke, neurotoxicity, RA, seizures, dysrhythmias, myasthenia gravis, diabetes, cardiovascular/ cerebrovascular disease, older adults. Side Effects: dizziness, syncope, anxiety, irritability, dry mouth, flushing, dyspepsia (upper abd. stomach pain), diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, constipation, headache, ocular irritation. pain/ulceration, restlessness, confusion, insomnia, weakness, tremor, tinnitus, tendon rupture, rash, hypersensitivity reactions, crystalluria (urine crystals), aortic aneurysm. Nursing Implications: Monitor intake & output & observe patients for signs of crystalluria. monitor for side effects. Patient Education: Tell patient to take drug as prescribed even after feeling better. Advise patient to drink plenty of fluids to reduce risk or crystalluria. Do not crush, split or chew the ER tablets. Warn patient to seek immediate medical attention for signs of aortic aneurysm. Inform HCP of any muscle weakness, confusion or serious side effects. Advise diabetes patients to monitor blood glucose. Avoid caffeine while taking drug because of the potential for increased caffeine effects. Avoid excessive sunlight or artificial UV light during drug usage. Trade Name: Ambien Generic Name: Zolpidem Drug Classification: Sedative-hypnotic Use: anxiety, short term tx of insomnia Action: inhibit GABA receptors Dose: A) Immediate release (tab/oral spray/sublingual): 5 & 10 mg B) Initial dose: Women: 5 mg q daily prior to bedtime Men: 5-10 mg orally q daily prior to bedtime C) Maintenance dose: 5-10 mg orally q daily prior to bedtime D) Maximum dose: 10 mg/day Onset: 30 min Peak: Unk ½ Life: 2.5 hr Duration: Unk Contraindications: hypersensitivity when taking other CNS medications; use caution may cause suicidal ideation, hx of drug addiction Side Effects: Musc: hyporeflexia Resp: respiratory depression Integ: clammy skin Neuro: dilated pupils Cardiac: decrease BP, Tachycardia, Nursing Implications: older patients need lower dose. supervise ambulation (dizziness), monitor s/s of OD Pt Teaching: do not stop med abruptly, take as directed. no alcohol or other CNS depressants Pregnancy Category: C GENERIC/TRADE NAME: alprazolam/Xanax DRUG CLASSIFICATION: Sedative-hypnotic USE: Used to treat anxiety and panic attacks INDICATION/ACTION: CNS depression, binds receptors in limbic system and reticular formation, increases GABA to GABA receptors; shift of chloride ions leads to less excitability and stabilizes neuronal membranes ONSET:PO unknown PEAK: PO 1-2 hr DURATION: PO unknown SIDE EFFECTS: Lethargy, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, constipation, anterograde amnesia, memory impairment, fatigue, agitation CONTRAINDICATIONS: Respiratory depression, acute alcohol intoxication, psychotic reactions, recent respiratory depressants, hypersensitivity NURSING INTERVENTIONS: Don’t withdraw drug abruptly; withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, may occur. Gradually reduce dosage. Abuse and dependence are possible. Watch for drug-seeking behavior. Monitor hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function periodically in patients receiving repeated or prolonged therapy. PT TEACHING: Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness and good coordination until effects of drug are known. Tell patient to avoid use of alcohol while taking drug. Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly because withdrawal symptoms or seizures may occur. Generic Name/Trade Name: Modafinil Classification: CNS stimulant Drug Indication/Action: Unknown. Similar to action of sympathomimetics, including amphetamines, but drug is structurally distinct from amphetamines and doesn’t alter release of dopamine or norepinephrine. ONSET: Unknown Duration: 2-4hr Half-life: 15hrs Recommended Dose Range for Adult Client and Routes: 200 mg PO daily, as a single dose in the morning. Patients with shift-work sleep disorder should take dose about 1 hour before the start of their shift. Maximum dose is 400 mg PO daily as a single dose. Contraindications: · Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to modafinil or armodafinil or its inactive ingredients. · Drug isn’t recommended in patients with a history of left ventricular hypertrophy or ischemic ECG changes, chest pain, arrhythmias, or other evidence of mitral valve prolapse linked to CNS stimulant use. · Use cautiously in patients with recent MI or unstable angina and in those with history of psychosis or mania. · Use cautiously and give reduced dosage to patients with severe hepatic impairment, with or without cirrhosis. · Use cautiously in patients taking MAO inhibitors. · Safety and effectiveness in patients with severe renal impairment haven’t been determined. · Modafinil isn’t approved for use in children. Side Effects: headache, nervousness, dizziness, drowsiness, insomnia, depression, anxiety, paresthesia, hypertonia, confusion, emotional lability, vertigo, tremor, dyskinesia, agitation. HTN, vasodilation, chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, edema. nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, gingivitis, thirst, dyspepsia, constipation, flatulence, taste perversion, decreased appetite, abdominal pain. abnormal urine. Weight loss, back or neck pain, asthma, sweating, chills. Nursing Implications: Life-threatening angioedema, SJS, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and DRESS syndrome can occur. Monitor patient for rash, dysphagia, bronchospasm, fever, and organ dysfunction. Stop drug and begin appropriate treatment. Monitor patient for emergence or exacerbation of psychiatric signs and symptoms and HTN. Patient Education: · Advise patient to stop drug and notify prescriber if rash, peeling skin, trouble swallowing or breathing, or other symptoms of allergic reaction occur. · Advise patient to notify prescriber about planned, suspected, or known pregnancy, or if she’s breastfeeding. · · Tell patient to avoid alcohol while taking drug. Warn patient to avoid activities that require alertness or good coordination until CNS effects of drug are known. Generic Name/Trade Name: eszopiclone Classification: sedatives/hypnotics, CSS IV Use: used for insomnia Drug Indication/Action: Potentiates the effects of GABA, depresses the CNS, and suppresses the spread of seizure activity. Onset: Rapid Peak: 1 hr Duration: unknown HALF-LIFE: 6 hours Recommended Doses/ Administration: adults: 1 mg PO immediately before bedtime. Increase to 2 or 3 mg as needed. Older adults and patients who are debilitated: 1 mg PO immediately before bedtime. Increase to 2 mg as needed. Maximum dose is 2 mg. Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to eszopiclone. Rarely, drug may cause angioedema and anaphylaxis that require emergency treatment and can be fatal. Don’t rechallenge patients who develop angioedema after treatment with drug. Boxed Warning: Opioid class warning: Opioids should only be prescribed with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when alternative treatment options are inadequate. Boxed Warning: Drug may cause rare but serious injury, including death, due to complex sleep behaviors, such as sleepwalking, sleep driving, and engaging in other activities while not fully awake. These behaviors can occur even at the lowest recommended dosages and after just one dose. Drug is contraindicated in patients with a history of complex sleep behavior while taking drug Side Effects: abnormal dreams, anxiety, complex sleep-related behavior, confusion, depression, dizziness, hallucinations, headache, nervousness, pain, somnolence, neuralgia. diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, unpleasant taste. Dysmenorrhea, UTI, decreased libido, gynecomastia. pruritus, rash Nursing Implications: Anaphylaxis and angioedema may occur as early as the first dose; monitor patient closely. Drug may increase risk of next-day impairment of driving and other activities that require full alertness. Recommended starting doses for all patients is 1 mg. Evaluate patient for physical and psychiatric disorders before treatment. Give drug immediately before patient goes to bed or after patient has gone to bed and has trouble falling asleep. Patient Education: Boxed Warning: Opioid class warning: Caution patient or caregiver of patient taking an opioid with a benzodiazepine, CNS depressant, or alcohol to seek immediate medical attention for dizziness, light-headedness, extreme sleepiness, slowed or difficult breathing, or unresponsiveness. Boxed Warning: Warn patient of the risk of injury or death related to complex sleep behaviors. Direct patient to stop drug and immediately inform prescriber if an episode of complex sleep behavior occurs or if patient doesn’t remember activities performed while taking drug. Caution patient not to take drug unless a full night’s sleep is possible. Tell patients to avoid activities that require mental alertness until the drug’s effects are known. Generic Name/Trade Name: cefdinir Classification: antibacterials: Cephalosporins Use: community acquired pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, pharyngitis, skin and skin-structure infections, acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, Citrobacter diversus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus agalactiae (group B), viridans streptococcus alpha, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis; gram-positive organisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Drug Indication/Action: Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, renders cell wall osmotically unstable, leads to cell death. Onset: Unknown Peak: 2-4 hours Duration: Unknown HALF-LIFE: 1.75 hours Recommended Doses/ Administration: Uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections/community-acquired pneumonia: Adults and children 13 +: PO 300 mg q12hr x 10 days or 600 mg q24hr Child 6 mo-12 yr: PO 7 mg/kg q12hr or 14 mg/kg q24hr x 10 days; Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis/acute maxillary sinusitis: Adult and child 13 yr +: PO 300mg q12hr or 600 mg q24hr x 10 days; pharyngitis/tonsillitis: Adult and child 13 yr+: PO 300 mg q12hr or 600 mgq24hr x10 days Child 6 mo-12 yr: PO 7 mg/kg q12hr x 5-10 days or 14 mg/kg q24hr x 10 days; RENAL Dose Adult/child > 13 yr: PO CCr <30 mL/min, 300 mg/day (adult); 7 mg/kg/day (child 6 mo-12 yr) Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, infants <1 month Side Effects: Headaches, dizziness, seizures, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abd. pain, rash, urticaria, dermatitis, injection site reaction Nursing Implications: Assess for infections: wound characteristics, sputum, urine, stool, WBC > 10,000/mm3, fever; obtain baseline and periodically during treatment. Assess cross-sensitivity to penicillin, other cephalosporins; hypersensitivity reaction may occur. Obtain C&S prior to treatment, may start treatment before results are received. Blood studies: AST, ALT, CBC, Hct, bilirubin, LDH, alk phos, Coombs’ test monthly if patient is on long-term therapy. Electrolytes: potassium, sodium, chloride monthly if patient is on long-term therapy Patient Education: If patient is diabetic, educate patient on the importance to check blood glucose. Instruct patient to report sore throat, bruising, bleeding, joint pain, may indicate blood dyscrasias (rare); diarrhea with mucus, blood, may indicate CDAD. Instruct patient to complete the full course of treatment and to take missed dose as soon as remembered unless close to next dose, do not double dose. Penicillin Antibiotic Action: inhibition of cell-wall synthesis dose and route: 12-24 million units/day, intramuscularly Onset: immediately Peak: 30mins half-life: 1hour Use: used to treat the symptoms of various serious bacterial infections such as strep and staph infections, meningitis, gonorrhea and syphilis Side effects includes: Hives, fast heart rate, swelling of vocal cords, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, diarrhea, fever, joint pain Contraindications: A history of a hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reaction to any penicillin Patient teaching: The patient should notify the health care provider (HCP) if fever or diarrhea develops, especially if the stool contains blood, pus, or mucus.