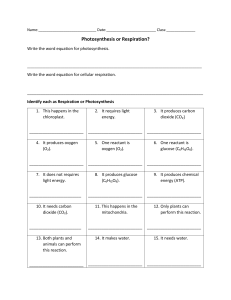
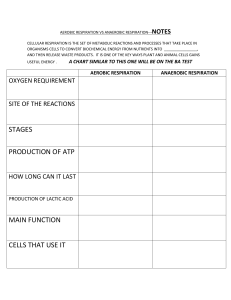
Wigmore High School Subject: Science Year group: 8 Date work set: 20th April Summer Learning 2020 Group/Set/Class: All Teacher: Date work to be completed by: All 24th April Topic: Ecosystem Processes Learning outcomes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Describe the process of photosynthesis. Describe the structure and function of the main components of the leaf. Describe how a plant uses minerals for healthy growth. Describe how chemosynthesis takes place. State the word equation for aerobic respiration. State the word equation for anaerobic respiration. Describe what food chains show. Describe the interdependence of organisms. Instructions: Please ensure you can successfully log in to the online Kerboodle Science textbook. Instructions for doing this were sent to you via your school email. Task Read and make notes from the information pack provided. Use pages 22-39 of your online textbook to help. Answer all question in the information pack. A copy of the pack in a word document will be emailed out to you. Please complete and return a copy to your teacher by email. This will allow your teacher to feed back to you. If you have any questions, please email your teacher or Mrs Cawthorne. Extension Task Turn to Page 40 in your online textbook. The Big Write Banana Power? Many tennis players eat a banana during a match to give them a boost of energy. The energy transferred to them from the banana has started off in the Sun. Almost all life on Earth depends on the transfer of the Sun’s energy to plants and algae in photosynthesis. Task Write a short essay explaining how the energy was transferred into the banana from the Sun, and what happens inside the tennis player’s body to transfer this energy to his muscles. Good luck Year 8 – Ecosystem Processes Photosynthesis Below is a food chain, it shows what an organism eats and the transfer of energy between organisms. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis. This process is a chemical reaction that uses light energy. The word photosynthesis comes from the Greek language: ‘photo’ means ‘light’ ‘synthesis’ means ‘putting together’. Photosynthesis just means ‘putting together with light’. Water + carbon dioxide → glucose + oxygen What do plants need? 1. Sunlight – the plants source of energy 2. Chlorophyll – the green stuff which makes plants look green found in chloroplasts, this chemical absorbs sunlight energy. 3. Water – travels up from the roots. 4. Carbon dioxide – diffuses in through the holes in the leaves, called stomata. Leaves Plant Minerals For healthy growth, plants need four important minerals: • Nitrates • Phosphates • Potassium • Magnesium Plants obtain minerals from the soil. The minerals are dissolved in water, this is then taken up by root hair cells and then transported around the plant via the xylem vessels. a) b) c) d) Nitrate deficiency ~ Plants have older, yellow leaves and poor growth. Phosphorous deficiency ~ Leaves look a purplish colour, poor root growth. Potassium deficiency ~ Leaves begin to yellow at the edges with dead patches appearing. Magnesium deficiency ~ Plant leaves will turn yellow. Aerobic Respiration Your body uses energy all the time, without energy your cells quickly die. You obtain energy from your food, your cells break down food molecules – glucose – to release the energy. • Mitochondrion - Contains the enzymes for aerobic respiration • Cell membrane – allows gases and water to pass freely into and out of the cell. • Nucleus – holds the genetic code for enzymes involved in respiration. • Cytoplasm – where enzymes are made, site of reactions in aerobic respiration. How does glucose and oxygen get into our cells? • Glucose is a carbohydrate found in food. As your food is being digested, larger molecules (e.g. starch) get broken down into smaller molecules of glucose. • These molecules eventually pass through the wall of the small intestine and into the blood stream, it is carried to your cells in the plasma (liquid part) of your blood. • When you breathe in, oxygen passes into your lungs, moves across the wall of your lungs and into your bloodstream. • Oxygen is carried around your body by red blood cells, it binds to a special chemical called hemoglobin. When it reaches a cell requiring oxygen, the oxygen diffuses into the cell. Anaerobic Respiration When you exercise quite hard your heart may not be able to pump oxygenated blood to your respiring cells quickly enough to carry out aerobic respiration. In the mean time, to carry on supplying your body with energy your cells can revert to anaerobic respiration, where glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen. Glucose Lactic Acid + Energy Less energy is released during anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid build up in the