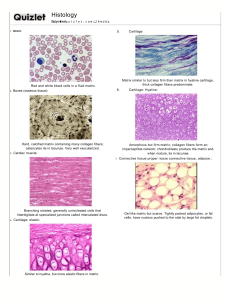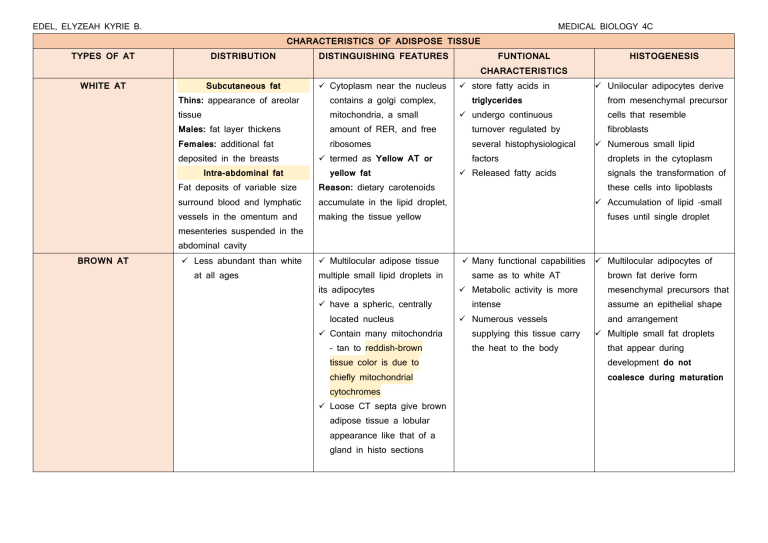
EDEL, ELYZEAH KYRIE B. MEDICAL BIOLOGY 4C CHARACTERISTICS OF ADISPOSE TISSUE TYPES OF AT DISTRIBUTION DISTINGUISHING FEATURES FUNTIONAL HISTOGENESIS CHARACTERISTICS WHITE AT Subcutaneous fat ✓ Cytoplasm near the nucleus Thins: appearance of areolar contains a golgi complex, Males: fat layer thickens Females: additional fat tissue from mesenchymal precursor amount of RER, and free turnover regulated by fibroblasts ribosomes several histophysiological mitochondria, a small ✓ termed as Yellow AT or Fat deposits of variable size Reason: dietary carotenoids surround blood and lymphatic accumulate in the lipid droplet, vessels in the omentum and making the tissue yellow mesenteries suspended in the ✓ Unilocular adipocytes derive triglycerides deposited in the breasts Intra-abdominal fat ✓ store fatty acids in yellow fat ✓ undergo continuous factors ✓ Released fatty acids cells that resemble ✓ Numerous small lipid droplets in the cytoplasm signals the transformation of these cells into lipoblasts ✓ Accumulation of lipid –small fuses until single droplet abdominal cavity BROWN AT ✓ Less abundant than white at all ages ✓ Multilocular adipose tissue multiple small lipid droplets in its adipocytes ✓ have a spheric, centrally located nucleus ✓ Contain many mitochondria – tan to reddish-brown tissue color is due to chiefly mitochondrial cytochromes ✓ Loose CT septa give brown adipose tissue a lobular appearance like that of a gland in histo sections ✓ Many functional capabilities same as to white AT ✓ Metabolic activity is more intense ✓ Numerous vessels supplying this tissue carry the heat to the body ✓ Multilocular adipocytes of brown fat derive form mesenchymal precursors that assume an epithelial shape and arrangement ✓ Multiple small fat droplets that appear during development do not coalesce during maturation EDEL, ELYZEAH KYRIE B. MEDICAL BIOLOGY 4C CHARACTERISTICS OF CARTILAGE TYPES TYPES OF CARTILAGE HYALIN CARTILAGE CELL TYPE Chondrocytes FIBER TYPE ✓ Matrix contains thin fibril of type II collagen ✓ Their small size and their refractive index make them difficult to distinguish with the LM GROUND SUBSTANCE ✓ GAG’s – mostly chondroitin sulfates and hyaluronic acid ✓ Proteoglycan ✓ Proteoglycan aggregates – covalently linked to long chains of hyaluronic acid by link proteins ORGANIZATION FUNCTIONS ✓ Consistency of Ability to grow The coastal results from maintaining its most of the hyaline cartilage extensive cross- linking among its components ✓ Matrix immediately surrounding the rapidly while rigidity makes hyaline cartilage an ideal fetal tissue chondrocytes chondroblasts and chondrocytes sheath is called mass both elastin and collagen rings supporting the trachea, HC protein perichondrium. cartilaginous the bronchi are Perichondrium composition from cartilages, the in the walls of chondroitin sulfate, and the fibrous laryngeal cartilage plates ✓ Glycoprotein wavy bundles of fibrils that differ in (rib) cartilages, and irregular ✓ Tissue fluid ELASTIC CARTILAGE LOCATION surrounds the elastic provides flexible support found in the auricle of the external ear, walls of the external auditory canals and auditory tubes, epiglottis, and the corniculate and cuneiform cartilages of the larynx EDEL, ELYZEAH KYRIE B. FIBROCARTILAGE MEDICAL BIOLOGY 4C Fibrochondrocytes Matrix immediately surrounding the chondrocytes resembles that of HC and contains some type II collagen collagen fibres (Type I collagen) contains equal amounts of dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate No distinguishable perichondrium important in Sites in bone and providing the annulus attaching bone to restricted mobility humans include fibrosus of the intervertebral disks, the symphisis pubis, and certain boneligament junctions EDEL, ELYZEAH KYRIE B. MEDICAL BIOLOGY 4C CHARACTERISTICS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE TISSUE TYPE Loose collagenous CT (areolar) CELLS Fibroblasts, Consist of loose mast cells, and types of fibers macrophages, some white blood cell Dense collagenous CT (CT proper) FIBERS network of different GROUND SUBSTANCE moderately viscous ORGANIZATION disorganize Fixed – many FUNCTIONS Conveys oxygen muscle fibers avascular epithelia CT sheaths and nutrients to and their dense Wandering – suspended predominantly Collagen fibers – identical to areolar its extracellular matrix Covering fragile in tendons, (fibrocytes) component abundant strands and protecting periosteum, fibroblast predominant tissue but less is organized into loose tissues and organs them from multidirectional mechanical process Reticular CT LOCATIONS reticular cells type III collagen fibrils ligaments, perichondrium, deep fascia and some organ capsules Supports motile hematopoietic body fluids marrow, spleen cells and filters tissues: bone and lymph nodes Elastic CT sparse and similar to provides flexible non-load- CT predominates in parts such as that of other dense support and the ligamenta flava of the vertebral column and the suspensatory ligaments of the penis bearing body the nose, ears and epiglottis. Lungs and arteries, dermis layer, EDEL, ELYZEAH KYRIE B. MEDICAL BIOLOGY 4C ligaments and tendons. Mucous CT primitive fibroblast Large stellate, fibroblasts with branching and anastomosed cytoplasmic processes. Wharton's jelly secretion of ground substance, fibers. umbilical cord