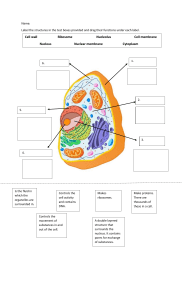
Cell Structure and Function Cell - basic structural and functional unit of life. Robert Hooke - discovered the tiny compartment in the thin slide of cork. Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann - Concluded that all living thing are made of cell. (Cell Theory) Robert Brown - identified a dark-stained structure at the center of every cell that he observed. He referred to it as nucleus. Prokaryotic Cells - Lack distinct nuclei and few organelles that are not membrane bound. Eukaryotic Cell - have distinct nuclei and contain several membrane bound organelles. Organelles - are small membrane bound structures that perform specific functions that make life possible. Cell wall (non living component) - provides mechanical support and maintains cell shape in plant cell. Plasma membrane (flexible and elastic) - it regulates the entry and exit of materials. - also serve as a boundary between the outside environment and inside of the cell. Mitochondria (Powerhouse of the cell) - it provides energy for the cell in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate. They are the center of cellular respiration. Vacuoles (Storage Tank of the Cell) - A compartment covered by a single membrane called tonoplast. - Stores water, food, or waste for the cells. Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Bodies ( Packaging Counters of the Cell) - it sorts, packages and secretes materials. - also involved in the processing and modification of proteins. Cytoplasm -(Complex fluid that fills the cell) - allows the distribution of materials throughout the cell due to cyclosis. Exoplasm outer cytoplasm (gel like), inner cytoplasm is fluid (sol like) Cyclosis - fluid part capable of streaming. Nuclear membrane - double membrane that encloses the cell nucleus. - It separates the nuclear contents from the contents of the cytoplasm. Nucleolus - Dense spherical body inside the nucleus. It contains the nucleic acid RNA. - It is responsible in the synthesis of RNA and production of ribosomes. Nucleoplasm/ nuclear sap - gel like material that fills the nucleus. - it function as the matrix of the chromosomes and nucleolus. Chromosomes - Highly coiled structures that form a network over the nucleoplasm. - these units carry genes responsible in transmitting hereditary characteristics. Nucleus (Control Center of the Cell) - it directs and coordinates all cellular activities. Endoplasmic reticulum (Manufacturers and Shippers of the Cell) - responsible for the translocation of materials within the cell, and in and out of the nucleus. - Rough ER contains ribosomes and Smooth ER does not contain ribosomes. Chloroplast - A double membrane structure that contains chlorophyll pigments. - It provides green pigment for plants and aid in photosynthesis. Centrioles (Helper in Cell Division) - Forms the spindle fibers during cell division and functions as the anchor for the cytoskeletons. Lysosomes (Suicide bag of the Cell) - Single membrane compartment containing powerful hydrolytic enzymes. - it is responsible in breaking down cellular waste. Ribosomes (Protein Factories of the Cell) - Found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or free-floating in the cytoplasm. - They use RNA synthesized by the nucleolus in making specific amino acid. Cytoskeletons (Framework of the Cell) - are the network of fibers that are scattered throughout the entire cytoplasm and interconnecting some organelles. Two types of cytoskeleton: Microtubules help to maintain the shape of the cell and aid in the movement. Microfilaments provides contractility to some cells and aid in changing the shape of some cells. Microbodies - very tiny membrane bound organelles that are scattered throughout cytoplasm together with the free ribosomes. Shapes of Cell Spherical - Round and oval (human red blood cells) Squamous - flat or tile-like (Human squamous cells) Stellate - star-like (nerve cell or neuron) Spiderlike - with several cytoplasmic extensions (Bone Cells) Columnar - rectangular set upright (Columnar cells) Fusiform/Spindle - tapering at both ends (smooth muscle cells)