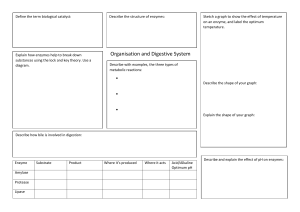
Wednesday May 24, 2017 Agenda (10) Catalyst (15) Review: Biomolecules and Enzymes (15) Cloze Practice (30) Trashketball (15) Daily Quiz I can: review the four classes of biomolecules, and enzymes Catalyst 1. Name 4 things that prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common. 2. What are 3 organelles that eukaryotes have that prokaryotes lack? 3. What type of cell has circular DNA (plasmids)? HW: Biology Released Form (BRF) #19-27 135 Things… (due June 2) Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Biology Released Form Big Idea By understanding the chemistry and molecules that make up life, we have deeper insight into how life functions. What do these Macromoleculesstructures all have in common? carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids Four groups of molecules make up the building blocks of life. In general, they are called macromolecules (aka organic molecules aka biomolecules). Macromolecules Macromolecules are formed by polymerization, in which large polymers are built by joining small subunits called monomers together. monomers = subunits = building blocks of molecules polymers = monomers joined up by polymerization Carbohydrates Carbohydrate Structure • made up of C, H, and O • polysaccharides are polymers made up of monosaccharides, or simple sugars Carbohydrate Function • organisms’ main source of immediate energy • structural purposes Carbohydrates, cont. • the tough fiber found in plants is made up of the carb cellulose • sugars end in –ose • examples of simple sugars: • complex sugars are called starches Detecting Carbohydrates Simple Sugars • simple sugars turn orange in the presence of Benedict’s solution no carbs carbs present Starches • starches turn deep purple in the presence of iodine, or Lugol’s solution Lipids Lipid Structure • made up of C, H, and O • made up of glycerol and fatty acids – long chains Lipid Functions • make up fats, oils, and waxes • store energy, makes up the cell membrane, and used in waterproof coverings waxy cuticle of leaf = lipids to repel water walrus blubber = lipids to store energy Detecting Lipids brown paper bag test Proteins Protein Structure • made up of C, H, O, N • amino acid subunits form long polypeptide chains – over 20 different amino acids an individual amino acid Protein Function • the most diverse macromolecules • various roles: – speed up reactions (enzymes) – form muscles – transport substances – fight disease Proteins, cont. • hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells • insulin is a protein that regulates blood sugar Protein Detection Biuret’s solution turns from blue to light purple in the presence of protein Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acid Structure • made up of C, H, O, N, and P • subunits: nucleotides – nucleotides are made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base Nucleic Acid Function • store and transmit hereditary information Nucleic Acids, cont. Two examples: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) Enzymes Bio.4.1.3. Explain how enzymes act as catalysts for biological reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions (to change one set of chemicals to another) by lowering their activation energy. • They have three important characteristics: 1. they are specific to a substrate 2. they work at an optimal pH and temperature 3. they are reusable Enzymes enzyme the active site is where the substrate molecule fits or binds the substrate is the molecule that the enzyme acts on enzyme-substrate complex the enzyme works its magic on the substrate… …and releases the new chemical products see how the enzyme and substrate fit together like a lock and key! Activation Energy Without an enzyme present, the reaction is slow and requires a lot of energy. The enzyme lowers the energy required in the reaction and speeds it up. Optimal pH and Temperature What happens if we go outside the optimal range? The enzyme DENATURES, or changes its folding/shape. What’s the optimal temperature that this enzyme works at? Enzymes have an optimal temperature and pH that they work at. You can find this optimal condition by looking at the tallest part of the hump in a graph of enzyme activity. pH Levels Low pH (0-7) is acidic High pH (7-14) is basic pH = 7 is neutral REVIEW WORKSHEET TRASHKETBALL! Whiteboard Question How can excessive heat affect the function of enzymes? a. Heat can increase the pH of enzymes. b. Heat can cause enzymes to become denatured. c. Heat can cause enzymes to absorb carbon dioxide. d. Heat can produce more substrate for enzyme reactions. Whiteboard Question An enzyme works optimally at a pH between 2 and 4. Which best explains what will happen to this enzyme at a pH of 12? a. It will lose its original shape and work on new substrates. b. It will work on a different substrate than at a pH range of 2–4. c. It will lose its original shape and not work on any substrate at all. d. It will work on the same substrate as it did at a pH range of 2–4, but it will not work as well. During which process in the mitochondria is glucose converted into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)? A. photosynthesis B. chemosynthesis C. cellular digestion D. cellular respiration Whiteboard Question Which characteristic would least likely be used to describe an enzyme? a. b. c. d. It speeds up a reaction It is consumed in the reaction It reacts with a specific substrate It