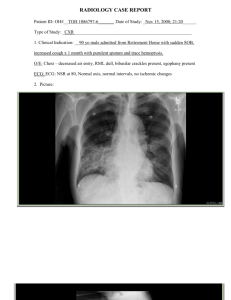
Assignment: Case Study 30 H.K’.s sister has brought her 71 year-old brother to the primary care clinic because he has had a fever for 2 days. She says he has chills and a productive cough and he cannot lie down to sleep because “he can’t stop coughing.” After H.K. is examined, he is diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and admitted to your floor at 1130. The resident is bussy and asks you to complete your routine admission assessment and call her with your finding. 1. Name 4 priority areas to include in your assessment. ○ Check for airway patency ○ Ascultate lung sound ○ Check oxygen saturation ○ Obtain other vital signs such as blood pressure, temperature, heart rate and asses his pain Your assessment findings are as follow: H.K.’s vital signs are 154/82, 105, 32, 103 degree fahrenheit , Spo2 84% on room air. You auscultate decreased breath sounds and coarse crackles in the left lower lobe anteriorly and posteriorly. His nail beds are dusky on fingers and toes. He has cough productive of rust colored sputum and complains of pain in the left side of his chest when he coughs. He is lifetime nonsmoker, his medical history includes coronay artery disease and myocardial infarction with a stent. He is currently on metoprolol, amlodipine, lisinopril, and furosemide; for his type 2 diabetes mellitus, he is taking metforming and glipizide. He has never gotten a pneumococcal or flu vaccination. He does not report getting hived when he took an anitibotic pill a few years ago but does not remember the name of the antibiotic 2. Which assessment findings are significant? Give your rationale ● Spo2 of 84% is significant because it indicates low oxygen level and when there is not enough oxygen in the body, it will cause damage to the individual organs especially the heart and brain and this can be fatal ● Decrease in breath sounds and crackles in the lungs is abnormal because it is indicating the collapsed of the alveoli and this condition will greatly disrupt the gas exchange leading to low oxygen ● The respiration is high, blood pressure is high, and dusky nails beds indicates abnormality; these condition are sign of low oxygen ● The body temperature is high (fever) and this indicate infection ● The patient’s medical history such as heart disease and diabetes puts him at a higher risk for infection Admission orders ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ Consistent carbohydrate diet VS q2hr IV D5 ½ NS at 125 ml/hr Ceftriaxone 1 gram every 12 hours albuterol 2.5mg/ ipratropium 250 mcg nebulizer Titrate oxygen to maintain Spo2 over 90% Obtain sputum for C&S STAT blood cultures & sensitivity Blood glucose ac and hs with sliding scale regular insulin per protocol #2 CBC with differential and basic metabolic panel CXR now and in the morning Continue home medication 3. You obtain order from the resident. Outline a plan of what you need to do in the next 2 to 3 hours. ○ Obtain first set of vital sign (5 minutes) ○ administer the 2.5 ml albuterol first and the ipratropium 250 mcg nebulizer treatment to stabilize the patient’s breathing (15 minutes) ○ titrate oxygen to bring the Spo2 back up (10 minutes) ○ Collect blood for blood culture & sensitivity test, CBC, sputum for C&S and get sent to the lab immediately (25) ○ Prepare patient for CXR (30 minutes) ○ initiate IV access to administer 1 gram of Ceftriaxone every 12 hours and D5 ½ NS at 125ml/hr (20 minutes) ○ Check blood sugar before meal (3 minutes) ○ Administer home medication if is due (15 minutes) ○ Consistent carbohydrate diet and set up the meals (15 minutes) ○ Get another set of vital sign (vital signs is taken every 2 hours) 4. Is D5 ½ NS an appropriate IV fluid for H.K? State your rationale ○ Fluid replacement is necessary for this patient because he has a fever, fast breathing, and inflammation of the lungs can cause him to lose a lot of fluid. This IV is the the appropriate tonicity for the patient because the patient has an elevated blood pressure so giving an isotonic solution might make it worse. 5. What is the rationale for ordering oxygen to maintain Spo2 over 90%? ● This patient is having issue with the gas exchange due to the inflammation of the lung tissue caused by pneumonia. Therefore, a supplemental oxygen is needed to bring his oxygen level up and maintain it over 90%. Having enough oxygen is very important because the tissue in each organ requires oxygen to function and if the tissues do not get enough oxygen, they will start to get damaged and eventually die if not intervened immediately. 6. What is the role of C&S test, and what role will blood and sputum cultures play in H.K.’s care? ● They all play in identifying specific organim that cause the infection. Once the right patoghens have been identified, an appropriate drugs will be prescribed which will specifically target the pathogens cause pneumonia in H.K 7. What would you expect the CXR results to reveal? ● It will reveal white spot on the affected lungs 8. Steps to obtain peripheral blood cultures 1. Verify patient’s identity and perform hand hygiene 2. Select venpuncture site. Clease and allow to dry 3. Peform venipuncture and collect 20 ml of venous blood return 4. Inject 10 ml of blood into the anaerobic bottle 5. Inject 10 ml of blood into the aerobic bottle 6. Attach identification to specimen and send to lab within 30 minutes 9. The pharmacy sends the ceftriaxone in 100 ml 0.9% NaCl with instructions to infuse over 40 minutes. At how many ml per hour will you regulate the IV infusion pump? ● 150 ml/h 10. How will you ensure H.K.’s home medication list is accurate? ● Ask if has a list of medication with him; use that to check for accuracy ● Ask the patient types of medication he is on ● Call his pharmacy and primary care doctor’s office to obtain his current medication upon his consent Case Study Progress The next morning you are again assigned to care for H.K. Your assessment finding are as follows : VS 154/82, 92, 26, 100 degree F, Spo2 94% on 2 L O2 per nasal cannula. He appears to be in no apparent distress and denies any dyspnea. You asucultate decreased breath sounds and coarse crackles in the left and complains of pain the left side of his chest when he coughs 11. Is H.K. recovering as expected? Explain you rational ● Yes. His oxygen is stable, his fever, respiration and heart rate have reduced. He denies of any dyspnea. 12. Outcome achieved by end of the shift and intervention: ● Outcome: Patient verbalizes releive of pain at level less than 3 and less discomfort caused by the infection ● Interventions: ○ Provide comfort measure through back rub, massage, repositioning, calm environment ○ Encourge to increase fluid intake to help with the dry mouth and thinning the mucous ○ Encourge patient to inform the pain soon before it becomes sever to ensure that pain medication can be given at appropriate time ○ Provide oral hygiene ○ Provide hard candy to suck on for dry mouth ○ Limit physical activity that make the breathing harder 13. Bye the end of the shift, which assessment finding would best indicate that H.K. is responding to the therapy? ● The correct option is A (cough productivity of yellow sputum; lung sounds clear; Spo2 96% on room air 14. Describe 4 strategis for preventing CAP infections including in H.K.’s discharge teaching plan ● Get pneumococcal vaccine and the yearly flu vaccine ● Washing hands regularly ● Avoid crowd and people who have cold or flu ● Practice healthy lifestyle such as eating and drinking healthy, get enough rest, moderate excersice daily 15. H.K. confides in you, “you know, my wife dies a year ago, and I live alone now. I’ve have thinking… this pneumonia stuff has been a little scary.” How will you respond? ● Listen and acknowledge his feelings. Encourage him to freely express his thought and feeling about things that are bothering him. 16. What are some communit resource from which H.K. Many benefit? ● Local senior center ● Local public library ● Community care service program ● Aging resource connection