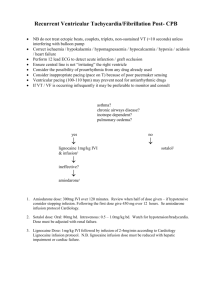
EMERGENCY DRUGS :Jocelyn Lauro, MAN, RN AMIODARONE HYDROCHORIDE AMIODARONE HYDROCHORIDE Amiodarone is intended for use only in patients with lifethreatening recurrent ventricular fibrillation or recurrent hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia unresponsive to adequate doses of other antiarrhythmics or when alternative drugs can't be tolerated Indications& Dosages PREVENTION OF RECURRENT LIFE-THREATENING VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS, SUCH AS VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR HEMODYNAMICALLY UNSTABLE VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA. IV DOSAGES: 50 MG/ML, 150 MG/100ML, 360 MG/200ML Preparation • 1 ampoule = 150 mg (3mL • LOADING DOSE : 1 ampule ( 150 mg/ 3 mL) + 12 mL D5W • A. MAINTANENCE DOSE : 360 mg in 6 hours & Computation 4. 360 mg x 3 mL = 7.2 ml 150 mg 5. 7.2 mL ( amiodarone) + 42. 8 mL D5%W = 50 mL = 8.3 mL/hr 6. 540 mg x 3 ml = 10.8 mL 150 mg 7. 10.8 mL (amiodarone) + 39.2 mL D5%W = 2.7 mL/hr Precautions • Avoid use in with Wolff- Adverse Reactions • CNS: Fatigue, Malaise, Parkinson White syndrome Tremor, Peripheral and preexcited atrial neuropathy, Ataxia, fibrillation or flutter. Paresthesia, Insomnia, Sleep • Dialyzable drug: No. disturbance, Headache, • Overdose S&S: AV block, Dizziness. bradycardia, hypotension, • CV: Hypotension, Asytole, cardiogenic shock, Atrial Fibrillation, Bradycardia, hepatotoxicity Arrhythmias, HF, Heart block, Sinus arrest, Edema, Flushing. Precautions • Avoid use in with Wolff- Adverse Reactions • EENT: Asymptomatic Parkinson White syndrome corneal microdeposits, Visual and preexcited atrial disturbance, optic fibrillation or flutter. neuropathy or neuritis • Dialyzable drug: No. resulting in visual impairment, • Overdose S&S: AV block, abnormal smell bradycardia, hypotension, cardiogenic shock, hepatotoxicity HEPARIN SODIUM HEPARIN SODIUM ia heterogeneous group of straight-chain anionic mucopolysaccharides, called glycosaminoglycans that have anticoagulant properties used to help prevent clot formation (for example, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolisms, coagulopathies and coronary artery clots). Indications& Dosages Full-dose continuous I.V infusion therapy for DVT or PE. Adults: 5,000 units subcut, every 8 to 12 hours for a minimum of 7 days or for 10 to 14 days for patients undergoing total hop arthroplasty, or hip fracture surgery according to American College of Chest Physicicans guidelines Preparation & Computation 1 ampule : 25,000 IU/ 5mL Rate of Infusion Desired dose x Quantity Drug Concentration PREPARATION Example :45 mL NSS + 25,000 (5mL) Heparin 100 units x 50 = 0.2 mL/hr 25,000 units Precautions • Dialyzable drugs: Unknown • Overdose S&S: Blood in Adverse Reactions • CNS: Fever EENT: Rhinitis Hematologic: Hemorrhage, stools or urine, excessive overly prolonged clotting bruising, persistent oozing time, thrombocytopenia, from superficial injuries, white clot syndrome. excessive menstrual Metabolic: Hyperkalemia, bleeding, melena, petechiae. hypoaldosterism • Musculoskeletal: Osteoporosis Precautions • Dialyzable drugs: Unknown • Overdose S&S: Blood in Adverse Reactions • Skin: Irritation, mild pain, hematoma, ulceration, stools or urine, excessive cutaneous or subcutaneous bruising, persistent oozing necrosis, pruritus, urticaria, from superficial injuries, transient alopecia. excessive menstrual bleeding, melena, petechiae. • Other: Hypersensitivity reactions, including chills, anaphylactic reactions reactions. CALCIUM GLUCONATE CALCIUM GLUCONATE used to treat conditions arising from calcium deficiencies such as hypocalcemic tetany, hypocalcemia related to hypoparathyroidism, and hypocalcemia due to rapid growth or pregnancy. Indications& Dosages • Calcium Gluconate should be administered intravenously either directly or by infusion. The dose is dependent upon the individual requirements of the patient. • Calcium Gluconate should be administered