Nursing Care Plan: Cardiac Output, Perfusion, Fluid, Infection
advertisement

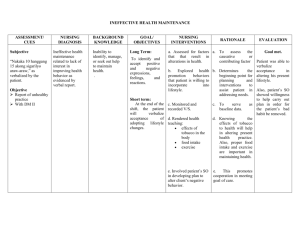
V. NURSING MANAGEMENT NURSING CARE PLAN Cardiac Output, decreased r/t altered stroke volume 36 CUES S: Ø O: Variation s in blood pressure , edema, shortnes s of breath. NURSING DIAGNOSI S SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATIO N Cardiac Output, decreased r/t altered stroke volume Increased blood pressure Vasospasm Increased vascular resistance PLANNING After 8 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize knowledge of the disease process, individual risk factors and treatment regimen. NURSING INTERVENTION >Monitor and record BP and pulse. Difficulty of the heart to pump blood Increased cardiac workload Decreased cardiac output > Institute bedrest with client in lateral position. RATIONALE > The client with PIH does not manifest the normal cardiovascular response to pregnancy (left ventricular hypertrophy, increase in plasma volume,). Hypertension (the second manifestation of PIH after edema) occurs EXPECTED OUTCOME After 8 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize knowledge of the disease process, individual risk factors and treatment regimen . to increased sensitization to angiotensin II, which increases BP, promotes aldosterone release to increase sodium/water reabsorption from the renal tubules, and constricts blood vessels. 37 > Increases Ineffective Tissue Perfusion r/t impaired transport of oxygen CUES S: Ø O: Altered blood pressure outside of acceptable parameter s. NURSING DIAGNOSI S SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATIO N Ineffective Tissue Perfusion r/t impaired transport of oxygen increased blood pressure vasospasm vasoconstricti on intravascular fluid redistribution decreased oxygen to different organs PLANNING Short Term: After 8 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize understanding of condition, therapy regimen, side effects of medications, and when to contact a health care provider. Long Term: After a week of nursing interventions, client will able to demonstrate behaviors/lifestyl e changes to improve circulation such as relaxation techniques, and NURSING INTERVENTION >Evaluate vital signs, noting changes in BP, heart rate, and respiration. >Identify changes related to systemic and/or peripheral alterations in circulation (e.g. vital sign changes) >Determine duration of problem/frequenc y of recurrence, precipitating factors. RATIONALE >Vital signs will determine if there are changes in the health status of the pt. >Alterations in systemic or peripheral circulation can be assessed primarily with vital sign >This will help determine if there is improvement in the EXPECTED OUTCOME Short Term: After 10 hours of nursing interventions, client shall verbalize understanding of condition, therapy regimen, side effects of medications, and when to contact a health care provider. Long Term: After a week of nursing interventions, client will demonstrate behaviors/lifestyl e changes to improve circulation such as relaxation techniques, and 38 exercise/dietary program. impaired tissue perfusion to ongans patients condition >Encourage quite, restful atmosphere. >Caution client to avoid activities that increase cardiac work load (e.g. straining at stool). >Instruct the pt. to take her prescribed medications (e.g. antihypertensive agents) >Discuss individual risk factors (e.g. family history, age) exercise/dietary program >This will promote rest and help in the proper distribution of oxygen in the body >To conserve energy/lower s tissue oxygen demand. >Proper medication will help the pt. condition >To prevent onset of complication s/ manage symptoms 39 when condition is present. >Instruct in blood pressure monitoring at home. >lifestyle changes (e.g. to much work) >Encourage use of relaxation techniques. >Review specific dietary >To facilitate management of hypertension . >Lifestyles of people have a very large effect to the pt. condition. Modification of it will help improve the pt. condition >To decrease tension level >Diet modification will help in 40 changes/restrictio ns with the client (e.g. reduction of cholesterol and triglyceride, high or low protein intake) improving the pt.’s condition Fluid Volume deficit [isotonic] related to: Plasma protein loss CUES S: Ø O: Edema formation, sudden weight gain, headaches, NURSING DIAGNOSIS Fluid Volume