Chapter 26: The Sun and the Solar System The Sun –
advertisement

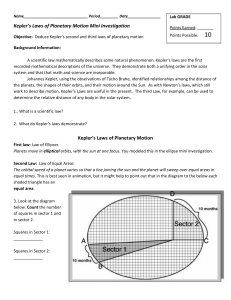
Chapter 26: The Sun and the Solar System The Sun – • Is a star • Is a main sequence star • 1 million Earth’s would fit inside the sun • 1.4 million kilometers f Hertzberg- Russel Diagram Fuel for the Sun is Fusion – • • • • • The union of hydrogen atoms into helium 4H = 1 He What happens when a star runs out of its fuel – hydrogen? It either becomes a red giant or a supergiant Our sun will become a red giant 1. Core: This is where all the sun's heat and light is made. 2. Radiative Zone: The heat and light move from the core into this layer. 3. Convection Zone: In this layer, the gases move like boiling water. 4. Photosphere: This is the part of the sun we see. 5. Chromosphere: This layer shoots out hot gases. 6. Corona: This layer can only be seen during an eclipse. It is the atmosphere around the sun. Sunspots: dark spots on the photosphere – the magnetic associated with a sunspot is about 1000 stronger than the magnetic field of the surrounding photosphere. Sunspots, as seen from Earth, move from left to right across the sun’s surface. Sunspots vary from day to day, but go through an 11 year cycle from peak activity to the next. Solar Wind: a constant stream of electrically charged particles given off by the corona, they reach Earth in a few days but are deflected by Earth’s magnetic field – creates auroras. Magnetic Storm: solar events that produce huge gusts of wind and large amounts of solar particles. 26.2 Aristarchus: A GREEK ASTRONOMER, WAS THE FIRST TO PROPOSE THAT THE EARTH REVOLVES (orbits) AROUND THE SUN. Aristotle: GREEK PHILOPOPHER WHO PROPOSED THAT THE EARTH WAS THE CENTER OF THE UNIVERSE. Copernicus: POLISH ASTRONOMER WHO DEVELOPED THE IDEA OF A HELIOCENTRIC, OR SUN CENTERED, SYSTEM. Galileo: ITALIAN SCIENTIST WHO WAS THE FIRST PERSON TO USE A TELESCOPE FOR ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATIONS. Kepler: DEVELOPED THE THREE LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION. Newton: DEVELOPED THE LAWS OF GRAVITY. Ptolemy: PROPOSED THAT THE EARTH WAS THE CENTER OF THE UNIVERSE. Tycho Brahe: DANISH ASTRONOMER NOTED FOR HIS RECORDINGS OF THE POSITIONS OF THE PLANETS IN THE SKY. Heliocentric: SUN CENTERED Geocentric: EARTH CENTERED The sun is 4.5 BILLION YEARS OLD Elliptical Orbits: Kepler’s first law of planetary motions – planets travel in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus. Instead of having a center has a circle does, an ellipse has two foci on opposite sides of its center. Because the sun is at one focus of the ellipse, a planet’s distance will change throughout its orbit. Equal Area Law: Kepler’s second law states that a line connecting Earth to the sun will pass over equal areas of space in equal times. Because Earth’s orbit is elliptical, it will move faster when it is nearer to the sun. Harmonic Law: Kepler’s third law – the time it takes a planet to travel one orbit around the sun is its period. This law is used to find the mean distance between the sun and a planet, if a period is known, or to find the period if a distance is known. The farther a planet is from the sun, the longer its period of revolution (orbit).