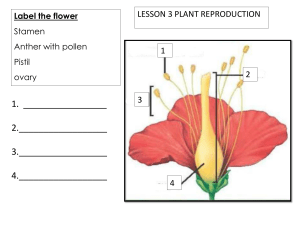
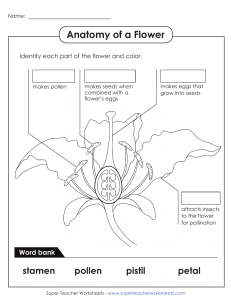
PLANTS: structure and function Plants: Grouped by characteristics Vascular Three main parts: roots, stems and leaves Roots can be different sizes: Storage roots; beets, carrots, sweet potatoes and turnips Fibrous and tap roots Roots have different functions: anchoring the plant, taking in water and minerals, and store food. Nonvascular Simple; most grow in moist places No vascular tissues. Vascular Plants: Stems Function of stems Support, transport of water & food Most stems grow upward Some stems grow sideward Types of stems Green Woody Transport of materials Xylem=_________________ phloem=_________________ Vascular Plants: Leaves Leaves come in variety of shapes and sizes Leaves are arranged in different ways What do plants do? All plants are alike in one way. They need three things in order to survive Water carbon dioxide energy from sunlight What do you suppose the plants use these things for? Classify – to sort into groups based on similarities and differences They turn it into sugar! photosynthesis – a process by which plants change light energy from the sun and use it to make sugar Plants and some protists conduct photosynthesis. Photosynthesis As a plant makes sugar, oxygen is released When the plant uses the sugar, water and carbon dioxide are released. chlorophyll – the green substance found in plants that traps energy from the sun and gives plants their green color carbon dioxide – a gas found in air How Do Plants Get Energy Plant leaves change light energy into energy the plant can use. They get sunlight, water, and air (CO2.) Stomata are tiny holes on the bottom of the leaf that let air (CO2.) in and (O2)out. Roots get water and minerals directly from the soil. The veins of a leaf bring water and minerals to the leaf from the stems and roots. Because of this process Scientists are able to classify living things by the way they get their food. Plants are producers (autotrophs) producer – it is a living thing that uses sunlight to make sugar. This sugar feeds others. Plants reproduce differently Reproduce – it means “to make more of the same kind” Plants are classified by characteristics. Plants that make seeds Flowering Plants Conifers Plants that do not make seeds Ferns Mosses a protective covering that surrounds the seed makes seeds. makes the plant's food. anchor the plant in place and absorb water and other minerals from the soil. carries water and food to the rest of the plant. What Are the Parts of a Flower Most flowers have four parts Sepal – one of the leaflike parts that protects a flower bud and that is usually green Pistil – part of a flower that makes the eggs that grow into seeds Stamen – part of a flower that makes pollen Flower parts Pollen – tiny grains that make seeds when combined with a flower’s egg How Do Flowers Make Seeds and Fruits? Great Plant EscapePlant parts Ovary – the bottom part of the pistil in which seeds form Ovule - the inner part of an ovary that contains an egg embryo – tiny part of a seed that can grow into a new plant How Fertilization Occurs When a pollen grain reaches a pistil, it grows a thin tube to the ovary. Sperm from the pollen grain combines with an egg, and a seed forms. Fertilization – the combination of sperm from a pollen grain with an egg to form a seed How Pollination Occurs Pollination- the movement of pollen from a stamen to a pistil Butterflies may carry pollen from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of the the same flower. Sometimes the butterfly may carry pollen from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of another flower of the same kind. Pollen: Nothing to Sneeze At Some flowering plants are monocot seed – a seed that has one seed leaf and stored food outside the seed leaf dicot seed – a seed that has two seed leaves that contain stored food How Do Other Living Things Get All living things need Energy? energy to survive Consumer – a living thing that gets energy by eating plants and other animals Animals cannot use light energy to make sugar. Animals depend on plants for food. Decomposer – a consumer that puts materials from dead plants and animals back into the soil, air, and water