deficit [isotonic] r/t Plasma protein loss, SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATIO N Pregnancy induced hypertension Decreased vascular perfusion Increased ECF PLANNING Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize understandin g of need for close monitoring of weight, BP, urine protein, and edema. NURSING INTERVENTION > Weigh client routinely. Encourage client to monitor weight at home between visits. RATIONALE > Sudden, significant weight gain (e.g., more than 3.3 lb (1.5 kg)/month in the second trimester or more than 1 lb (0.5 kg)/wk in the third trimester) EXPECTED OUTCOME Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize understanding of need for close monitoring of weight, BP, urine protein, and edema. . 41 EDEMA Decreased water absorption to cells maintaining some sodium inside Cell or tissue dehydration Fluid volume deficit (isotonic) . Long Term: After a week of nursing interventions, client will able to be free of signs of edema. > Distinguish between physiological and pathological severe, edema of pregnancy. Monitor location and 3+ to 4+) of face, hands, legs, sacral area, or abdodegree of pitting. > Note signs of progressive or excessive edema Assess for possible eclampsia. > Reassess reflects fluid retention. Fluid moves from the vascular to interstitial > space, resulting in edema. Long Term: After a week of nursing interventions, client will able to be free of signs of edema. > The presence of pitting edema (mild, 1+ to 2+;3+ to 4+) of face, hands, legs, sacral area, or abdominal wall, or edema that does not disappear after 12 hr of bedrest is significant. >monitor Cerebral edema, possibly leading to seizures 42 dietary intake of proteins and calories. Provide information as needed. > Monitor intake and output. Note urine color And measure specific gravity as indicated. > Test clean, > Adequate nutrition reduces incidence of prenatal hypovolemia and hypoperfusion ; inadequate protein/calorie s increases the risk of edema formation and PIH. Intake of 80–100 g of protein may be required daily to replace losses > Urine output is a sensitive indicator of circulatory blood volume. Oliguria and specific gravity of 43 voided urine for protein each visit, daily/hourly as appropriate if hospitalized. Report readings of 2+, or greater. > Assess lung sounds and 1.040 indicate severe hypovolemia and kidney involvement > Aids in determining degree of severity/ progression of condition. A 2+ reading suggests glomerular edema or spasm. Proteinuria affects fluid shifts from the vascular tree. Note: Urine contaminated by vaginal secretions may test positive for protein, or dilution may result in a false-negative result. In 44 respiratory rate/effort. addition, PIH may be present without significant proteinuria. >Monitor BP and pulse. > Dyspnea and crackles may indicate pulmonary edema, which requires immediate treatment. > Answer questions and review rationale for avoiding use of diuretics to treat edema. > Elevation in BP may occur in response to catecholamine s, vasopressin, prostaglandin s, and, as recent findings suggest, decreased levels of prostacyclin. > Diuretics further 45 > Review moderate sodium intake of up to 6 g/day. Instruct client to read food labels and avoid foods high in sodium (e.g., bacon, luncheon meats, hot dogs, canned soups, and potato chips). >Refer to dietitian as indicated > Place client on strict regimen of increase state of dehydration by decreasing intravascular volume and placental perfusion, and they may cause thrombocytop enia, hyperbilirubin emia, or alteration in carbohydrate metabolism in fetus/newborn . > Some sodium intake is necessary because levels below 2–4 g/day result in greater dehydration in some clients. However, 46 bedrest; encourage lateral position. > Refer to home monitoring/daycare program, as appropriate. excess sodium may increase edema formation. > Nutritional consult may be beneficial in determining individual needs/dietary plan. > Lateral recumbent position decreases pressure on the vena cava, increasing venous return and circulatory volume >Replace fluids either orally or parenterally via infusion pump, as indicated. > Some mildly hypertensive clients without proteinuria may be managed on an outpatient 47 basis if adequate surveillance and support is provided and the client/family actively participates in the treatment regimen. > Fluid replacement corrects hypovolemia, yet must be administered cautiously to prevent overload, especially if interstitial fluid is drawn back into circulation when activity is reduced. With renal involvement, fluid intake is restricted; i.e., 48 if output is reduced (less than 700 ml/24 hr), total fluid intake is restricted to approximate output plus insensible loss. Use of infusion pump allows more accurate control delivery of IV fluids. 