Autism Spectrum Disorder: Overview
advertisement

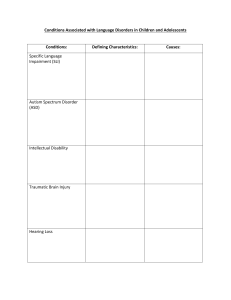
Group-2 Aomong-200310703 Kisuiyile2003107011 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Levels 3. Causes 4. Signs and symptoms 5. Treatments. ● DSM-5 classified autism as a neurodevelopmental disorder. ○ ○ ○ ● ● ● Difficulty with communication and interaction with other people Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors Symptoms that hurt the person’s ability to function properly in school, work, and other areas of life Some autistic people also have intellectual disabilities, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and/or learning difficulties. Others have mental health issues, mostly commonly anxiety and depression. Across the CDC surveillance sites, an average of 1 in every 44 (2.3%) 8-year-old children were estimated to have ASD in 2018. ASD is 4.2 times as prevalent among boys (3.7%) as among girls (0.9%). Level of Autism DSM IV 1. DSM IV is the fourth version of diagnostic statistical manual of mental disorders, 2. Criteria includes stereotyped repetitive motor movements, ritualized patterns or non-verbal movements, insistence on sameness, and hyper or hypo activity. 3. DSM IV autism appear at early development DSM V 1. DSM V is the fifth version of diagnostic statistical manual of autism disorders. 2. criteria include encompassing preoccupation, apparent inflexible adherence, repetitive motor movements, and persistent preoccupation. 3. DSM V autism appear prior to age 3 in humans Signs and Symptoms of ASD Interventions and Treatments Goal of treatment - to maximize the child's ability to function by reducing autism spectrum disorder symptoms and supporting development and learning. Approaches to help people with Autism Spectrum Disorder: 1. Behavioral Approach: widely accepted among educators and healthcare professionals. ● Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). ● Two ABA teaching styles are Discrete Trial Training (DTT); step-by-step instructions ● Pivotal Response Training (PRT); natural setting;to improve a few “pivotal skills” 2. Developmental Approaches: focus on improving specific developmental skills. ● ● ● ● ● Speech and Language Therapy. Occupational Therapy. Sensory Integration Therapy. Physical Therapy. The Early Start Denver Model (ESDM):used with children 12-48 months of age. 3. Educational Approach: given in a classroom setting. ● Treatment and Education of Autistic and Related Communication-Handicapped Children (TEACCH) approach. 3. Social-Relational Approaches:focus on improving social skills and building emotional bonds. ● Floor time: It is centered on building relationships with your autistic child by getting down on the floor with them and playing. ● The Relationship Development Intervention (RDI). ● Social Stories. ● Social Skills Groups. 4. Pharmacological Approaches: treat co-occurring symptoms. 5. Psychological Approaches: can help people with ASD cope with anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. 6. Family therapies: Parents and family plays an important role. Conclusion ● Characterised by difficulties with the social aspects of communication, and repetitive and restricted interests and behaviours ● commonly also have language difficulties,. ● DSM–5 now lists three different levels of ASD according to the amount of support an individual requires. ● Numerous therapies and behavioral interventions can help improve the specific challenges that autistic people face. ● Treatment is likely to be most effective when it is individualized ● it is therefore important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the child’s developmental status. ● Additional services can help improve health and daily functioning, and facilitate social and community engagement. For eg; vocational training, job coaching, and interventions to improve social and behavioral adjustment are crucial to support independence in living and working in community settings. References ● https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/autism-spectrum-disorders-asd ● https://uihc.org/childrens/health-topics/interventions-autism-spectrumdisorders-asd ● https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/autism-spectrumdisorder/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352934 ● https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/treatment.html ● https://www.altogetherautism.org.nz/strengths-and-abilities-in-autism/ ● https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/autism-spectrumdisorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20352928