intravenously either directly or by infusion. The dose is dependent upon the individual requirements of the patient. Preparation & Assessment DIRECTIONS FOR DISPENSINGFROM 100 mLPHARMACYBULK PACKAGE- NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION. • The 100 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package is for use in a Pharmacy Admixture Service only • The 100 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package should be suspended (inverted) by its IV hang label in a laminar flow hood or biological safety cabinet • Prior to entering a Pharmacy Bulk Package remove the flip-off seal and cleanse the rubber closure with a suitable antiseptic agent • Entry into the Pharmacy Bulk Package must be made with a sterile transfer set or other sterile dispensing device and the contents dispensed in aliquots using aseptic technique Preparation & Assessment DIRECTIONS FOR DISPENSINGFROM 100 mLPHARMACYBULK PACKAGE- NOT FOR DIRECT INFUSION. 5. Use of a syringe needle is not recommended as it may cause leakage 6. ANY UNUSED PORTION MUST BE DISCARDED WITHIN 4 HOURS AFTER INITIAL ENTRY 7. The date and the time initially opened should be recorded in the space provided on the Pharmacy Bulk Package label. Precautions • Contraindicated in cancer Assessment • CNS: Tingling sensation, sense patients with bone metastases of oppression, or heat waves and in those with ventricular with I.V; use syncope with rapid fibrillation, hypercalcemia, I.V. use hypophosphatemia, or renal calculi. • CV: bradycardia, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest with rapid I.V. • Dialyzable drug: Yes use, mild drop in BP, • Overdose S&S: Hypercalcemia, vasodilation. confusion, delirium, stupor, coma Precautions • Contraindicated in cancer Assessment • GI: constipation, irritation, patients with bone metastases chalky taste, hemorrhage, and in those with ventricular nausea, vomiting, thirst, fibrillation, hypercalcemia, abdominal pain hypophosphatemia, or renal • GU: polyuria, renal calculi calculi. • Metabolic: hypercalcemia • Dialyzable drug: Yes • Overdose S&S: Hypercalcemia, • Skin: local reactions, including burning necrosis, tissue confusion, delirium, stupor, sloughing, cellulitis, soft-tissue coma calcifications with I.M. uses. VASOPRESSIN VASOPRESSIN a man-made form of hormone called "anti-diuretic hormone" that is normally secreted by the pituitary gland used to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and cathecholamines Indications& Dosages Vasostrict® is indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and catecholamines. Vasopressin is a polypeptide hormone that causes contraction of vascular and other smooth muscles and antidiuresis. Vasostrict is a sterile, aqueous solution of synthetic arginine vasopressin for intravenous administration Preparation & Assessment 1 ampoule = 20 units / 1mL USUAL DOSE: 0.01 to 0.03 units/minute PREPARATION: 20 units in 50mL NS DRUG CONCENTRATION: 20 units/50mL = 0.4 units/mL Rate of Infusion: Desired Dose x 60 Drug Concentration • Example: 0.01 units/min x 60 = 1.5mL/h 0.4 units / mL • • • • • Precautions Adverse Reactions • Contraindicated in patients • CNS: headache, vertigo allergic or hypersensitive to • CV: hemorrhagic shock, HF, 8-arginine vasopressin or atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, chlorobutanol. Use in patients vasoconstriction, myocardial with an impaired cardiac ischemia, decreased cardiac response may worsen cardiac output, distal limb ischemia. output. • Dialyzable drug: Unknown • Hematologic: thrombocytopenia. Precautions • Overdose S&S: Adverse Reactions • GI: mesenteric ischemia. Hyponatremia, ventricular • GU: acute renal insufficiency. arrhythmias, rhabdomyolysis, • Metabolic: hyponatremia nonspecific GI symptoms, • Skin: cutaneous gangrene peripheral, mesenteric, or coronary ischemia OPIUM TINCTURE OPIUM TINCTURE belongs to the same class of medicines as the narcotic pain relievers. However, this medicine is used to decreased the number and