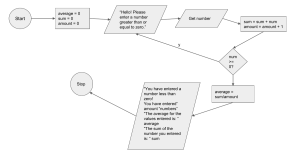
Grade 11 IB Computer Science SL Test #2 Topic 1.2 - System design basics: 1.2.1 - 1.2.3 Topic 2.1 - Computer Organisation: 2.1.1 - 2.1.5 Topic 4 - Introduction to programming: 4.3.1 - 4.3.9 Date: Monday 7 November, 2022 Name:Markscheme Computer science Standard level/Higher level Paper 1 Time allowed: 55 minutes ___________________________________________________________________ Instructions to candidates ● ● ● ● Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Section A: answer all questions. Section B: answer all questions. The maximum mark for this examination paper is [40 marks]. Section A: /34 Section B: /6 Total: /40 Section A 1. Identify two essential features of a computer language. [2] Award up to [2 max]. Fixed vocabulary; Unambiguous meaning; Consistent grammar; Consistent syntax; Provide a way to define basic data types and operations on those types (ability to write functions/procedures); Provide ability of Input and output handling; Provide some kind of loop that can be stopped / conditional statement / branching (conditional and unconditional branching); It should have variables that reference computer memory, syntax for basic arithmetic and logical; Operations on those memory locations; It has to run on/be able to be processed by a computer (ie it must have a compiler/interpreter) Note: do not accept aspects that address interoperability/portability/standards/user friendliness [2] 2. Two fundamental operations of a computer are add and retrieve. State another two fundamental operations. [2] Compare (accept Check); Store (accept Write / Save) Note: Accept the following wording for categories of operations Input (Read); Processing/execution (eg calculate, decode, fetch, delete, evaluate, sort, transfer, transmit); Output; Control; Remark: Beware of repetitions with the wording in the question paper, or repetitions between the two given examples. Marks should not be awarded twice in those cases. For example Search/look up, or comparable wording, are synonyms of the given Retrieve; Insert/put, or comparable wording, are synonyms of the given Add; Lists of repeated arithmetic operations that fall under examples of calculations (subtract, divide, multiply, square) are all examples of calculations, and hence processing. [2] 2 3. (a) State the purpose of cache memory. [1] Is used to save time in accessing RAM; [1] (b) Draw a diagram to show the relationship between random access memory (RAM), the processor and cache memory. [1] 4. Describe the function of the control unit (CU) in the central processing unit (CPU). [2] Award up to [2 max]. Obtains the data/instructions from the memory; Interprets/decodes them into commands/steps/signals; Controls transfer of data and instructions among other units of a CPU (for example, command to ALU for execution); Manages/coordinates all the units of the computer; etc. [2] 5. Describe a disadvantage of the use of virtual memory. [2] Award [1 mark] for naming the disadvantage and [1 mark] for an explanation up to [2 marks max]. Possible answers (there may be others) Performances drop; Because of the time to switch among applications; The time to search/access files on the hard disk; Access speed of secondary memory versus primary; May require more HW; Because part of the hard disk is reserved to virtual memory, hence additional storage space might be necessary; Increase power consumption; Because the overall processing time slows down; [2 marks] 3 6. Consider the following algorithm written in pseudocode: sum = 0 count = 1 num = input loop A from num = sum = end loop ("Enter an integer") 1 to 3 num + 1 sum + num output sum What will be output if num = 2? Show your working. [3] Output = 12 [1] Add 1 to the number [1] Sum the numbers [1] Loop 3 times 7. Write pseudocode to: Input the dimensions of a rectangle and print the area and perimeter. [3] output "Program to calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle" output "" a = input ("Enter the length of the rectangle") b = input ("Enter the width of the rectangle") perim = 2 * a + 2 * b area = a * b output "The perimeter is: ", perim output "The area is: ", area [1] - inputs [1] - formulas [1] - outputs 4 8. Write pseudocode using if and else to: Input 3 numbers (a, b and c), and print the largest. [5] Output “Program to find the largest of 3 numbers”) a = input ("Enter your first number") b = input ("Enter your second number") c = input ("Enter your third number") if a > b then biggest = a else biggest = b end if if c > biggest then biggest = c output "The biggest number is", c else output "The biggest number is", biggest end if [1] Input [2] if loops [1] output [1] logic correct 9. What does the following code print? [2] if 4 + 5 == 10: output ("TRUE") else: output ("FALSE") output ("TRUE") FALSE TRUE 5 10. What is the output of the following code? [2] loop X from 1 to 5 if X mod 2 = 0 then output "even" else output "odd" end if end loop odd even odd even odd 11(i) The given flowchart models the generation of some numbers in a certain range. Write the first two and the last two numbers that it generates. [4] 1, 3 36, 45 (ii) Write pseudocode that corresponds to the logic indicated by the flowchart. [3] X=1 T=1 loop until T > 50 output T X=X+1 T=T+X end loop (iii) State how to modify the given flowchart to display the number sequence 1, 4, 9, 25, 36, 49. [2] T = X ** 2 6 Section B 9. A new higher level programming language is being developed. (a) Identify two reasons why consistent grammar and syntax should be essential features of a higher level programming language. [2] a) Award up to [2 max]. Easy to learn/use; Otherwise time may be wasted learning the new language/writing programs in this HLL; There will be no/less compilation errors; There will be no/less logical errors; (Reduction of time to create software;) Future maintenance/development is possible by other programmers; [2] Application programmers who use this programming language will be able to choose to use either an interpreter or a compiler. (b) (i) Outline the need for an interpreter or a compiler. [2] Award up to [2 max]. Must be translated from a higher level language understandable by humans/not understood by machines; Must be translated into machine code; For the CPU to execute it; [2] (ii) Describe one advantage to application programmers of having both an interpreter and a compiler available. [2] Award up to [2 max]. Interpreter is faster/immediately warns about syntax errors/executes commands and they could use it instead of the compiler while coding and debugging their programs; Compiler is required when there is a need to produce an executable version of a program; [2] 7