muscles causes muscle fatigue, eventually this can lead to muscle cramps and the muscle stops working. Lactic acid is cleared from the muscles by an increase in oxygen concentration, replacing the oxygen debt by breathing more deeply. Aerobic respiration in other organisms: Other microorganisms, like yeast, form ethanol and carbon dioxide. This is known as fermentation. Glucose Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide + Energy Plant cells respire anaerobically to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide, as well as energy. Glucose Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide + Energy Yeast is an important microorganism in food production. It is needed to make bread, beer and wine. These products are made using fermentation. Food Chains & Webs A food chain is a diagram which show what an organism eats. The arrows → show the transfer of energy between organisms. a) Producer – The lettuce, it is a plant and so it harnesses energy from the sun to make its own food. b) Herbivore – The rabbit, as this organism will eat plants (the lettuce) but not animals. c) Consumer – Both the rabbit and the fox, both these organisms to consumer another organism to survive. d) Carnivore – The fox, this organism eats only meat to survive. As energy is transferred along a food chain, much of it is lost to the surroundings as heat energy and through excretion of waste products. This means that at level of the food chain, less energy is transferred to the level above. Most animals eat more than just one type of organism, scientists can show this in a food web. Disruption to food chains and food webs Interdependence: All species live in ecosystems composed of communities of animals, plants and other organisms that are dependent on each other and are adapted to particular conditions What affects animal populations? 1. If the number of predators increased, the animal population that is being predated would decrease in numbers. 2. If the number of prey increased, the number of predators would eventually also start to increase as there is more food available. If the numbers of prey decreased, the number of predators would decline due to lack of food sources. 3. If a disease was present within an animal population, the number of organisms would begin to decline. This would have a knock-on effect to other animal populations. • A stable community is one where all of the species and the environmental factors are in balance so that population sizes remain fairly constant. Three examples of a stable community are mature coral reefs, oak woodlands and tropical rainforests. • Bioaccumulation is when toxins build up in the food chain. The animals at the top of the food chain – the apex predator – are the organisms which are affected the most severely. Ecosystems An ecosystem is the name given to the plants and animals that are found in a location, and the area in which they live. Community ~ the collection of different populations of species all co-existing in the same habitat at one time Ecosystem ~ a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment Habitat ~ an area or environment in which an organism naturally lives Niche ~ the role of a species within an ecosystem Population ~ all organisms of the same species living in a habitat at one time Interdependence ~ the relationship between different organisms within the same community and their dependence on each other for survival. What is an ecological niche? A niche is a particular place or role that an organism has within the ecosystem it lives in. For example, the greater spotted woodpecker, lesser spotted woodpecker and green woodpeckers will feed in different areas of the same habitat. This means they avoid competition with each other for vital resources. Year 8 – Ecosystem Processes Questions 1. Write a definition for each of the following terms: (4) Producers ~ Consumers ~ Carnivore ~ Herbivore ~ 2. Explain how each of the following adaptations helps a leaf it’s function: (4) It is green ~ The leaf is thin ~ It has a large surface area ~ The leaf has veins ~ 3. Name four minerals that plants need for healthy growth. (2) ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 4. Match the following terms to the correct definition: Food chain Food web Predator Prey (4) A diagram showing a series of linked food chains. An animal that is eaten by another animal. An animal that eats another animal. A diagram which shown the transfer of energy between organisms. 5. Complete the following sentences: (2) When two organisms depend on each other for something, this is called ____________. The number of plants or animals that live in the same area is called a ___________. In a food web, if the producer population decreases the consumer population will _______. When toxic chemicals build up within a food chain, this is called ____________. 