frequency of bowel movements. It is used to treat diarrhea. Indications & Dosages • • • • For oral dosage form (tincture): For diarrhea: Adults—0.6 milliliters (mL) four times a day Children—Use is not recommended. Preparation & Assessment • The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor's orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so • This medicine is to be taken by mouth even if it comes in a dropper bottle. The amount you should take is to be measured with the special dropper provided with your prescription and diluted with water just before you take each dose • The amount of medicine that you take depends on the strength of the medicine. Also, the number of doses you take each day, the time allowed between doses, and the length of time you take the medicine depend on the medical problem for which you are using the medicine. Precautions • Opium should be used with caution in the elderly, in debilitated individuals, and in patients with increased intracranial pressure, cerebral arteriosclerosis, hepatic cirrhosis or liver insufficiency, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, myxedema, emphysema, and bronchial asthma Adverse Reactions • Constipation • Nausea and vomiting may occur in some patients. • Pruritus • Urticaria Precautions • When preparations containing opium are administered in combination with other drugs, the cautions applicable to each ingredient should be borne in mind. • Reduced dosage is indicated in poor-risk patients, in the very young or very old patient, and in those who are receiving other central nervous system depressants Adverse Reactions • Constipation • Nausea and vomiting may occur in some patients. • Pruritus • Urticaria LIDOCAINE (XYLOCAINE) LIDOCAINE(XYLOCAINE) an over-the-counter and prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of skin irritation, premature ejaculation, and as an anesthetic intubation or urethra in urologic procedure. Xylocaine may be used alone with other medications. Indications & Dosages Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl) 2% Jelly is indicated for prevention and control of pain in procedures involving the male and female urethra, for topical treatment of painful urethritis, and as an anesthetic lubricant for endotracheal intubation (oral and nasal). For Surface AnesthesiaOf The Male&Female Adult Urethra When using Xylocaine 2% Jelly 30 mL tubes, sterilize the plastic cone for 5 minutes in boiling water, cool, and attach to the tube. The cone may be gas sterilized or cold sterilized, as preferred Preparation & Computation Example calculation - Lidocaine when administered without vasoconstriction • The total dose that can be used ⚬ The maximum dose of lidocaine (plain, without vasoconstrictor) is 4.5 mg/kg (not to exceed 300 mg) ⚬ Example patient weight - 10 kg ⚬ Total dose that can be used for this patient = 4.5 mg/kg x 10 kg = 45 mg Preparation & Computation Example calculation - Lidocaine when administered without vasoconstriction • Maximum volume of lidocaine administered ⚬ Depends on concentration (see conversion table below) ⚬ E.g. for 1% lidocaine: contains 10 mg of lidocaine per 1 mL ⚬ Max volume of 1% lidocaine that can be administered to a 10 kg patient = 45 mg / 10mg/mL = 4.5 mL Precautions Adverse Reactions • Contraindicated in patients • CNS: Confusion, tremor, hypersensitive to amide- stupor, restlessness, type local anesthetics. lightheadedness, seizures, • Contraindicated in those with lethargy, somnolence, Adams-Stokes syndrome, anxiety, hallucinations, Wolff-Parkinson-White nervousness, paresthesia, syndrome, and severe muscle twitching degrees of SA, AV, or • CV: Hypotension, intraventricular block in the bradycardia, new or absence of an artificial worsened pacemaker Precautions • Dialyzable drug: No • Overdose S&S: Circulatory Adverse Reactions • EENT: Blurred or double vision, tinnitus depression, change in level of • GI: Vomiting consciousness, seizures, • Respiratory: Respiratory hypoventilation depression and