Core Ch 15 Detecting the Environment (Part II)
15.2 Detecting sound by the ear
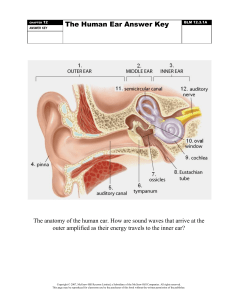
15.2.1 Structures of the ear
Structure
Functions
Pinna
Helps collect and direct sound waves into
the auditory canal
Auditory canal
Ear drum
Directs the sound waves to the ear drum
-converts the sound waves into
mechanical vibrations
-transmits the vibrations to the ear bones
in the middle ear
Ear bones
Amplify and transmit the vibrations to
oval window
Eustachian tube
Equalizes the air pressure between
middle ear and the atmosphere
Oval window
Transmits the vibrations from the ear
bones to the fluid in the inner ear
Round window
Releases the fluid pressure within the
inner ear
Cochlea
Contains sensory hair cells to detect
sound
Semicircular canals
Contains sensory hair cells to detect head
movements
15.2.2 Equalizing pressure in middle ear
(a) If the external air pressure decreases
(e.g. in an uphill tram, ascending lift/plane)
the pressure inside the middle ear becomes higher than the external air pressure
the ear drum bulges outwards and cannot vibrate freely
such hearing difficulty can be solved by yawning (opening the mouth
cavity->decreasing the pressure inside the cavity)
(b) If the external air pressure increases
(e.g. in a downhill tram, descending lift/plane)
the pressure inside the middle ear becomes lower than the external air pressure
the ear drum bulges inwards and cannot vibrate freely
such difficulty can be solved by swallowing air (increasing the pressure inside the
mouth cavity)
15.2.3 Process of hearing
1. Sound waves are collected by the pinna and directed to the ear drum through the
auditory canal
2. Sound waves cause the ear drum to vibrate at the same frequency
3. Vibrations of the ear drum are amplified and transmitted by the ear bones to the oval
window
4. Vibrations of the oval window cause the perilymph in the upper canal of the cochlea to
vibrate
5. Vibrations in the perilymph in turn cause the endolymph in the middle canal to
vibrate
6. Sensory hair cells in the middle canal are stimulated to produce nerve impulses
7. The nerve impulses are transmitted by the audiotry nerve to the cerebrum where
sensation of hearing is produced
8. Vibrations in the perilymph are transmitted to the round window which bulges
outwards to release fluid pressure inside cochlea
Sensitivity (★★★★)
1. Rods vs cones (functions, distribution)
{DSE 14 P1-10, DSE PP-P1-3, AL 04 PIIB-4(a), CE 10-5}
2. Yellow spot vs blind spot
3. Formation of image on retina and signal transduction along the optic nerve
4. Eye Defects (Glaucoma, cataract, etc)
5. Pupil reflex {CE 03-3(a)}
6. Accommodation {CE 01-2(a)}
(a) Focusing near object and distant object (the role of ciliary muscle,
suspensory ligaments, lens)
(b) Short-sightness
7. Sensation in ears {DSE 15 P1-1, AL 01-PIIA-1(a), CE 02-4(a), CE 99-4(a)}