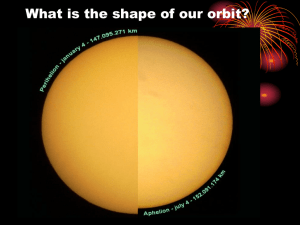
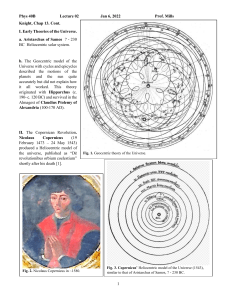
Johannes Kepler (1571 – 1630) • Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician and astronomer who discovered that the Earth and planets travel about the sun in elliptical orbits. He gave three fundamental laws of planetary motion. He also did important work in optics and geometry. Kepler’s Laws This law describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. • Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun as a focus. • A planet covers the same area of space in the same amount of time no matter where it is in its orbit. • A planet's orbital period is proportional to the size of its orbit (its semi-major axis). Kepler's first law is called the Law of Ellipses. It states that "the path of the planets about the sun is elliptical in shape, with the center of the sun being located at one focus". An ellipses includes any circular shape. • Kepler's Second Law • It says that a line running from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas of the ellipse in equal times. This means that the planet speeds up as it approaches the sun and slows down as it departs from it. Let's use the diagram above to think through how this is so. Kepler’s third Law • The cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun is directly proportional to the square of time it takes to move around the sun. Kepler's Third Law implies that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit.