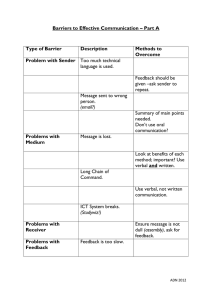
COMMUNICATION BARRIERS By Dr. Nadeem Khan Lecturer IER, University of Peshawar Semester 2nd Subject: Communication Skills • What is Communication? Communication is a process through messages evoke response. Communication is not a one way process ,rather it is two way process • Barrier: Barrier is a hurdle or hindrance • Communication Barrier: Communication Barrier is a hurdle or hindrance in the process of communication which makes the process of communication ineffective • Following are the Barriers of communication: • Psychological Barriers: The psychological state of the receiver will influence how the message is received. For example, if someone has personal worries and is stressed, they may be preoccupied by personal concerns and not as receptive to the message as if they were not stressed. Stress management is an important personal skill that affects our interpersonal relationships. Anger is another example of a psychological barrier to communication. When we are angry it is easy to say things that we may later regret and also to misinterpret what others are saying. More generally, people with low self-esteem may be less assertive and therefore may not feel comfortable while communicating - they may feel shy about saying how they really feel, or read negative subtexts into messages they hear. • Physiological Barriers Physiological barriers may result from the receiver’s physical state. For example, a receiver with reduced hearing may not grasp the entirety of a spoken conversation, especially if there is significant background noise. • Physical Barriers An example of a physical barrier to communication is geographic distance between the sender and receiver(s). Communication is generally easier over shorter distances as more communication channels are available and less technology is required. Although modern technology often serves to reduce the impact of physical barriers, the advantages and disadvantages of each communication channel should be understood so that an appropriate channel can be • Attitudinal Barriers: Attitudinal barriers are behaviors or perceptions that prevent people from communicating effectively. Attitudinal barriers to communication may result from personality conflicts, poor management, resistance to change, or a lack of motivation. Effective receivers of messages should attempt to overcome their own attitudinal barriers to facilitate effective communication. • Semantic Barriers: Semantic is the science of meaning. The same words and symbols carry different meanings to different people. Difficulties in communication arise when the sender and the receiver of the message use words or symbols in different senses. The meaning intended by the sender may be quite different from the meaning followed by the receiver. People interpret the message in terms of their own behaviour and experience. Sometimes, the language used by the sender may not at all be followed by the receiver. • Language Barriers: Communicating with people whose native language is not English can pose problems. However, it’s not the only language issue communication face. The way people speak is different from each generation, speech impediments can cause comprehension issues, and industry specific language may be difficult to understand for someone unaccustomed to it. Utilising common sense strategies such as translation services, learning the basics of the foreign language, and using multiple methods of communication such as video can overcome these language barriers. • Status Barriers (Superior-Subordinate Relationship): Status or position in the hierarchy of an organization is one of the fundamental barriers that obstructs free flow of information. A superior may give only selected information to his subordinates so as to maintain status differences. Subordinates, usually, tend to convey only those things which the superiors would appreciate. • Organizational Structure Barriers: Effective communication largely depends upon sound organizational structure. If the structure is complex involving several layers of management, the breakdown or distortion in communication wall arise. • Barriers Due to Inadequate Attention: Inadequate attention to the message makes communication less effective and the message is likely to be misunderstood. • Barriers Due to Lack of Mutual Trust: Communication means sharing of ideas in common. “When we communicate, we are trying to establish a commonness.” Thus, one will freely transfer information and understanding with another only when there is mutual trust between the two. When there is a lack of mutual trust between the communicator and the communicate, the message is not followed. Credibility gaps, i.e., inconsistency in saying and doing, also causes lack of • Cultural Barriers Modern business is conducted in a global community, whether it's the mix of staff in the workplace, or working with colleagues, suppliers, and retailers in other parts of the world. By understanding cultural sensitivities of any business stakeholder, and respecting their values and beliefs, cultural barriers can be removed from the process. Respect is the key, at times, you will have to adapt to others while other occasions people joining your organisation will have to adjust. By identifying cultural differences and developing strategies to accommodate them, you are far more likely to enjoy more exceptional communication in your business. • Gender Barriers Men and women are different, and while workplace relations between genders have improved over recent years, there are times when communications break down for one reason or another. Communication styles between genders are often different, which could cause problems between work colleagues, so it’s important to be respectful of each other. Effective communication can only be achieved between genders if everyone feels safe when offering their ideas and opinions. • Interpersonal Barriers Poor self-esteem or an inability to make connections with others can prohibit us from actually communicating with our colleagues. This challenge can lead to withdrawal from communicating effectively, keeping your opinions and ideas to yourself and removing yourself from the workplace community. And because forcing yourself to communicate with others is the best way to overcome this barrier, it can be tough to break. Taking small steps by keeping your communications simple, listening to others and staying calm, will build self-confidence over time.