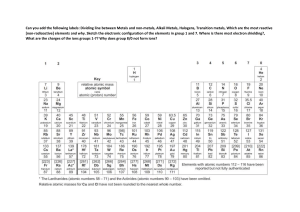
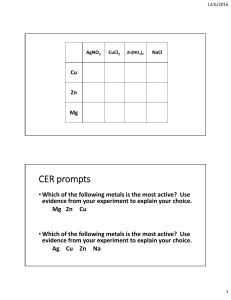
Figure 3.6 Metals are good conductors of electricity. Physical properties of metals - Summary 6. Sonorous Non-Metals Examples of common metals are carbon, sulphur, iodine, oxygen, hydrogen, etc. Physical properties of non-metals Bromine (Br2) is only non-metal that exists in liquid state. Exceptions in metals and non-metals (i) All metals except mercury exist as solids at room temperature. In Activity 3.5, you have observed that metals have high melting points but gallium and caesium have very low melting points. These two metals will melt if you keep them on your palm. (ii) Iodine is a non-metal but it is lustrous. (iii) Carbon is a non-metal that can exist in different forms. Each form is called an allotrope. Diamond, an allotrope of carbon, is the hardest natural substance known and has a very high melting and boiling point. Graphite, another allotrope of carbon, is a conductor of electricity. (iv) Alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potassium) are so soft that they can be cut with a knife. They have low densities and low melting points. Chemical properties of metals and non-metals Most non-metals produce acidic oxides when dissolve in water. On the other hand, most metals, give rise to basic oxides. Chemical properties of metals What happens when metals are burnt in air? Chemical reactions of metals Reactivity of metals Reaction of metals such as Cu and Al Reaction of Al oxide Reaction of alkali metal oxide Amphoteric oxides Reactivity of metals – Some important points • • • • • • • • Reactivity of all metals are different. Some react fast and some slow. Na and K react fast while Cu reacts slow. Mg reacts less vigorously. Na and K are kept in kerosene. Fe, Zn, and Al reacts with O2 to form oxide coating which gives resistance for corrosion. Fe do not burn but fillings burn vigorously. Ag and Au do not react with O2 even at high temperatures. What happens metals react with water? Chemical reactions of metals with water Reaction of metals such as Na, K, Ca, Fe, and Al with cold and hot water and steam Reaction of metals such as Na, K, Ca, Fe, and Al with cold and hot water and steam What happens metals react with acids? Write equations for the reactions of magnesium, aluminium, zinc and iron with dilute hydrochloric acid. Nitric acid effect on metals? Reactivity of metals based on hydrogen evolution? How do metals react with other metal salts?