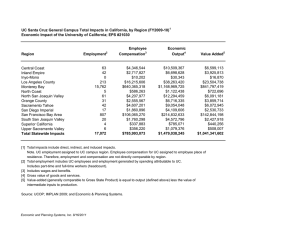
California Agriculture AGST 3000 Agriculture, Society and the Natural World Size of California A. 158,693 sq. mi. (exceeded in size only by Texas) B. Largest agricultural area = Central Valley (400 mi. long and 50 mi. wide) Early California Agriculture Native American Cultures A. Primitive compared to Aztecs of Mexico or Iroquois of Northeast B. Primarily all hunter-gatherers -Miwok -Yokut C. Miwok cultural development: -Harvest celebrations -No weapons -Changing seasons -No political hierarchy -Marriage and divorce -No warfare D. By 1852 this peaceful population was wiped out due to typhoid, diphtheria, small pox, bounty hunters, enslavement, and starvation -50 years to destroy a population that had existed for untold generations The Spanish Regime A. CA. was discovered by a Portuguese-born navigator, Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo, San Diego Harbor in 1542 B. Sir Francis Drake camped at Point Reyes on the northern coast in 1579 C. The “Franciscans” a roman Catholic religious order led by “Father Serra” established missions from San Diego to Sonoma, 36 miles apart (1 day horseback ride) 17691824 Built by Indians that were converted by the Spanish fathers D. Many of CA fruit and nut crops were established at the missions: oranges, and other citrus, almonds, cherries, apricots, pears, plums, etc. E. The Russian Presence – fur traders in the northern most part of CA established Fort Ross. The Mexican Regime: (1821-1848) A. Provided large tracts of land to anyone accepting the Catholic faith and becoming a Mexican citizen. These areas were called “Ranchos” B. Hides and tallow were the principle products exported from California during this time. San Diego was the primary port. C. Influx of foreigners – 1840’s, California was becoming difficult to control as more pioneer settlers began to appear via the overland routes. D. John Bidwell led the first group of immigrants to California via the California Trail. E. 1846 Mexican – American War separated California from Mexican rule (Bear Flag Rebellion) Statehood and the Gold Rush continued… Jan. 24, 1848, James William Marshall discovered gold at Coloma on the American River. California received its statehood in September, 1850 -Population of San Francisco in 1847 was 462 and 4 ships had visited the port. -In 1848 695 ships arrived bringing 100,000 new immigrants Statehood and the Gold Rush continued… The industry behind the Gold Rush -Levi Strauss outfitted gold miners in denim jeans -“Market hunters”- Tule elk, deer, ducks, geese all were commercially hunted to provide food for hungry miners. -Miller and Lux Cattle Company – demand for beef, started as a butcher and ended as a cattle baron. – 750,000 acres of land in CA., OR., NV. -Citrus industry – “gold nuggets on trees” Anaheim -Petaluma Poultry Industry - $1.00 each for eggs -Grain industry – near large cities, counties bordering San Francisco, Santa Cruz, and Sacramento, highest yields in the U.S., short lived because of insects and disease (mild winters allowed these pests to survive) Statehood and the Gold Rush continued… Ethnic diversity -1870 50% of all men in CA had been born abroad -Germans owned the most farmland, Italians 2nd, Portuguese 3rd -Chinese were indentured slaves for gold mining and weren’t allowed to own property, important cultural influence -Japanese largest group of tenant farmers -French in the 1830’s brought the first grape vines (wine) -Armenians introduced new crops: asparagus, raisins, figs California Continues to Grow Desirable climate, shipping ports and healthy economy encouraged continued growth in CA long after the Gold Rush ended (35-40th latitude) What geographic, climatic, socioeconomic conditions supported this continued growth…? Is it the same today? Latitudes and Longitudes of the Earth California Continues to Grow…continued Markets changed to reflect increasing land values -Southern California lost hundreds of acres of orange groves due to urban growth, growth of military industry (Navy, Air Force, NASA, and Intelligence Agencies began during the Cold War 1950’s and continued through the 1970’s) -The dairy industry shifted from Chino to Tulare -Hewlett and Packard worked in their garage to manufacture a transistor that led to the development