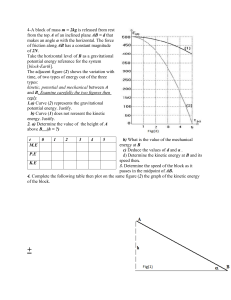
Student Name: Date: Revision 1) The position at which potential energy is defined to be zero is a . 2) Match each form of energy to its description. sum of the kinetic and potential energy of a system stored energy of an Earth-object system as a result of gravitational attraction between the object and Earth depends on an object's moment of inertia and angular velocity sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of an object's particles energy of a compressed spring or stretched rubber band rotational kinetic energy thermal energy elastic potential energy gravitational potential energy mechanical energy 3) Translational kinetic energy is best defined as the energy that results from any motion of an object. the energy due to linear motion of an object. the change in energy of an object. the ability of an object to produce change. Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 1/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 4) Match each vocabulary term to its definition. energy a unit of power defined as 1 joule per second ability of an object to produce a change in itself or its surroundings joule efficiency power watt rate at which energy is transformed the SI unit used for work compares a machine's output work to its input work 5) A 7.00 N weight is raised from the ground to 1.80 m above the ground. How much work is done on the weight? J 6) It takes an electric motor 12 s to move a 450-N load a distance of 25 m. How much power is developed by the motor? W 7) Heidi and her mother exert a total force of 8.90×102 N in moving a heavy sofa 14.0 m to another room. Her mother exerts twice as much force as Heidi exerts. How much work does each person do in moving the sofa? WHeidi = J Wmother = J 8) An adult exerts a force of 25 N to pull a child 350 m across the snow on a sled. If the rope that joins the sled is at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal, how much work is done on the sled? J 9) A shelf stocker lifts a 7.5-kg carton from the floor to a height of 0.70 m, carries it 45 m at constant speed across the store and places it on a shelf 1.5 m above the floor. How much work does the worker do on the carton? J 10) At what speed can a 120-W motor lift a 2800-N load? m/s Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 2/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 11) A mover uses a force parallel to the ramp of 720.0 N to push a 370.0-kg piano on wheels up a ramp onto a stage. The ramp is 8.00 m long, and the stage is 1.50 m above the floor. a. How much work does the mover do on the piano? J b. What is the output work of the ramp? J 12) If the external world does work on a system, the . external world becomes warmer energy of the system increases amount of work done on the system has a negative value energy of the system decreases 13) Work is done on an object when a force is exerted on the object causing the object to be displaced . in a circle perpendicular to the force in the direction of the force opposite the direction of the force 14) In which of the following situations is no work done on a book? dropping the book picking up the book pushing the book across the desk carrying the book down the hall 15) In which of the following situations is work done on a rock by a gravitational force? pushing the rock across the driveway dropping the rock picking up the rock carrying the rock across the yard 16) Which of the following items relates to power but not to work? distance time mass force Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 3/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 17) When you throw a ball into the air, mechanical energy at any point is the difference in the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy. True False 18) As an object falls towards Earth, the gravitational potential energy of the object-Earth system increases. True False 19) The total amount of energy of an isolated, closed system remains constant. True False 20) If a tabletop is used as a reference point in a mechanical-energy problem, the gravitational potential energy for an object on the floor is greater than zero. True False 21) Match each item on the left to its corresponding expression. KE GPE 1 joule result of an elastic collision 1 kg·m²/s² mgh 0.5mv² KE after = KE before 22) A 5.000-kg stone is perched near the edge of a cliff 25.00 m high. Using the base of the cliff as the reference level, the mechanical energy of the system is J. 23) Fill in the blanks using the available answer choices. A biker and her bike have a combined mass of 80.0 kg and are traveling at a speed of 3.00 m/s. If the same biker and bike travel twice as fast, their kinetic energy will by a factor of . (Blank 1) Blank 1 options increase decrease remain the same (Blank 2) Blank 2 options 1 2 4 Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 4/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 24) Arrange the following systems from greatest gravitational potential energy to least gravitational potential energy. 