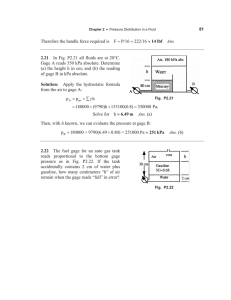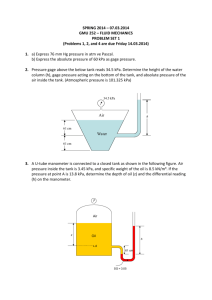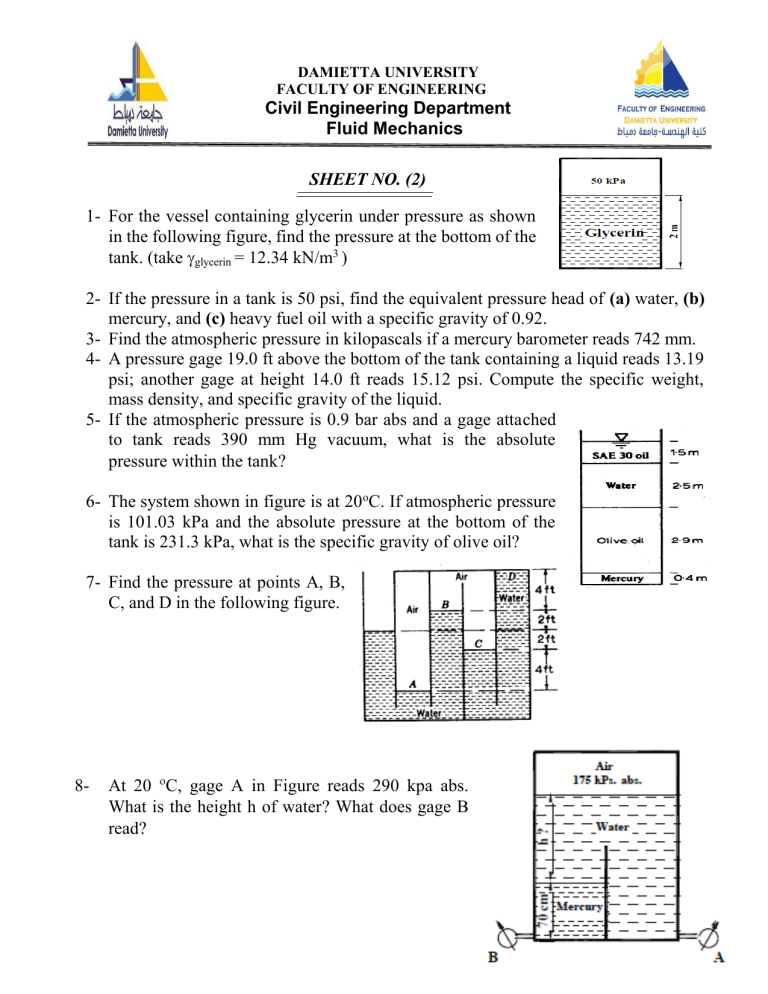
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics SHEET NO. (2) 1- For the vessel containing glycerin under pressure as shown in the following figure, find the pressure at the bottom of the tank. (take glycerin = 12.34 kN/m3 ) 2- If the pressure in a tank is 50 psi, find the equivalent pressure head of (a) water, (b) mercury, and (c) heavy fuel oil with a specific gravity of 0.92. 3- Find the atmospheric pressure in kilopascals if a mercury barometer reads 742 mm. 4- A pressure gage 19.0 ft above the bottom of the tank containing a liquid reads 13.19 psi; another gage at height 14.0 ft reads 15.12 psi. Compute the specific weight, mass density, and specific gravity of the liquid. 5- If the atmospheric pressure is 0.9 bar abs and a gage attached to tank reads 390 mm Hg vacuum, what is the absolute pressure within the tank 6- The system shown in figure is at 20 oC. If atmospheric pressure is 101.03 kPa and the absolute pressure at the bottom of the tank is 231.3 kPa, what is the specific gravity of olive oil? 7- Find the pressure at points A, B, C, and D in the following figure. 8- At 20 C, gage A in Figure reads 290 kpa abs. What is the height h of water What does gage B read 9- Pressure gage B, In the figure is to measure the pressure at point A in a water flow. If the pressure at B is 87kPa, estimate the pressure at A, in kPa. Assume all fluids are at 20°C. (The specific weight for water = 9810 N/m3, for mercury =133700 N/m3 , for oil = 8720 N/m3 ) 10- In the following figure the tank contains water and immiscible oil at 20°C. What is h in centimeters if the density of the oil is 898 kg/m3. For water take the density =998 kg/m3.? 11- In the following figure the 20oC water and gasoline are open to the atmosphere and are at the same elevation. What is the height h in the third liquid? Take specific weight of water = 9810 N/m3 and specific weight of gasoline = 6670 N/m3. 12- A mercury manometer is connected at two points to a horizontal 20°C water pipe flow, as shown in figure. If the manometer reading is h =35 cm, what is the pressure drop between the two points? (γw = 9810N/m3,γmercury= 133700N/m3 ) 13- Water flows upward in a pipe slanted at 30°, as in Figure (6). The mercury manometer reads h = 12 cm. What is the pressure difference between points (1) and (2) in the pipe? (γw = 9810 N/m3 , γmercury= 133700 N/m3 ) 14- In the following figure all fluids are at 20oC. Gage A reads 350 kPa absolute. Determine (a) the height h in cm; and (b) the reading of gage B in kPa absolute. 15- A gasoline line is connected to a pressure gage through a double-U manometer, as shown in Figure. If the reading of the pressure gage is 370 kPa, determine the gage pressure of the gasoline line. 16- A hydraulic lift is to be used to lift a 2500 kg weight by putting a weight of 25 kg on a piston with a diameter of 10 cm. Determine the diameter of the piston on which the weight is to be placed. 17- A tank holding water has a triangular gate, hinged at the top, in one wall. Find the moment at the hinge required to keep this triangular gate closed. 18- Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force of water on the gate shown in the figure. 19- The dam in figure is a quarter-circle 50 m wide into the paper. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of hydrostatic force against the dam and the point CP where the resultant strikes the dam. 20- Find the position and magnitude of the resultant force on a vertical wall of a tank which has oil of relative density 0.8 floating on water as shown in figure 21- A 1.5 long cylinder, radius 1m lies as shown in the figure, holds back oil of relative density 0.8. If the cylinder has a mass of 2250 kg, find: a) the reaction at A b) The reaction at B . 23- Gate AB in figure is 1.0 m long and 0.9 m wide. Calculate force F on the gate and the position X of its center of pressure. 24- Gate AB in figure, hinged at B. What horizontal force P required at A for equilibrium? 25- Find the net hydrostatic force per unit width on rectangular panel AB in figure and determine its line of action.