49 Risk for infection r/t inadequate primary defense secondary to broken skin CUES S=Ǿ O = may manifest fever, swelling on the affected part, pain on the affected part. NURSING DIAGNOSI S SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATIO N Risk for infection r/t inadequate primary defense secondary to broken skin Patient undergone episiotomy PLANNING Short Term: After 8 hours of nursing interventio Patient has an ns, client open wound will remain can be a free of all source of signs and infection symptoms of infection. Bacteria, fungus and viruses can easily break in NURSING INTERVENTION Establish rapport Monitor Vital sign Report fever >38°c, chills, diaphoresi s, swelling, heat, pain, erythema, exudates RATIONALE To gain trust and cooperation Serves as primary indicators of changes in health status Early detection of infection facilitates early intervention . EXPECTE D OUTCOM E Short Term: Client remains free of all signs and symptoms of infection. 50 the body Bacteria, fungus and viruses can easily flow through the bloodstream Patient is at risk of infection on anybody surfaces. Initiates measures to minimize infection Discuss with patient and family the importanc e of patient avoiding contact with people who have known or recent infection. Instruct all Exposure to infection is reduced Preventing contact with pathogens helps prevent infection Hands are significant source of 51 personnel in careful hand hygiene before and after entering the room Assist patient in practice of meticulou s personal hygiene Avoid insertion of urinary catheter, if catheter are necessary , use strict aseptic technique contaminati on This prevents skin irritations Rates of infection greatly increases after urinary catheterizat ion 52 Knowledge deficit [pregnancy induced hypertension] r/t lack of exposure to the present condition CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATIO N PLANNING NURSING INTERVENTIO N RATIONALE EXPECTED OUTCOME 53 S: “hindi ko alam baket ako nag ka ganito, nung una ok naman pagbubu ntis ko” O: Ø Knowledge deficit r/t lack of exposure to the present condition Patient never had PIH with her previous pregnancy Knowledge deficit Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize understanding of disease process and appropriate treatment plan. >Assess client’s knowledge of the disease process. Provide information about pathophysiolog y of PIH, implications for mother and fetus; and the rationale for interventions, procedures, and tests, as needed. > Provide information about signs/symptoms indicating worsening of condition, and instruct client when to notify >Establishes data base and provides information about areas in which learning is needed. Receiving information can promote understanding and reduce fear, helping to facilitate the treatment plan for the client. Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, client will be able to verbalize understanding of disease process and appropriate treatment plan. > Helps ensure that client seeks timely treatment and may prevent worsening of preeclamptic state to eclamptic state or additional complications. > Encourages 54 healthcare provider. > Assist family members in learning the procedure for home monitoring of BP, as indicated. participation in treatment regimen, allows prompt intervention as needed, and may provide reassurance that efforts are beneficial. > Reinforces importance of client’s responsibility in treatment. > Review techniques for stress management and diet restriction. > Provide information about ensuring adequate protein in diet for client with possible or mild preeclampsia. > Protein is necessary for intravascular and extravascular fluid regulation. > A test result of 2+ or greater is significant and needs to be 55 > Review selftesting of urine for protein. Reinforce rationale for and implications of testing. reported to healthcare provider. Urine specimen contaminated by vaginal discharge or RBCs may produce positive test result for protein. 56