6. Write down the word equations for the following reactions: (4) a) b) c) d) Photosynthesis ~ Aerobic Respiration ~ Anaerobic respiration (animals) ~ Anaerobic respiration (plants) ~ 7. Compare the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (4) ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 8. Describe some of the adaptation of plants which help to maximise the rate of photosynthesis. (3) _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 8. Using the food web below, answer the following questions: (6) a) Great White Sharks eat clown fish, what will happen to the number of clown fish if the sharks become vegetarian? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ b) What effect will this have on the number of zooplankton? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ c) What will happen to the Blue Clownfish if a disease wipes out the small invertebrates? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 9. Describe the journey of an oxygen molecule from the air to a cell, to be used in aerobic respiration (4) ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Year 8 – Ecological Processes Answers 1. Write a definition for each of the following terms: (4) Producers ~ they make their own food. Consumers ~ they must eat other organisms to get the nutrients they need to survive. Carnivore ~ this is an animal that eats other animals. Herbivore ~ this is an animal that eats only plant materials. 2. Explain how each of the following adaptations helps a leaf it’s function: (4) It is green ~ contains chlorophyll, to absorb sunlight for photosynthesis. The leaf is thin ~ this means gases can pass in and out of the leaf easily. It has a large surface area ~ to absorb as much sunlight as possible. The leaf has veins ~ xylem to carry water and phloem to carry sugars. 3. Name four minerals that plants need for healthy growth. (2) Nitrates, phosphates, potassium and magnesium. 4. Match the following terms to the correct definition: Food chain Food web Predator Prey (4) A diagram showing a series of linked food chains. An animal that is eaten by another animal. An animal that eats another animal. A diagram which shown the transfer of energy between organisms. 5. Complete the following sentences: (2) When two organisms depend on each other for something, this is called interdependence. The number of plants or animals that live in the same area is called a population. In a food web, if the producer population decreases the consumer population will decrease. When toxic chemicals build up within a food chain, this is called bioaccumulation. 6. a) b) c) d) Write down the word equations for the following reactions: carbon dioxide + water → (light energy) → glucose + oxygen Oxygen + glucose → carbon dioxide + water Glucose → Lactic acid + energy Glucose → Ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy (4) 7. Compare the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. (4) Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration require glucose and in both reactions the end result is the release of energy. In aerobic respiration, oxygen reacts with oxygen to product carbon dioxide and water. In anaerobic respiration, glucose reacts without the presence of oxygen and the end product is lactic acid. 8. Describe some of the adaptation of plants which help to maximise the rate of photosynthesis. (3) • Plants have a very large surface area, so that as much light as possible can be absorbed. • Plants are green as they contain a pigment called chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight • Plants contain veins, these contain xylem tubes which transport water and phloem tubes which transfer glucose. • Plants are thin, this allows gases to diffuse in and out of the leaf easily. 8. Using the food web below, answer the following questions: (6) a) The clownfish would lose one of their main predators, which could mean that their numbers would most likely start to increase. b) If there are now more clownfish, then more zooplankton will be consumed to support this larger animal population. This would mean zooplankton numbers would decline. c) Blue Clownfish numbers could start to decrease if a disease wipes out the small invertebrates, as there would be a smaller food source available for the Bluw Clownfish to consume. 9. Describe the journey of an oxygen molecule from the air to a cell, to be used in aerobic respiration (4) As a person breathes in oxygen will be drawn out of the air and into the persons lungs. It will travel through the lungs until is reaches the tiny air sacs (alveoli) where it will pass across the wall and into the blood vessels surrounding it. The oxygen molecule will bind to the hemoglobin of a red blood cell, it will be transported this way around the body. When the oxygen reaches a respiring cell it will detach from the hemoglobin and pass into the cell.