arrest • Skin: Soreness at the injection site • Other: Anaphylaxis, sensation of cold. OXYTOCIN (PITOCIN) OXYTOCIN (PITOCIN) a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of postpartum hemorrhage , labor induction, and incomplete or inevitable abortion. Pitocin may be used alone or with other medications. Indications & Dosages • Oxytocin is indicated for the initiation or improvement of uterine contractions, where this is desirable and considered suitable for reasons of fetal or maternal concern, in order to achieve vaginal delivery • To reduce postpartum bleeding after expulsion ofplacenta. Incomplete, inevitable, or elective abortion. Precautions • The standard solution for • Establish the infusion with a infusion of Pitocin is prepared separate bottle of physiologic by adding 1 mL (containing 10 electrolyte solution not units of oxytocin) to 1000 mL of containing Pitocin. 0.9% aqueous sodium chloride • Attach (piggyback) the or Ringer's lactate. The Pitocin-containing bottle with combined solution containing 10 the infusion pump to the milliunits (mU) of oxytocin/mL infusion line as close to the is rotated in the infusion bottle infusion site as possible. for thorough mixing. Administration The initial dose should be 0.5–1 mU/min (equal to 3–6 mL of the dilute oxytocin solution per hour). At 30–60 minute intervals the dose should be gradually increased in increments of 1–2 mU/min until the desired contraction pattern has been established. Once the desired frequency of contractions has been reached and labor has progressed to 5–6 cm dilation, the dose may be reduced by similar increments. • May cause antidiuretic effect Adverse Reactions • CNS: Subarachnoid MATERNAL Precautions and risk of severe water hemorrhage, seizures, coma intoxication, seizures, or • CV: arrhythmias, HTN, PVCs. death, particularly with large • GI: nausea, vomiting doses or when given by slow • GU: abruptio placentae, tetanic infusion over 24 hrs and if the uterine contractions, patient is receiving fluids by postpartum hemorrhage, mouth. uterine rupture, impaired uterine blood flow, pelvic hematoma, increased uterine motility. • Dialyzable: Unknown • Overdose S&S: Uterine hypersensitivity, tumultuous labor, uterine rupture, cervical and vaginal lacerations, postpartum hemorrhage, uteroplacental hypoperfusion, variable decleration of fetal HR. Adverse Reactions • CNS: Infant brain damage, seizures. • CV: bradycardia, arrhythmias, PVCs. • EENT: neonatal retinal hemorrhage • Hepatic: neonatal jaundice FETAL Precautions DIGOXIN (IV) DIGOXIN (IV) indicated in the management of chronic cardiac failure where the dominant problem is systolic function. The therapeutic benefit of digoxin is greater in patients with ventricular dilatation. Indications & Dosages • Each dose should be given by intravenous infusion over of 10 - 20 minutes. The total loading dose should be administered in divided doses with approximately half of the total dose given as the first dose and further fractions of the total dose given at intervals of 4 - 8 hours. Precautions • Digoxin Injection is for administration by slow intravenous infusion • The dose of digoxin for each patient has to be tailored individually according to age, lean body weight, and renal function. Suggested doses are intended only as an initial guide Administration • Parenteral loading should only be used in patients who have not been given cardiac glycosides within the preceding two weeks. • The total loading dose of parenteral digoxin is 500 to 1000 micrograms (0.5 to 1.0 mg) depending on age, lean body weight and renal Precautions Administration • Each dose should be given by • The total loading dose should be intravenous infusion over a administered in divided doses period of 10 - 20 minutes. with approximately half of the total dose given as the first dose and further fractions of the total dose given at intervals of 4 - 8 hours. • An assessment of clinical response should be performed before giving each additional dose Computation