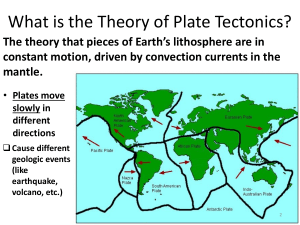
Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Let’s Get Organized Please start a t-chart in your notes Continental Drift Theory and Evidence Plate Tectonics Theory and Evidence Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Once upon a time…. ● A German guy, Alfred Wegener, started noticing interesting things about the continents ● Ever noticed how some of the land masses seem to fit together? Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Theory ● Wegener continued his research, eventually finding many pieces of evidence that proved all of our modern continents were once one supercontinent….Pangea ● He called this theory Continental Drift Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Continental Drift ● Wegener proposed that the continents “floated” on top of the oceanic crust ● The Pangea Supercontinent broke up ~200 million years ago and the land has drifted to form the modern continents Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics How did he know? 1…. ● Matching mountain ranges Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics How did he know? 2…. ● Coal Fields ● Salt Deposits ● Reefs Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics How did he know? 3…. ● Fossil evidence Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics How did he know? 4…. ● Climate Evidence ○ Warm-weather plants and animal fossils have been found in ice-covered regions Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics How did he know? 5…. ● Glaciers where they shouldn’t be Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Wegener had it all figured out except for one thing…. WHY and HOW this continental drift happened ● Wegener’s “friends” picked up on this and let him have it Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● It took a few years, but new technologies allowed scientists to gather new evidence ● World War II….warships carried new equipment, sonar and magnetometers, to find submarines ○ They found a lot more than they bargained for Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● ● Sonar was used to map the seafloor for the first time They found a couple things ○ ○ Deep sea trenches: found at the edges of continents or in the sea near chains of active volcanoes; e.g. the very deepest blue, off of eastern Asia Abyssal plains: flat areas, although many are dotted with volcanic mountains; e.g. consistent blue off of southeastern South America Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Magnetometer data eventually found anomalies in the Earth’s magnetic field ● Different sections of the ocean floor had different polarities ● These sections were all around high points (ridges) that sonar had found Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Sea Floor Spreading Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● This new evidence brought Wegener back into the spotlight ● There was now evidence of a mechanism causing continents to move ● This new theory was called Plate Tectonics ○ ○ All crust is part of a plate that is in motion This motion is caused by movement of the mantle Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Causes ● Ridge-push causes a plate to move away from the crest of an ocean ridge ● Slab-pull = cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Paleomagnetism ○ Fancy name for the record of magnetic field reversals Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Earthquake and Volcano Location Patterns ○ ○ Scientists found a close link between deep earthquakes and ocean trenches The absence of deep earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system is consistent with the new theory ● Ring of Fire outlines where oceanic plates are subducting ○ Going under continental plates Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Ocean Drilling ○ Analysis of rock samples shows that the oldest rock is farthest away from the ocean ridges Continental Drift vs. Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics ● Hot Spots ○ ○ ● Spots where magma from the mantle concentrates and is capable breaking through the Earth’s surface Hawaii is situated right above a hot spot Hot spots don’t move….the continental plate above them moves ○ The Pacific Plate shifts over the hot spot building an archipelago as it goes Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Boundary Types You will need your lab notebook and TWO colored pencils Plate Tectonics Boundaries ● Divergent boundaries (spreading centers) ○ ○ Two plates move apart Produces new rock ● Convergent boundaries ○ ○ Two plates move together Produces new rock, recycles old rock ● Transform fault boundaries ○ Two plates grind past each other without production or destruction of the lithosphere Plate Tectonics Divergent Boundary ● Motion ○ Plates move apart ● Effect ○ Constructive: builds onto each adjoining plate ● Topography ○ ○ Land: rift valleys Ocean: ridges that move apart ● Volcanic activity, small earthquakes, geysers, hot springs Plate Tectonics Convergent Boundary ● Motion ○ Two plates move together ● Effect ○ ○ Destructive: oceanic crust pushed underneath continental….melts Constructive: volcanic mountains built on continental ● Topography ○ Trenches underwater, mountains, islands ● Volcanic and earthquake activity Plate Tectonics Oceanic-Continental Convergence ● ● ● ● Deep, large earthquakes Coastal volcanoes Tsunamis Andes and Sierra Nevadas Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence ● Oceanic volcanoes ● Deep trenches ● Deep, large earthquakes ● Tsunamis ● Aleutians, Tonga, Hawaii Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Continental-Continental Convergence ● Mountain chains ● Smaller earthquakes ● Himalayas Plate Tectonics Transform Boundary ● Motion ○ ● Effect ○ ● Nothing new is created or destroyed Topography ○ ● Two plates slide across each other Lines may be visible No volcanoes, big earthquakes Plate Tectonics Review Boundaries ● Divergent boundaries (spreading centers) ○ ○ ○ ○ Two plates move apart Produces new rock Ocean ridges, rift valleys Volcanoes and small earthquakes ● Convergent boundaries ○ ○ ○ ○ Two plates move together Produces new rock, recycles old rock Trenches, mountains, islands Volcanoes, earthquakes, tsunamis ● Transform fault boundaries ○ ○ Two plates grind past each other BIG earthquakes Plate Tectonics Review ● Please take out your cell phone ● Go to kahoot.it ● If you do not have a phone with internet, I have a few iPads to checkout