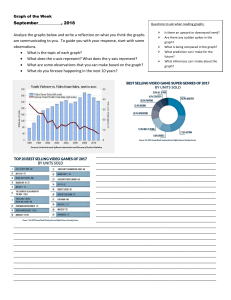
How to Analyze a Graph 1. Read the title and the axes of a graph to determine the information included. The x-axis is the line on a graph that runs horizontally (left to right), and the y-axis is the line that runs vertically (up and down). For example, in Figure 1-10, different healthcare occupations are listed along the y-axis, and projected job opportunities (in hundreds of thousands) are listed on the x-axis. Based on your interpretation of this information, how many positions did the Bureau of Labor Statistics project for medical assistants? 2. Determine the general trend of the graph. For example, if you review the growth chart graph of a 2-year-old girl, you would be able to see whether her height and weight have consistently increased over time or whether she has had a sudden increase (maybe a growth spurt) or a decrease that might reflect a recent illness. 3. Graphs can also be useful in visualizing information that doesn't seem to fit. For example, if you are responsible for measuring the length and weight of a 4-month-old infant and the measurements that you took are markedly different (either larger or smaller) than the measurements recorded at the last well-child examination, perhaps your measurements are incorrect. If you check them again and come up with the same numbers, document your results but inform the provider of the differences so the provider can investigate the changes with the baby's caregiver. Can you see how being able to use graphs can help you gain insight into patient healthcare results? image FIGURE 1-9 Projected percentage change in employment of medical assistants (2012 to 2022). Image found in Graphs and Tables Assignment FIGURE 1-10 Projected change in total employment of select health care occupations, 2006-2016. Bureau of Labor Statistics, http://www.bls.gov/spotlight/2009/health_care/home.html Accessed August 31, 2015.