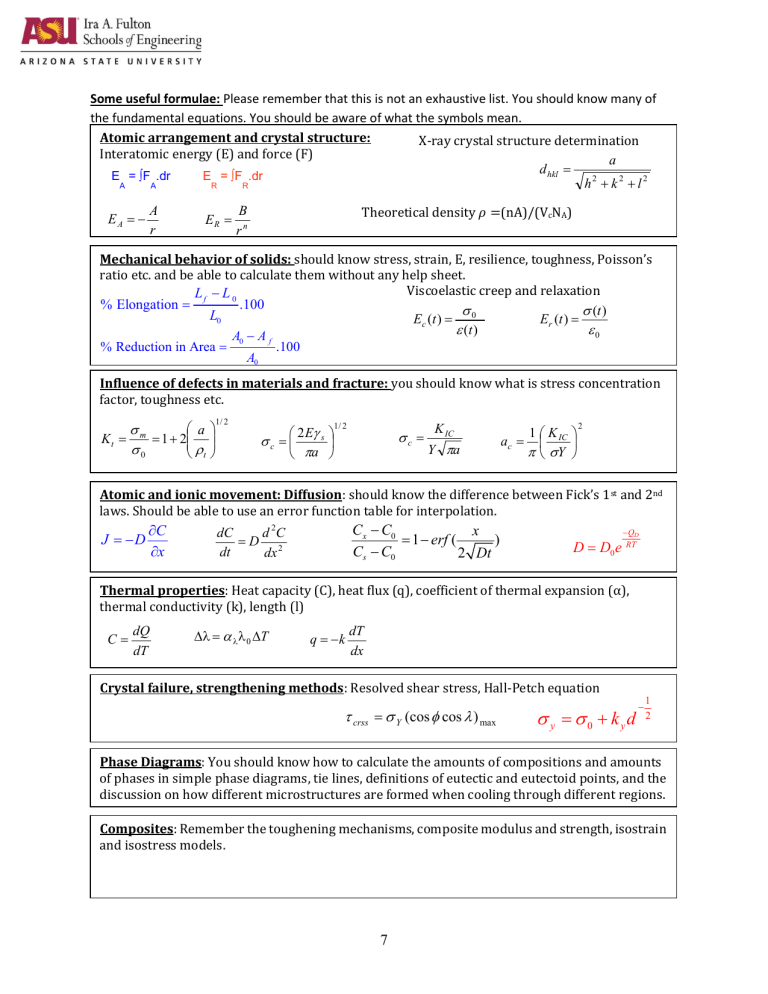
Some useful formulae: Please remember that this is not an exhaustive list. You should know many of the fundamental equations. You should be aware of what the symbols mean. Atomic arrangement and crystal structure: X-ray crystal structure determination Interatomic energy (E) and force (F) a d hkl E = ∫F .dr E = ∫F .dr h2 k 2 l 2 A A R R EA A r ER B rn Theoretical density 𝜌 =(nA)/(VcNA) Mechanical behavior of solids: should know stress, strain, E, resilience, toughness, Poisson’s ratio etc. and be able to calculate them without any help sheet. Viscoelastic creep and relaxation Lf L 0 % Elongation .100 (t ) L0 Ec (t ) 0 E r (t ) 0 (t ) A0 A f % Reduction in Area .100 A0 Influence of defects in materials and fracture: you should know what is stress concentration factor, toughness etc. a K t m 1 2 0 t 1/ 2 1/ 2 2 E s a c c K IC Y a ac 1 K IC Y 2 Atomic and ionic movement: Diffusion: should know the difference between Fick’s 1st and 2nd laws. Should be able to use an error function table for interpolation. J D C x Cx C0 x 1 erf ( ) Cs C0 2 Dt dC d 2C D 2 dt dx D D0 e QD RT Thermal properties: Heat capacity (C), heat flux (q), coefficient of thermal expansion (α), thermal conductivity (k), length (l) C dQ dT 0 T q k dT dx Crystal failure, strengthening methods: Resolved shear stress, Hall-Petch equation crss Y (cos cos ) max y 0 kyd 1 2 Phase Diagrams: You should know how to calculate the amounts of compositions and amounts of phases in simple phase diagrams, tie lines, definitions of eutectic and eutectoid points, and the discussion on how different microstructures are formed when cooling through different regions. Composites: Remember the toughening mechanisms, composite modulus and strength, isostrain and isostress models. 7