reduced the activation energy of the reaction Whiteboard Practice Whiteboard Question Which is a carbohydrate? a. b. c. d. Amylase Cellulose Glycerol Polypeptide Whiteboard Question Which characteristic can best distinguish between two different proteins? a. b. c. d. the presence of nitrogen in the proteins the sequence of amino acids in the proteins the number of amino acids found in the proteins the location of the peptide bonds in the proteins Whiteboard Practice Whiteboard Question Which best describes the importance of carbohydrates to organisms? a. Carbohydrates provide storage for water molecules. b. Carbohydrates provide an immediate energy source. c. Carbohydrates provide an additional source for amino acids. d. Carbohydrates provide permanent storage for genetic information. • Which experiment could be conducted to determine if baked potato chips have less fat than fried potato chips? A. Place potato chips in water and test the pH B. Place potato chips on a paper bag and test for oil spots. C. Mix crushed potato chips with iodine to observe color change. D. Mix crushed potato chips with Benedict’s solution to observe color change. End • What is the significance of nucleic acids for cells? A. They generate energy for the cell. B. They restrict what enters and leaves the cell. C. They support and maintain the shape of the cell. D. They provide all instructions for cellular activities. End • Which is the best example of a monosaccharide, or simple sugar? A. Starch B. Glucose C. Cellulose D. Glycogen End • Which best describes the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells? A. It hydrates human body tissues. B. It supplies support to human body tissues. C. It transports oxygen to human body tissues. D. It increases the rate of reactions in body tissues. End • Which best describes the importance of carbohydrates to organisms? A. Carbohydrates provide storage for water molecules. B. Carbohydrates provide an immediate energy source. C. Carbohydrates provide an additional source for amino acids. D. Carbohydrates provide permanent storage for genetic information. • Which are the building blocks of most lipid molecules? A. glucose and protein B. glucose and fatty acids C. fatty acids and glycerol D. amino acids and glycerol End Whiteboard Practice • When a student drops a piece of liver into a beaker of hydrogen peroxide, the peroxide bubbles vigorously as the peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen. However, if the student cooks the liver first, the reaction fails to occur. What is the best explanation for these results? A. Boiling the liver altered the shape of the enzyme in the liver so that it could not interact with the peroxide. B. Heating the liver killed the germs that caused the bubbling reaction. C. Lower temperatures result in a higher rate of enzyme activity. D. Heating the liver removed the water and oxygen from the hydrogen peroxide. End • How are the transported molecules moved in active transport? A. Molecules are moved through the cytoplasm. B. Molecules are pumped into ribosomes within the cell. C. Molecules are pumped against their concentration gradient using energy. D. Molecules are moved into the cell from areas of higher concentration without energy. End • Alpha-amylase, an enzyme present in saliva, breaks down starch. Which food does it help to digest? A. Milk B. Candy C. Steak D. Potato End Whiteboard Practice • Which best explains why enzymes are important in biological systems? A. They hold all genetic information of a cell. B. They are necessary to maintain skin moisture. C. They accelerate the rate of chemical reactions. D. They support structures to maintain body temperature. End • Thermophiles are prokaryotes that live in water that is almost boiling. How must they be different from other organisms? A. Their flagella beat in a fanning motion. B. Their genetic material is RNA instead of DNA. C. Their proteins do not denature at high temperatures. D. They are able to maintain a cooler internal temperature. End Which describes how the plasma membrane helps to maintain homeostasis? A. by allowing any substance to enter the cytoplasm of the cell B. by controlling the synthesis of proteins within the ribosome C. by preventing all substances from entering or leaving the cell D. by regulating the contents of the cell from the external and internal environments Whiteboard Practice • Most human enzymes operate under an optimal pH near neutral. Which pH range would best represent this environment? A. 4-6 B. 6-8 C. 8-10 D. 10-12 End • Many people are lactose intolerant and cannot digest dairy products. What enzyme are their bodies most likely lacking? A. Lipase B. Lactase C. Maltase D. Protease End Whiteboard Practice • Many enzymes in the human body function best at 37°C. What is the most likely result of a great increase in body temperature? A. Enzymes become hormones. B. Enzymes become denatured. C. Enzymes become more active. D. Enzymes become more sluggish. End Whiteboard Practice • A single cell may contain several different types of enzymes. Which must occur for an enzyme to be able to catalyze a specific reaction? A. An enzyme must catalyze at least two different reactions. B. An enzyme must attach to a substrate like a lock in a key. C. An enzyme must react with the substrate that has the same composition as the enzyme itself. D. An enzyme must react with the substrate that has the opposite composition as the enzyme itself. End