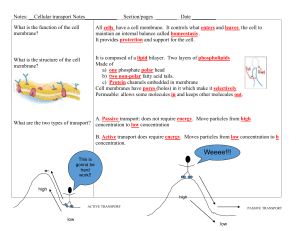
Transport Through Membrane Plasma Membrane ✦ Surrounds the cell, controls what enter/exits the cell ✦ Selectively Permeable- allows certain particles to pass and blocks others ✦ “bouncer” ✦ Small items pass through, large can not ✦ What enters? ✦ Oxygen, nutrients ✦ What leaves? ✦ Carbon dioxide, waste Plasma (cell) Membrane Structure ✦ 1. Phospholipid bilayer- two rows of phospholipids, tails facing each other ✦ Water loving on outside ✦ Water fearing in middle, staying together Membrane Structure cont. ✦ 2. Steroids- fit between tails of phospholipids ✦ Cholesterol in animals cells ✦ Allows the membrane to stay fluid and increases movement of molecules 3. Carbohydrateslocated on outside of membrane 4. Proteins✦ Peripheral- located on the surface of the membrane ✦ Integralembedded within the membrane can go through to other side ✦ Fluid Mosaicterm used to describe the movement of the membrane, fluidpieces are moving not stationary; mosaic- many pieces Types of Transport ✦ 1. Passive ✦ 2. Active ✦ Cells are surrounded by aqueous solutions with many substances dissolved ✦ Concentration Gradientdifferences in concentration of molecules in a space Passive Transport ✦ Movement of substances through membrane ✦ From high to low concentration ✦ No energy required ✦ Types of Passive ✦ 1. Diffusion ✦ 2. Facilitated diffusion ✦ 3. Osmosis Diffusion ✦ Simplest form of passive transport ✦ Examples- oxygen, carbon dioxide ✦ Equilibrium- state where concentration is the same, no net movement Facilitated diffusion ✦ Movement across membrane that requires assistance by proteins because molecules are too large or have a charge ✦ Examples- Glucose, Cl- ✦ Carrier protein- name of proteins that help move molecules Osmosis ✦ Passive transport of water only Direction of osmosis ✦ Hypotonic- water moves into cell ✦ Water conc. is high outside of cell ✦ Solute conc. is low outside of cell ✦ Hypertonic- water diffuses out of cell ✦ Water conc. is low outside cell ✦ Solute conc. is high outside of cell 7 ✦ Isotonic- when two environments are equal, no net movement ✦ “equilibrium” Human Blood Cells Cell Deal with Extra Water ✦ Animal- fills vacuole, pump back out ✦ Some burst- cytolysis (cell death) ✦ Plants- can swell, pushing against cell wall ✦ Called turgor pressure Cells Deal with Limited Water ✦ Animal cellsshrivel, eventually die ✦ Plant- shrink away from cell wall ✦ Called plasmolysis ✦ Reason plants wilt Active Transport ✦ Type of transport in which molecules ✦ Move from low to high concentrations ✦ Requires energy ✦ Types of Active Transport ✦ Cell membrane pumps ✦ Endocytosis ✦ Exocytosis Cell Membrane Pump ✦ Uses protein (pump) to force molecules into higher concentration Sodium-Potassium Pump ✦ Specific protein that moves Na+ out and K+ into the cell ✦ Carrier protein can hold either 3 Na+ or 2 K+ Sodium-Potassium Pump ✦ 1. 3 Na+ enter protein, move to outside ✦ 2. 2 K+ enter protein, move to inside ✦ 3. Cycle repeats Endocytosis ✦ Process in which large particles or fluids are moved into the cell ✦ Vesiclemembrane which encloses the particles and moves them around cell Types of Endocytosis ✦ Pinocytosistransport of fluid “cell drinking” ✦ Phagocytosistransport of large particles or entire cells “cell eating” ✦ Ex.- White Blood Cells ingesting bacteria Exocytosis ✦ Process in which large particles are removed out of the cell ✦ Starts in vesicle then moves to cell membrane ✦ Ex.- waste and proteins are removed