1) 2) 3) A flower pot-Earth system with a 350-g flower pot sitting on a 1.8-m high shelf. A flower pot-Earth system with a 620-g flower pot sitting on a 1.0-m high shelf. A flower pot-Earth system with a 550-g flower pot sitting on a 1.2-m high shelf. 25) A weight trainer lifts a 90.0-kg barbell from a stand 0.90 m high and raises it to a height of 1.75 m. What is the increase in the potential energy of the barbell-Earth system? J 26) A child having a mass of 35.0 kg is on a sled having a mass of 5.0 kg. If the child and sled traveling together have a kinetic energy of 260 J from their motion, they must be moving at a speed of m/s. 27) During a contest that involved throwing a 7.0-kg bowling ball straight up in the air, one contestant exerted a force of 810 N on the ball. If the force was exerted through a distance of 2.0 m, how high did the ball go from the point of release? m 28) A 25.0-kg shell is shot from a cannon at Earth’s surface. The reference level is Earth’s surface. a. What is the shell-Earth system’s gravitational potential energy when the shell’s height is 425 m? kJ b. What is the change in the system's potential energy when the shell falls to a height of 225 m? kJ 29) This is a file upload question and cannot be printed. Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 5/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 30) In the 1950s an experimental train with a mass of 2.50×104 kg was powered along 509 m of level track by a jet engine that produced a thrust of 5.00×105 N. Assume friction is negligible. a. Find the work done on the train by the jet engine. ×108 J b. Find the change in kinetic energy. ×108 J c. Find the final kinetic energy of the train if it started from rest. ×108 J d. Find the final speed of the train. m/s 31) Shawn and his bike have a combined mass of 45.0 kg. Shawn rides his bike 1.80 km in 10.0 min at a constant velocity. What is the system's kinetic energy? J 32) A 10.0-kg test rocket is fired vertically. When the engine stops firing, the rocket’s kinetic energy is 1960 J. After the fuel is burned, to what additional height will the rocket rise? m 33) A 36.0-kg child slides down a playground slide that is 2.5 m high, as shown in the image. At the bottom of the slide, she is moving at 3.0 m/s. How much energy was transformed by friction as she slid down the slide? J Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 6/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 34) A 98.0-N sack of grain is hoisted to a storage room 50.0 m above the ground floor of a grain elevator. a. How much work was done? J b. What is the increase in potential energy of a system containing the sack of grain and Earth? J c. The rope being used to lift the sack of grain breaks just as the sack reaches the storage room. What kinetic energy does the sack have just before it strikes the ground floor? J 35) A 20 kg rock sits on the edge of a cliff that is 100 m high, as shown in the image. a. What potential energy does the rock-Earth system possess relative to the base of the cliff? kJ b. The rock falls without rolling from the cliff. What is its kinetic energy just before it strikes the ground? kJ c. What is the rock’s speed as it hits the ground? m/s 36) During a tug-of-war, team A does 2.20×105 J of work in pulling team B 8.00 m. What average force did team A exert? N Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 7/8 Student Name: Date: Revision 37) A student librarian lifts a 2.2-kg book from the floor to a height of 1.25 m. He carries the book 8.0 m to the stacks and places the book on a shelf that is 0.35 m above the floor. How much work does he do on the book? J 38) A 17.0-kg crate is to be pulled a distance of 20.0 m, requiring 1210 J of work to be done on the crate. The job is done by attaching a rope and pulling with a force of 75.0 N. At what angle is the rope held? ° 39) A 4.2×103-N piano is wheeled up a 3.5-m ramp at a constant speed. The ramp makes an angle of 30.0° with the horizontal. Find the work done by a man wheeling the piano up the ramp. J 40) An electric motor develops 65 kW of power as it lifts a loaded elevator 17.5 m in 35 s. How much force does the motor exert? N 41) Suppose you are pushing a stalled car. As the car gets going, you need less and less force to keep it going. For the first 15 m, your force decreases at a constant rate from 210.0 N to 40.0 N. How much work did you do on the car? J 42) A mover loads a 185-kg refrigerator into a moving van by pushing it at a constant speed up a 10.0-m, friction-free ramp at an angle of inclination of 11°. How much work is done by the mover on the refrigerator? J 43) A 0.180-kg ball falls 2.5 m. How much work does the force of gravity do on the ball? J 44) A forklift raises a box 1.2 m and does 7.0 kJ of work on it. What is the mass of the box? kg 45) Mary weighs 505 N. She walks down a 5.50-m-high flight of stairs. What is the change in the potential energy of the Mary-Earth system? kJ 46) A science museum display about energy has a small engine that pulls on a rope to lift a block 1.00 m. The display indicates that 1.00 J of work is done. What is the mass of the block? kg Copyright © 2022, McGraw-Hill Education. This content was printed for the exclusive use of licensed students. 8/8