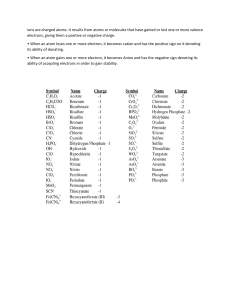
IB Chem Definition for Topic 1,2,3,4,9,10,11 By Logan An element is a pure substance that contains only one type of atom An atom is the smallest part of an element that can still be recognised as that element. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more elements combine chemically. A mixture contains two or more substances mixed together. A homogeneous mixture has the same (uniform) composition throughout the mixture and consists of only one phase. A heterogeneous mixture does not have uniform composition and consists of separate phases. Heterogeneous mixtures can be separated by mechanical means. The relative atomic mass (Ar) of an element is the average of the masses of the isotopes in a naturally occurring sample of the element relative to the mass of 1/12 of an atom of carbon12. The relative molecular mass (Mr) of a compound is the mass of a molecule of that compound relative to the mass of 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12. The relative formula mass is the mass of one formula unit relative to the mass of 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12. Empirical formula: the simplest whole number ratio of the elements present in a compound. Molecular formula: the total number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of the compound. (The molecular formula is a multiple of the empirical formula.) Avogadro’s law: equal volumes of ideal gases measured at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules. Solute: a substance that is dissolved in another substance. Solvent: a substance that dissolves another substance (the solute). The solvent should be present in excess of the solute. Solution: the substance that is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent. Atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number (A) is the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Ions are charged particles that are formed when an atom loses or gains (an) electron(s). Isotopes are different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers: i.e. different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. The relative atomic mass (Ar) of an element is the average of the masses of the isotopes in a naturally occurring sample of the element relative to the mass of 1/12 of an atom of carbon12. Line spectrum – only certain frequencies/wavelengths of light present. Continuous spectrum – all frequencies/wavelengths of light present. An orbital is a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. It represents a discrete energy level. The full definition of first ionisation energy is: the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms under standard conditions. periodicity: repeating pattern of (physical and chemical) properties; Electron Affinity is defined more precisely as the enthalpy change when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms under standard conditions. Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction of an atom in a molecule for the electron pair in the covalent bond of which it is a part. Amphoteric oxides react both with acids and with bases. An ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons, and a covalent bond is the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the atoms that are bonded. // A covalent bond is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged nuclei of both atoms and the shared pair of electrons. A coordinate covalent bond is a type of covalent bond in which both electrons come from the same atom. These individual structures differ only in the position of the double bond and are called resonance structures. Allotropes are different forms of the same element. Van der Waals’ forces is the collective name given to the forces between molecules and includes London (dispersion) forces, dipole−dipole interactions and dipole−induced dipole interactions. London forces are temporary (instantaneous) dipole–induced dipole interactions. The requirements for hydrogen bonding are that the H atom is attached to a very electronegative atom – N, O or F – which possesses at least one lone pair of electrons. Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between the positive ions in the lattice and the delocalised electrons. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or of a metal with a non-metal. Oxidation is the loss of hydrogen or the gain of oxygen, and reduction is the gain of hydrogen or the loss of oxygen. Oxidation – loss of electrons Reduction – gain of electrons Reduction – decrease in oxidation number Oxidation – increase in oxidation number Oxidising agents (oxidants) oxidise other species and, in the process, are themselves reduced. An oxidising agent takes electrons away from something. Reducing agents (reductants) reduce other species and, in the process, are themselves oxidised. A reducing agent gives electrons to something. The salt bridge provides an electrical connection between the two half-cells to complete the circuit. It allows ions to flow into or out of the half-cells to balance out the charges in the half-cells. An anode is defined as the electrode at which oxidation occurs. The cathode is defined as the electrode at which reduction occurs. Electrolysis is the breaking down of a substance (in molten state or solution) by the passage of electricity through it. An electrolyte is a solution or a molten compound that will conduct electricity, with decomposition at the electrodes as it does so. Electrolytes contain ions that are free to move towards the electrodes. Hydrocarbon: a compound containing only carbon and hydrogen. A homologous series is a series of compounds that have the same functional group. Each member differs from the next by a common structural unit (usually –CH2–). A functional group is the atom or group of atoms in a molecule that gives it its characteristic chemical properties – this is the reactive part of a molecule. Alcohols are described as primary, secondary or tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon with the –OH group. Structural isomers are two or more compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas – the atoms are joined together in different ways. Random uncertainties are caused by the limitations of the measuring apparatus and other uncontrollable variables that are inevitable in any experiment. Precision relates to the reproducibility of results. If a series of readings is taken with high precision, it indicates that the repeated values are all very close together and close to the mean (average) value. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the actual value of a particular quantity.