of the “silicon chip”. Atari, Apple Computers, IBM -San Jose (Santa Clara Valley) was once an important fruit production area, canneries and agriculture provided income and has since transformed into the “Silicon Valley” -Urban growth throughout the Central Valley competes with farmland -- causes concern for farmland preservation California Continues to Grow…continued Efforts for Ag Land Preservation Williamson Act = California Land Conservation Act of 1965 -Designed to prevent the loss of valuable farmland -Provides a tax break to property owners if they agree to restrict land to agricultural use for 10 years -Voluntary program We also know that historically: 1-CA is most populated state in the US since 1963 Today…36.8 million 2-Ca has been leading Ag in US since 1948(most productive 1. CA (incl. nursery) San Joaquin Valley 2. Texas 3. Iowa 4. Nebraska 5. Minnesota 31.8 billion 20.1 16.5 14.7 11.8 9.8 USDA, NASS, California Field Office, 2004 13.2% of US Total is from California San Joaquin Valley accounts for 63.2% or 8.34% of US Top 10 Ag counties in CA. (2004) 1. Fresno 2. Tulare 3. Monterey 4. Kern 5. Merced 6. Stanislaus 7. San Joaquin 8. San Diego 9. Ventura 10. Kings 13. Madera $4.688 B $4.037 B $3.398 B $3.142 B $2.365 B $1.978 B $1.613 B $1.462 B $1.387 B $1.197 B $1.070 B San Joaquin Valley Market value of Ag products State(04) Nation(02) Fresno Tulare Kern Merced Stanislaus San Joaquin Kings Madera Billion $ USDA, NASS 2004 1 2 4 5 6 7 10 13 31.8 1 2 4 5 6 7 18 23 State%04 Nation% 14.7 1.4 12.7 1.2 9.9 7.4 6.2 5.1 3.8 3.4 1.0 .70 .61 .61 .40 .35 6.27 What types of crops are grown in California? For the top 10 Agricultural Counties in California, list the major crops grown in each. California's Top 20 Commodities - 2004 (CDFA) Millions Billions 1.Milk and Cream $5.366 11.Cotton, All $ 808 2.Grapes, All $2.757 12.Chickens, All $ 714 3.Nursery $2.649 4.Almonds $2.200 13.Broccoli $ 625 5.Cattle and Calves $1.634 14.Oranges, All $ 557 6.Lettuce, All $1.462 15.Carrots $ 448 7.Strawberries $1.219 16.Pistachios $ 444 8.Tomatoes, All $1.091 17.Walnuts $ 439 9.Hay, All $1.010 18.Avocados $ 380 10.Flowers $1.002 19. Rice $ 353 20. Peppers, All $ 332 National Rankings http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/census97/rankings/tablist.htm Irrigated land Dairy Products Fresno 1 Tulare 1 Kern 2 Merced 2 Tulare 3 Stanislaus 4 San Joaquin 4 San Joaquin 9 Merced 5 2/3 of valley 11.4% of nation Stanislaus 11 California…17 % of nation California…15.8 % California’s No. 1 Ag Product of nation Fruits, nuts and berries 23 % of nation Specialty Crops Commercially Produced Only in California (99% or more of total U.S. production)* Almonds Artichokes Clingstone Peaches Figs Seed, Ladino Clover Sweet Rice Olives Persimmons Pomegranates Plums, Dried (Prunes) Raisins Walnuts Important trends 1-decline in farms (144,000 in 1950 to 77,000 in 2004) There was a large decline, but more productivity/ more value per acre. What about family farms? 2- decrease in total land in farms (37,500,000 acres in 1950 to 26,700,000 in 2004) Loss of acreage because of urbanization and environmental issues causes expansion to lesser quality soils, less access to water 3-increase in acres per farm, economies of size (260 A in 1950 to 347 in 2004) California's Top 10 Agricultural Export Markets - 2002* 1 Canada $1,199 Lettuce, Processed Tomatoes, Table Grapes 2 European Union $1,128 Almonds, Wine, Walnuts 3 Japan $ 905 4 China/Hong Kong $ 345 Table Grapes, Oranges, Cotton 5 Mexico $ 293 Dairy, Table Grapes, Processed Tomatoes 6 Korea $ 274 Oranges, Beef, Cotton 7 Taiwan $ 212 Cotton, Peaches and Nectarines, Rice 8 Indonesia $ 101 Cotton, Table Grapes, Dairy 9 India $ Almonds, Cotton, Table Grapes 10 Malaysia $ Rice, Almonds, Hay 94 60 Table Grapes, Oranges, Almonds* Source: CDFA Resource Directory 2003 Assignment … Access the National Agricultural Statistics Service and California Department of Food and Agriculture – look at the CDFA and NASS Statistical Review and Ag Commissioners Reports What are the top 10 commodities in 2002 and 2005 for Stanislaus, San Joaquin and Merced Counties? Using the CDFA Statistical Review, what are the Top 10 Agricultural Export markets for 2005 and what products are exported to each. http://www.nass.usda.gov http://www.cdfa.ca.gov/